OSPF
OSPF configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0 interface-type p2p
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0 metric 100
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface lo0.0
or
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface 172.16.1.1 # Exact lo0 IP address
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 nssa
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 interface ge-0/0/3.0
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.2 stub
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.2 interface ge-0/0/4.0
|
Verify OSPF neighborship
Set Router ID
1
| set routing-options router-id 192.168.1.1
|
OSPF verification commands
1
2
3
4
| show ospf database
show ospf database summary
show ospf database detail
show ospf database area x.x.x.x
|
Display OSPF learned routes
Display information about the Router LSA: Type 1
1
| show ospf database router extensive
|
Display information about the Network LSA: Type 2
1
| show ospf database network extensive
|
Display information about the Summary LSA: Type 3
1
| show ospf database netsummary extensive
|
Display information about the ASBR SummaryLSA: Type 4
1
| show ospf database asbrsummary extensive
|
Display information about the External LSA: Type 5
1
| show ospf database external extensive
|
Display information about the NSSA LSA: Type 7
1
| show ospf database nssa extensive
|
OSPF Route Selection Order
- Intra-Area links
- Interarea links
- External Type E1
- External Type E2
OSPF Reference Bandwidth
Default OSPF cost for all links is 10^8 / bandwidth (bps). With these defauls, links with bandwidth >= 100 Mbps have a cost of 1.
Suggestion is to modify it:
1
| set protocols ospf reference-bandwidth 1000g
|
OSPF Cost on interfaces
1
2
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0 metric 12
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.100 metric 73
|
Verify OSPF interface metric with
1
| show ospf interface ge-0/0/0.0 detail
|
OSPF overload
Sets metric 65,535 in the Router LSA on all transit links. The large metric values ensure that transit traffic through the overload router uses alternative paths.
1
| set protocols ospf overload
|
OSPF Authentication
1
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/2.0 authentication simple-password <PASSWORD>
|
1
2
3
4
5
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/2.0 authentication md5 <KEY_ID_0-255> key <PASSWORD>
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/2.0 authentication md5 2 key <PASSWORD> start-time now
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/2.0 authentication md5 2 key <PASSWORD> start-time "2016-1-20.12:00:00 +0000"
|
Verify OSPF authentication with
1
| show ospf interface detail
|
OSPFv3
Must have family inet6 configured since OSPFv3 uses IPv6 link-local addresses to pass messages between Routers on the same network segment. Requires a Router-ID.
IPv6 OSPFv3
1
| set protocols ospf3 ...
|
IPv4 OSPFv3
1
| set protocols ospf3 realm ipv4-unicast ...
|
Flooding scope
| S2 | S1 | Flooding Scope |
|---|
| 0 | 0 | Link-local scope |
| 0 | 1 | Area scope |
| 1 | 0 | AS scope |
| 1 | 1 | Reserved |
OSPFv3 LSA Types
- U-bit: Used to show how a router that does not understand the LS function code should handle the LSA
- S-bit and flooding scope: Used to show the flooding scope for the LSA
| LSA Function | LS type | Description | Like OSPFv2 |
|---|
| 1 | 0x2001 | Router LSA | Type 1 Router LSAs |
| 2 | 0x2002 | Network LSA | Type 2 Network LSAs |
| 3 | 0x2003 | Inter-Area-Prefix LSA | Type 3 Summary LSAs |
| 4 | 0x2004 | Inter-Area-Router LSA | Type 4 ASBR-Summary |
| 5 | 0x4005 | AS-External-LSA | Type 5 AS-External LSA |
| 6 | 0x2006 | Group Membership LSA | Type 6 Multicast |
| 7 | 0x2007 | Type-7 LSA | Type 7 NSSA External |
| 8 | 0x0008 | Link LSA | None |
| 9 | 0x2009 | Intra-Area-Prefix LSA | Types 1 and 2 |
OSPF debugging
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| set protocols ospf traceoptions file trace-ospf.log size 10m files 3
set protocols ospf traceoptions flag error detail
set protocols ospf traceoptions flag hello detail
set protocols ospf traceoptions flag hello send receive
show log trace-ospf.log
show log trace-ospf.log | match mismatch
|
To disable it
1
2
3
| set protocols ospf deactivate traceoptions
run file delete /var/log/trace-ospf
|
Stub Area configuration
1
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 stub
|
This is the ABR configuration to inject an OSPF Type 3 Summary LSA 0.0.0./0 route into the Stub Area with a specific metric.
1
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 stub default-metric 10
|
Totally Stub Area configuration
The Totally Stub Area configuration is only required on the ABRs.
1
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 stub no-summaries default-metric 10
|
NSSA Area configuration
1
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa
|
For the ABR to inject a 0.0.0.0/0 default route into the NSSA area as OSPF LSA Type 7
1
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa default-lsa default-metric 10
|
When an ASBR is also an ABR with an NSSA area attached to it, all NSSA areas receive the LSA type 7 from it. To disable the behaviour, use this command:
1
| set protocols ospf no-nssa-abr
|
Totally NSSA Area configuration
1
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa no-summaries
|
For the ABR to inject a 0.0.0.0/0 default route into the NSSA area as OSPF LSA Type 3
1
2
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa default-lsa default-metric 10
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa no-summaries
|
For the ABR to inject a 0.0.0.0/0 default route into the NSSA area as OSPF LSA Type 7
1
2
3
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa default-lsa default-metric 10
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa default-lsa type-7
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.3 nssa no-summaries
|
Summarize OSPF Type 1 and Type 2 LSAs advertised to the Backbone Area by the ABR
1
| set protocols ospf area 1 area-range 192.168.16/20
|
Block OSPF Type 1 and Type 2 LSAs from being advertised to the Backbone Area by the ABR
1
| set protocols ospf area 1 area-range 192.168.16/20 restric
|
Summarize OSPF Type 7 LSAs advertised to the Backbone Area by the ABR
1
| set protocols ospf area 1 nssa area-range 192.168.16/20
|
Block OSPF Type 7 LSAs from being advertised to the Backbone Area by the ABR
1
| set protocols ospf area 1 nssa area-range 192.168.16/20
|
OSPF Multi-Area Adjacencies
Interfaces can belong to more than one Area. In this example, ge-0/0/1 is configured on both, Area 0 and Area 1.
Note that the secondary is configured as OSPF point-to-point.
1
2
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.0
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.1 interface ge-0/0/1.0 secondary
|
OSPF Virtual Links
Router A
1
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 virtual-link neighbor-id 192.168.0.2 transit-area 0.0.0.10
|
Router B
1
| set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 virtual-link neighbor-id 172.16.0.4 transit-area 0.0.0.10
|
Redistribute Static Routes into OSPF
By default external routes into OSPF are advertised as type E2.
1
2
3
4
5
| set policy-options policy-statement REDISTRIBUTE-STATICS term STATIC-ROUTES from protocol static
set policy-options policy-statement REDISTRIBUTE-STATICS term STATIC-ROUTES then external type 1 <<< To make the routes type E1
set policy-options policy-statement REDISTRIBUTE-STATICS term STATIC-ROUTES then accept
set protocols ospf expoert REDISTRIBUTE-STATICS
|
OSPF Prefix Limit
If the number of network prefixes to be redistributed into OSPF exceed prefix-export-limit <#> then none is redistributed.
1
| set protocols ospf prefix-export-limit <#>
|
Display Routing
| # | Source | Command |
|---|
| 1 | Link State Databse | show ospf database |
| 2 | Tree Database | show ospf route |
| 3 | inet.0 | show route protocol ospf |
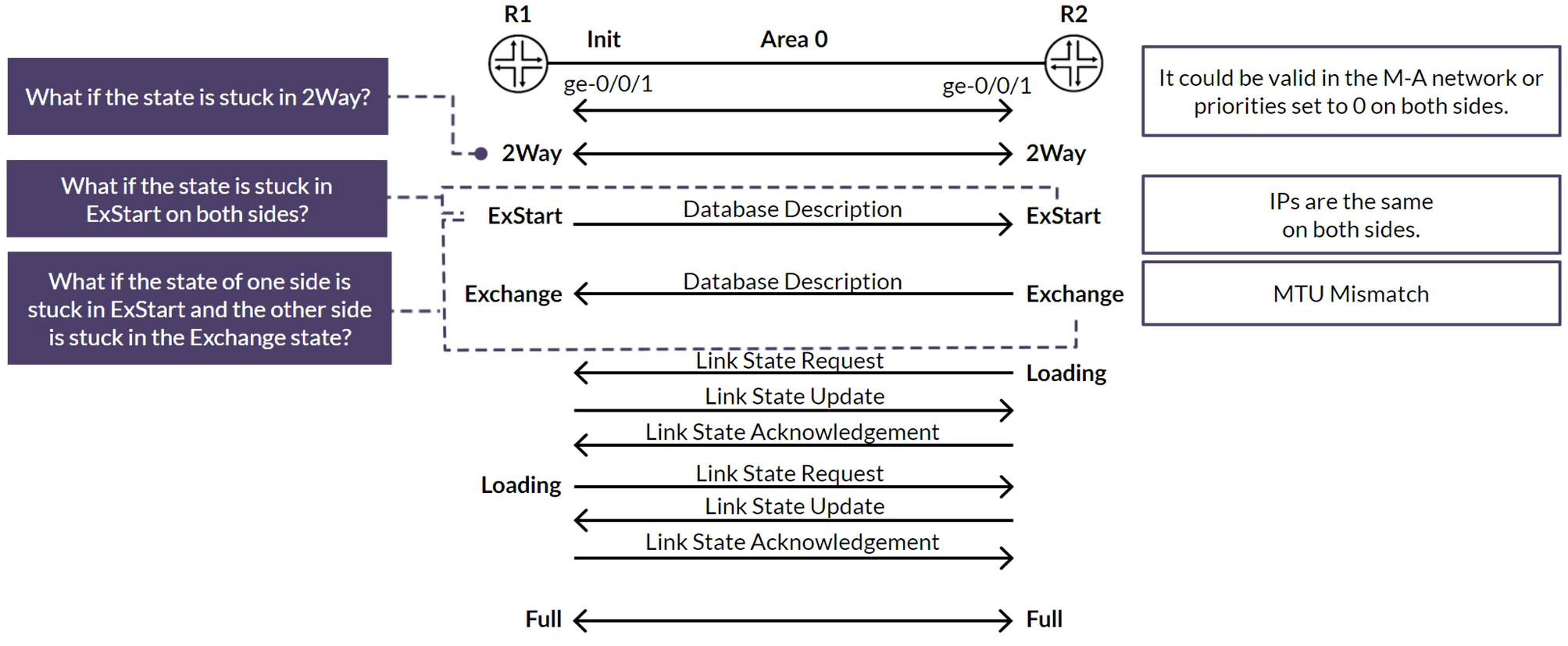
OSPF Neighbor State Machine
- Down
- Init
- 2Way
- ExStart
- Exchange
- Loading
- Full
NOTE: If 2 directly connected Routers have the same Router ID, OSPF will NOT form adjacency.
Items that Must Match:
- Interface Types (p2p or MultiAccess)
- Network (MultiAccess only)
- Hello Intervals
- Dead Intervals
- Area Types
- Area Numbers
- Authentication
1
2
| clear ospf statistics
show ospf statistics
|
Internal command that displays some timing statistics about SPF runs. Not very useful.
Monitor Traffic Interface
1
2
| monitor traffic interface ge-0/0/1 detail no-resolve
monitor traffic interface ge-0/0/1 matching dst 224.0.0.5
|
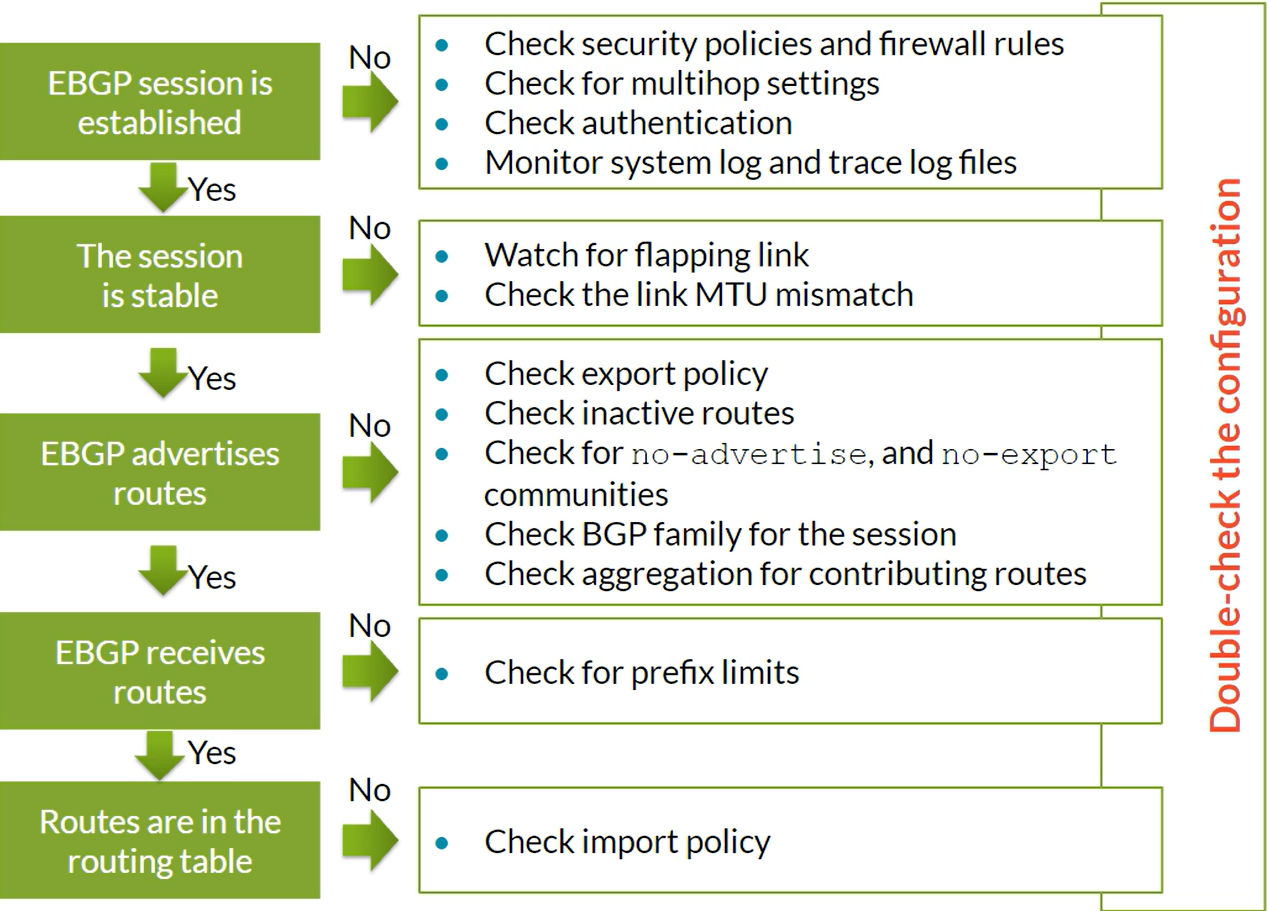
Troubleshoot OSPF Routing issues
show route protocol ospf Displays OSPF-computed routes and their attributesshow ospf route Notifies the type (intra-area, interarea, external type-1 and type-2 and so on) of each of the prefixes computed by OSPFshow ospf database Enables you to check the content of the link-state database (LSDB)
BGP
BGP Message Types:
- Open
- Keepalive
- Update
- Notification
- Refresh
BGP Neighbor States
| TCP Connectivity | BGP Connectivity |
|---|
| Idle | OpenSent |
| Connect | OpenConfirm |
| Active | Established |
1
2
| set routing-options autonomous-system 65503
set routing-options router-id 192.168.100.1
|
iBGP Configuration example
1
2
3
| set protocols bgp group int-65503 type internal
set protocols bgp group int-65503 local-address 192.168.100.1
set protocols bgp group int-65503 neighbor 192.168.100.2
|
eBGP Configuration example
1
2
3
| set protocols bgp group ext-65501 type external
set protocols bgp group ext-65501 peer-as 65501
set protocols bgp group ext-65501 neighbor 172.30.1.2
|
BGP Authentication
BGP Authentication configured at BGP protocol level
1
| set protocols bgp authentication-key <PASSWORD>
|
BGP Authentication configured at BGP group level
1
| set protocols bgp group int-65503 authentication-key <PASSWORD>
|
BGP Authentication configured at BGP neighbor level
1
| set protocols bgp group ext-65501 neighbor 172.30.1.2 authentication-key <PASSWORD>
|
BGP Authentication using Key Chains
1
2
3
4
5
| set security authentication-key-chains key-chain KEY-CHAIN-NAME key 1 secret SECRET-DATA
set security authentication-key-chains key-chain KEY-CHAIN-NAME key 1 start-time YYYY-MM-DD.HH:MM:SS
set security authentication-key-chains key-chain KEY-CHAIN-NAME key 2 secret SECRET-DATA
set security authentication-key-chains key-chain KEY-CHAIN-NAME key 2 start-time YYYY-MM-DD.HH:MM:SS
|
1
2
3
4
| set protocols bgp group int-65503 type internal
set protocols bgp group int-65503 local-address 192.168.100.1
set protocols bgp group int-65503 authentication-key-chain KEY-CHAIN-NAME
set protocols bgp group int-65503 neighbor 192.168.100.2
|
BGP TTL Security - Generalized TTL Security Mechanism (GTSM)
BGP peer 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| set firewall filter TTL-SECURITY term GTSM from soruce-address 10.1.2.1/32
set firewall filter TTL-SECURITY term GTSM from protocol tcp
set firewall filter TTL-SECURITY term GTSM from ttl-except 255
set firewall filter TTL-SECURITY term GTSM from port 179
set firewall filter TTL-SECURITY term GTSM then discard
set firewall filter TTL-SECURITY term ELSE then accept
set interfaces ge-1/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.2.2/30 filter input TTL-SECURITY
|
BGP peer 2
1
2
3
4
| set protocols bgp group toAS2 type external
set protocols bgp group toAS2 peer-as 2
set protocols bgp group toAS2 ttl 255 <<<<<<<<<<<<<<-----------
set protocols bgp group toAS2 neighbor 10.1.2.2
|
Protecting BGP session
1
2
| set protocols bgp group ext-peers family inet unicast prefix-limit maximum 25000
set protocols bgp group ext-peers family inet unicast prefix-limit teardown 80 idle-timeout 10 <<< Optional
|
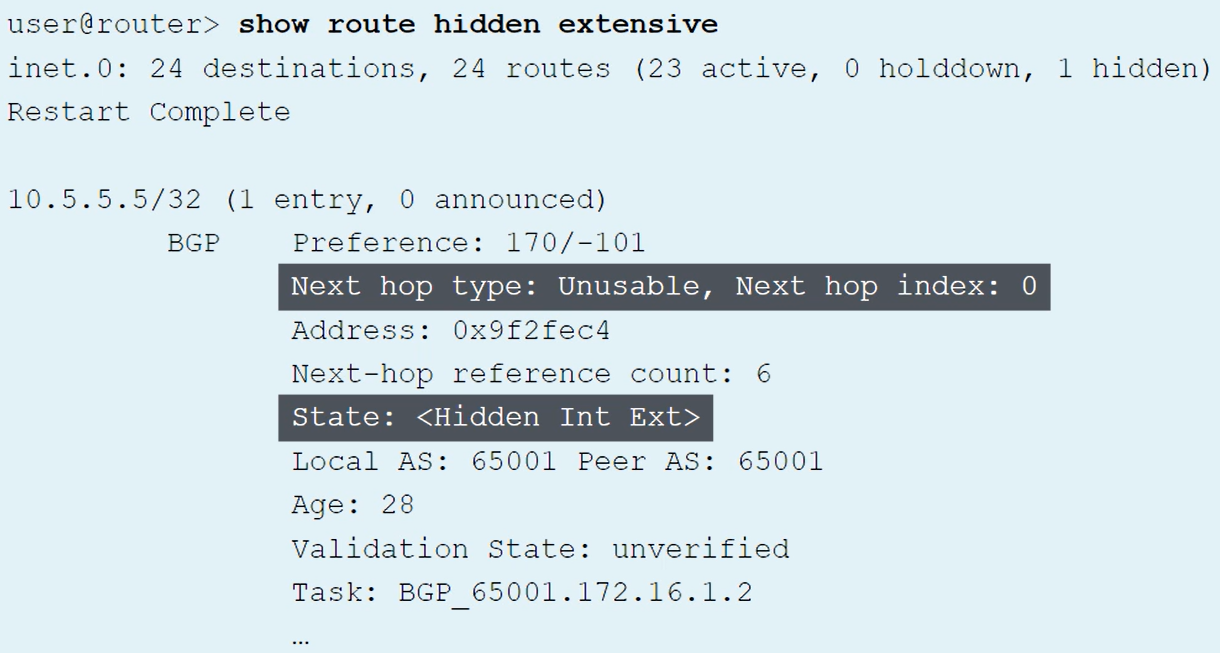
show route hidden extensive
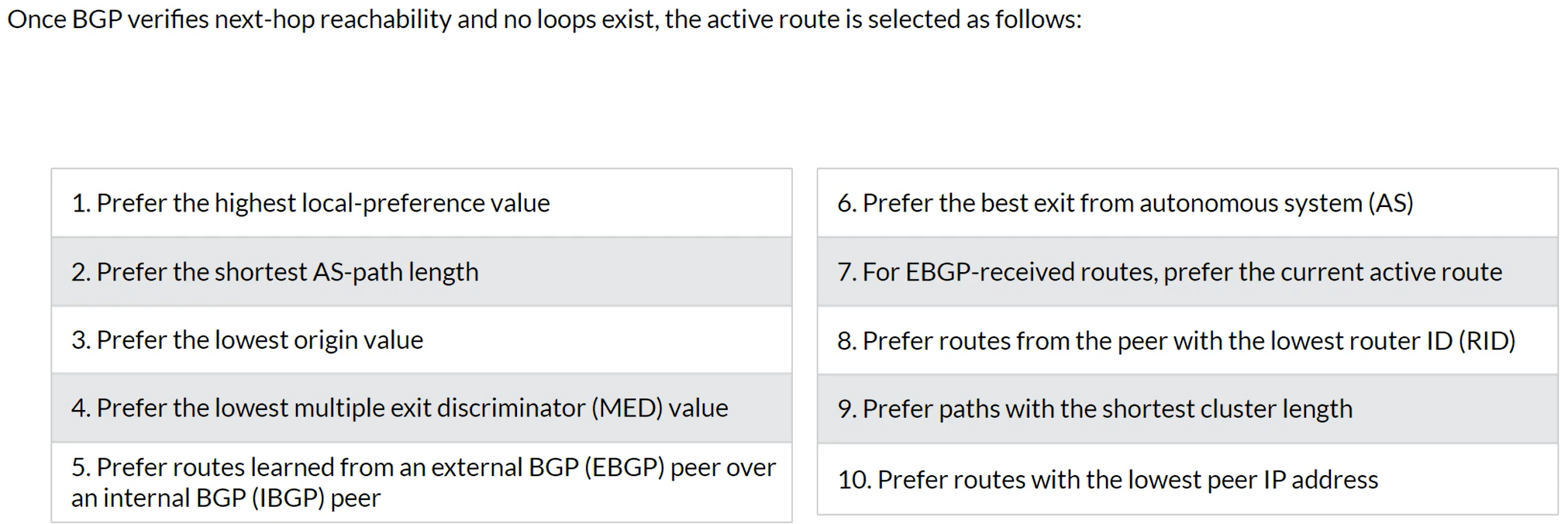
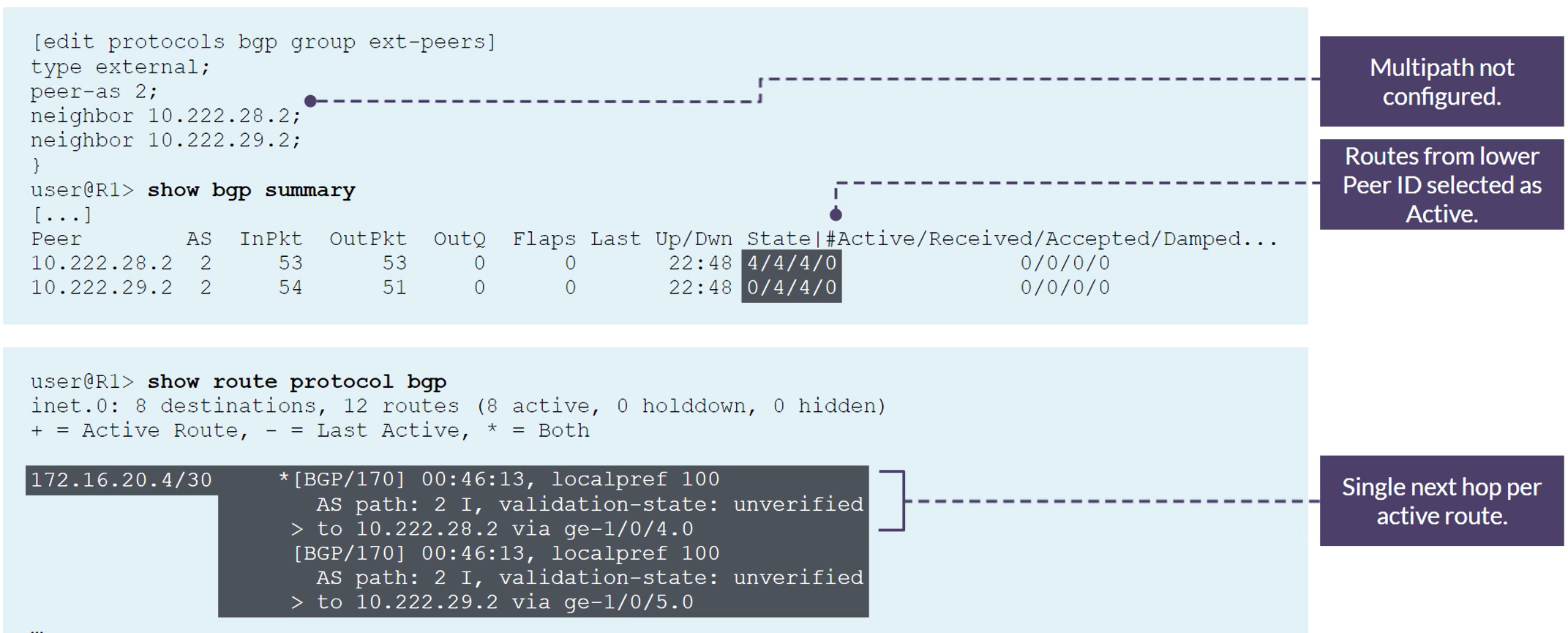
Selecting the Active BGP Route
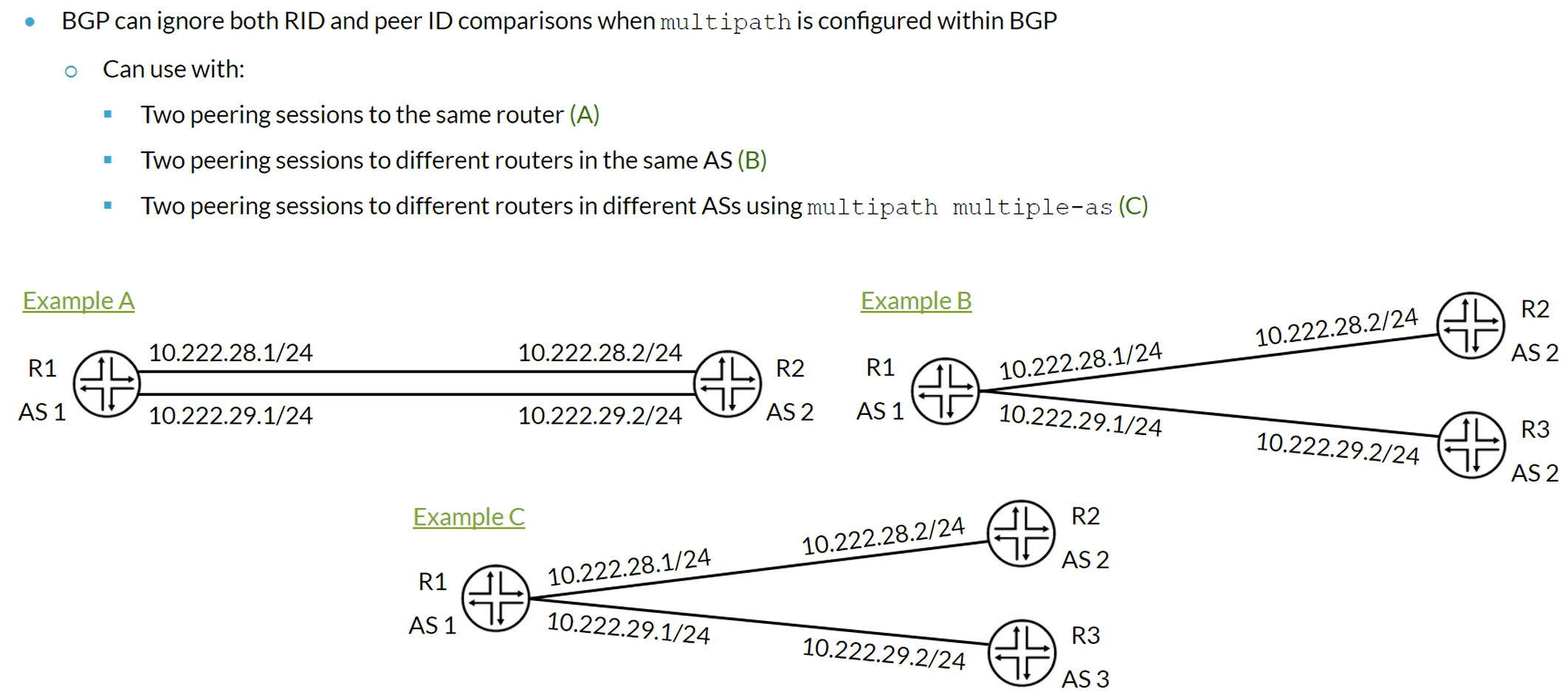
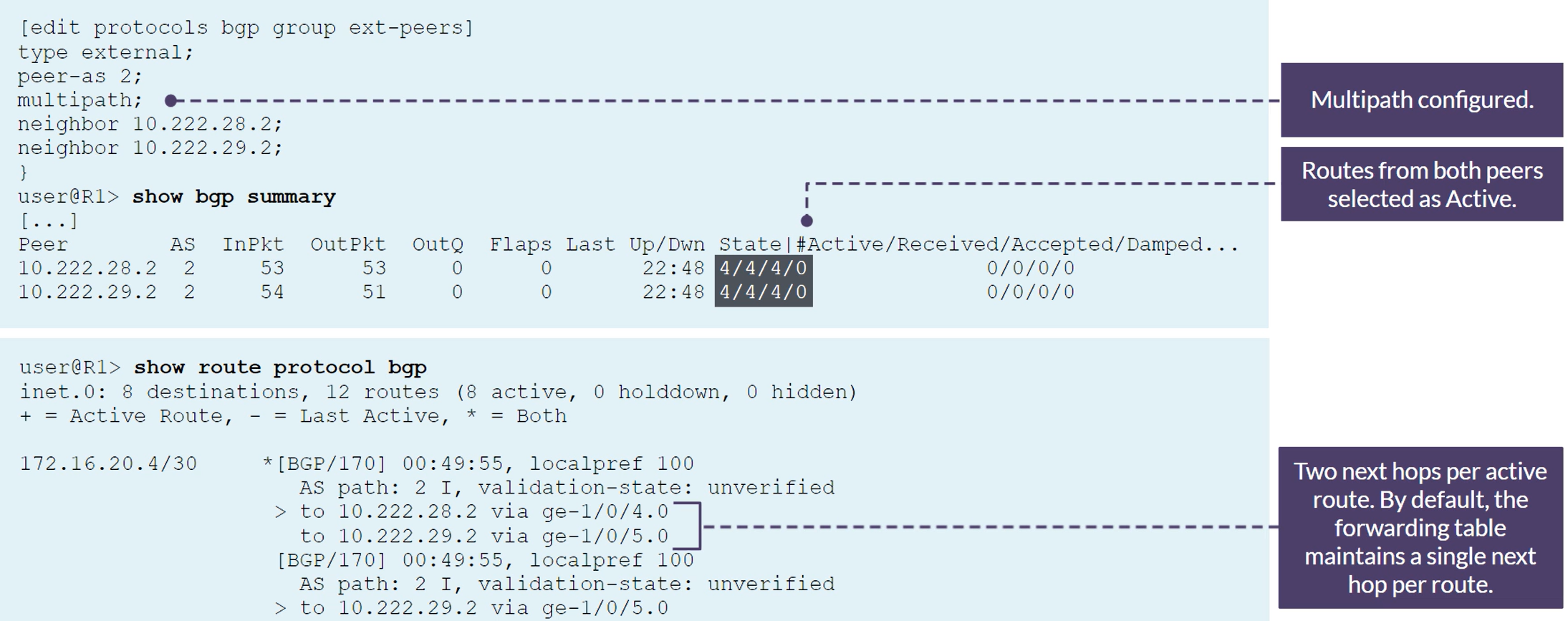
BGP Multipath
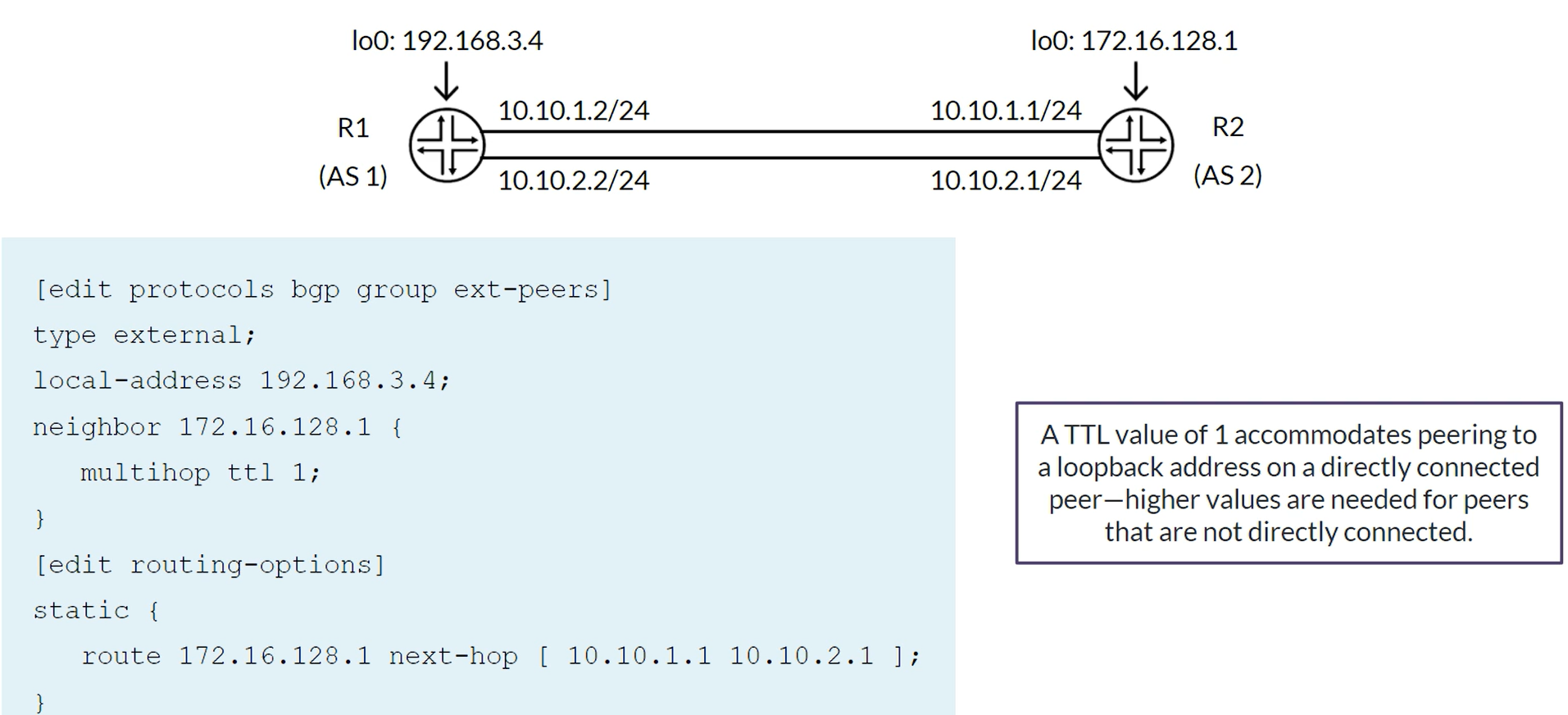
BGP Multihop peering
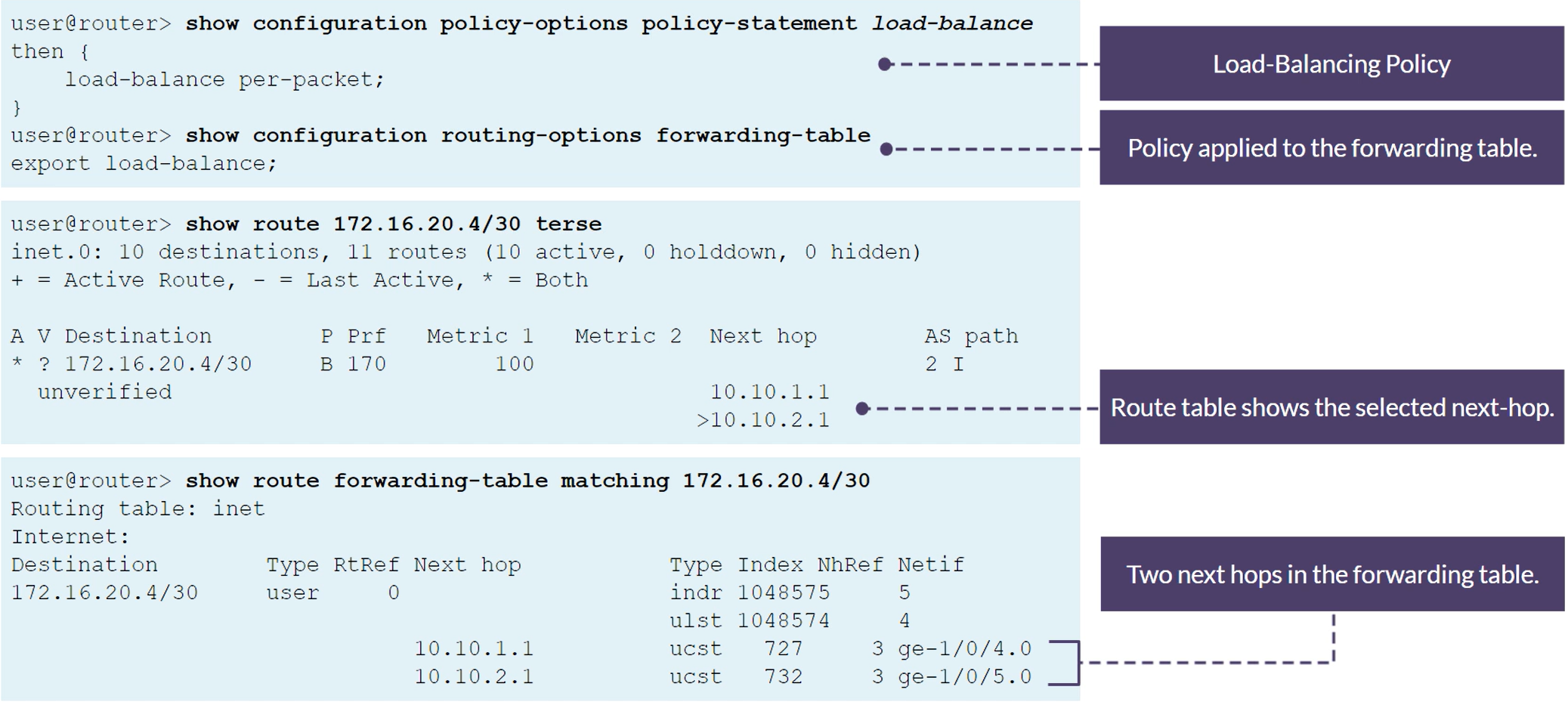
Multiple Hops with Per-Flow Load Balancing
Advertise-inactive
Overrides the default behavior and advertise BGP routes that are not currently selected as active because of route preference.
1
| set protocol bgp advertise-inactive
|
Aggregate routes
1
2
3
4
| set routing-options aggregate route 172.21.0.0/22
set routing-options aggregate route 172.22.0.0/22
set routing-options aggregate route 192.168.1.0/30
set routing-options aggregate route 192.168.2.0/30
|
1
2
3
| set routing-options policy-options policy-statement ADV-AGGREGATES term MATCH-AGGREGATE-ROUTES from protocol aggregate
set routing-options policy-options policy-statement ADV-AGGREGATES term MATCH-AGGREGATE-ROUTES then accept
set routing-options policy-options policy-statement ADV-AGGREGATES term DENY-OTHER then reject
|
1
| set protocols bgp group MY-EXT-GROUP export ADV-AGGREGATES
|
Verify BGP
1
2
3
| show route receive-protocol bgp <X.X.X.X> [hidden]
show route protocol bgp [source-gateway <X.X.X.X>]
show route advertising-protocol bgp <X.X.X.X>
|
1
2
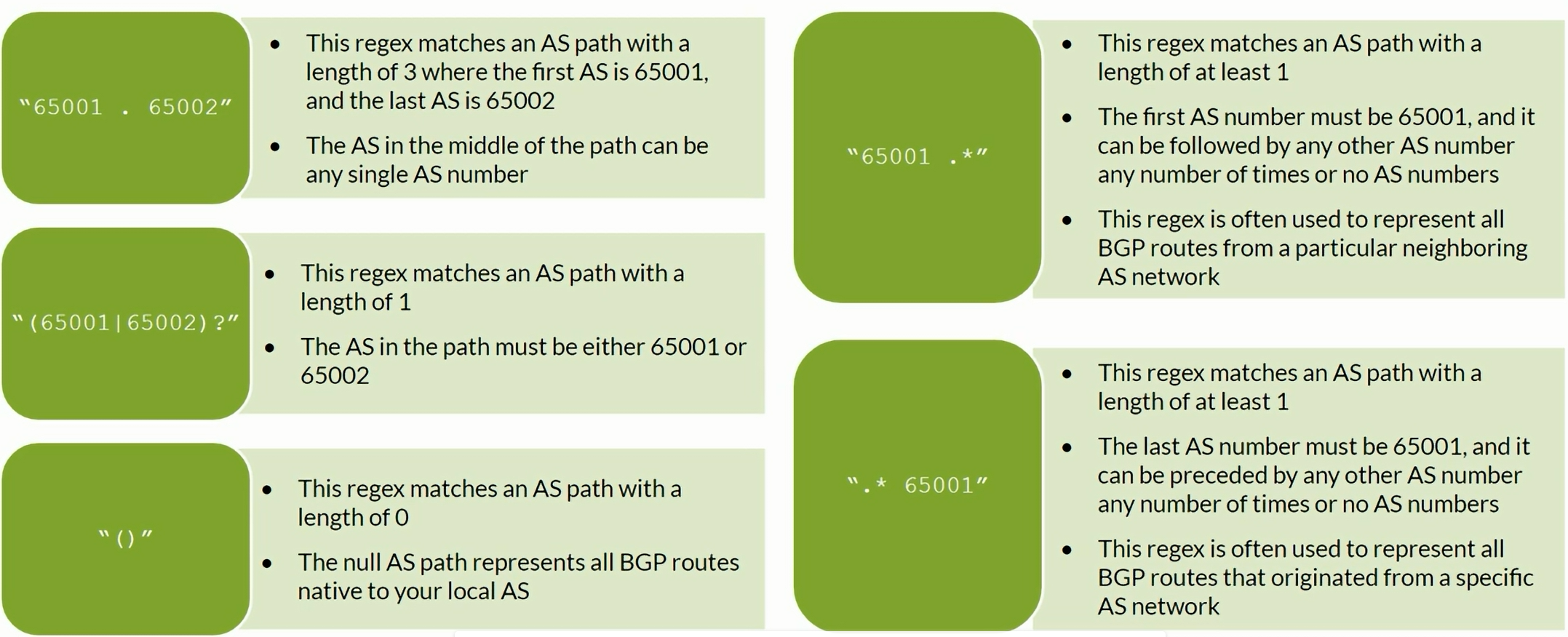
| show route aspath-regex "65510 .*"
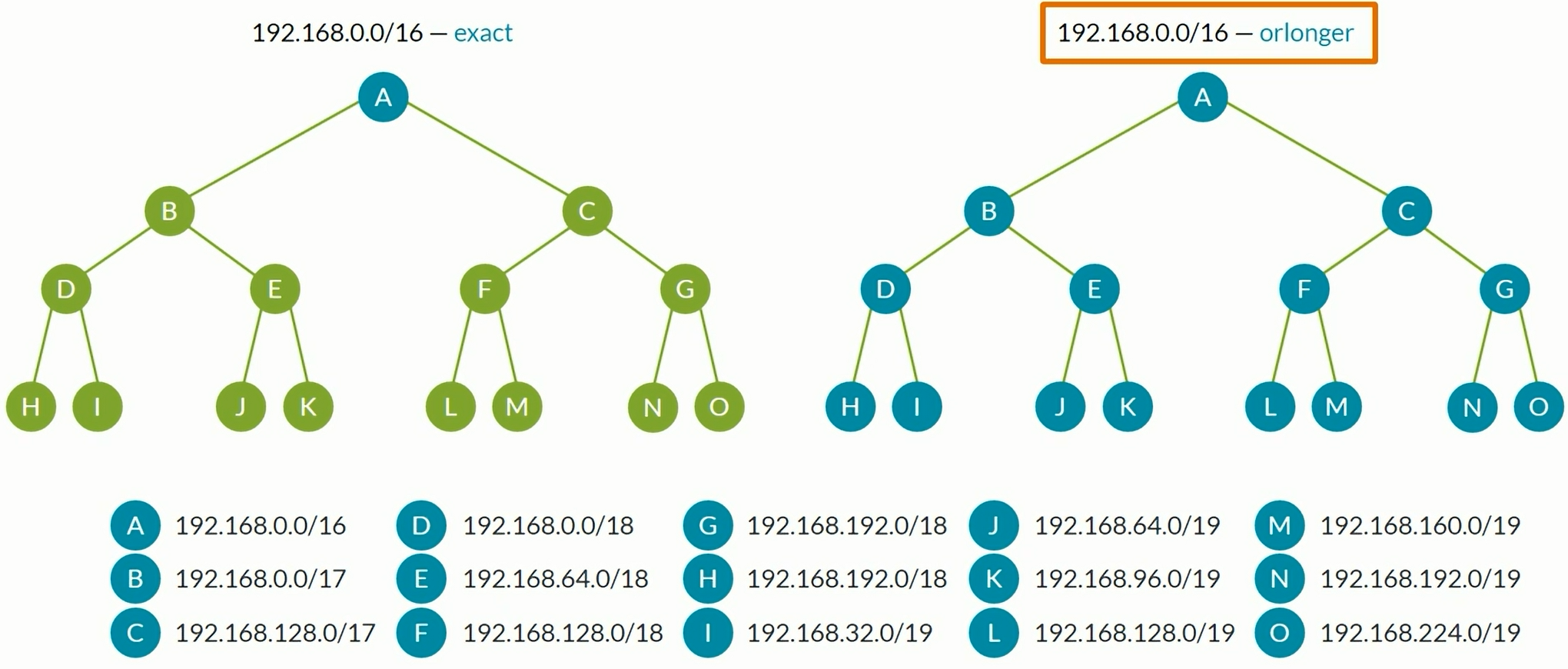
show route 0/0 exact extensive
|
BGP sessions
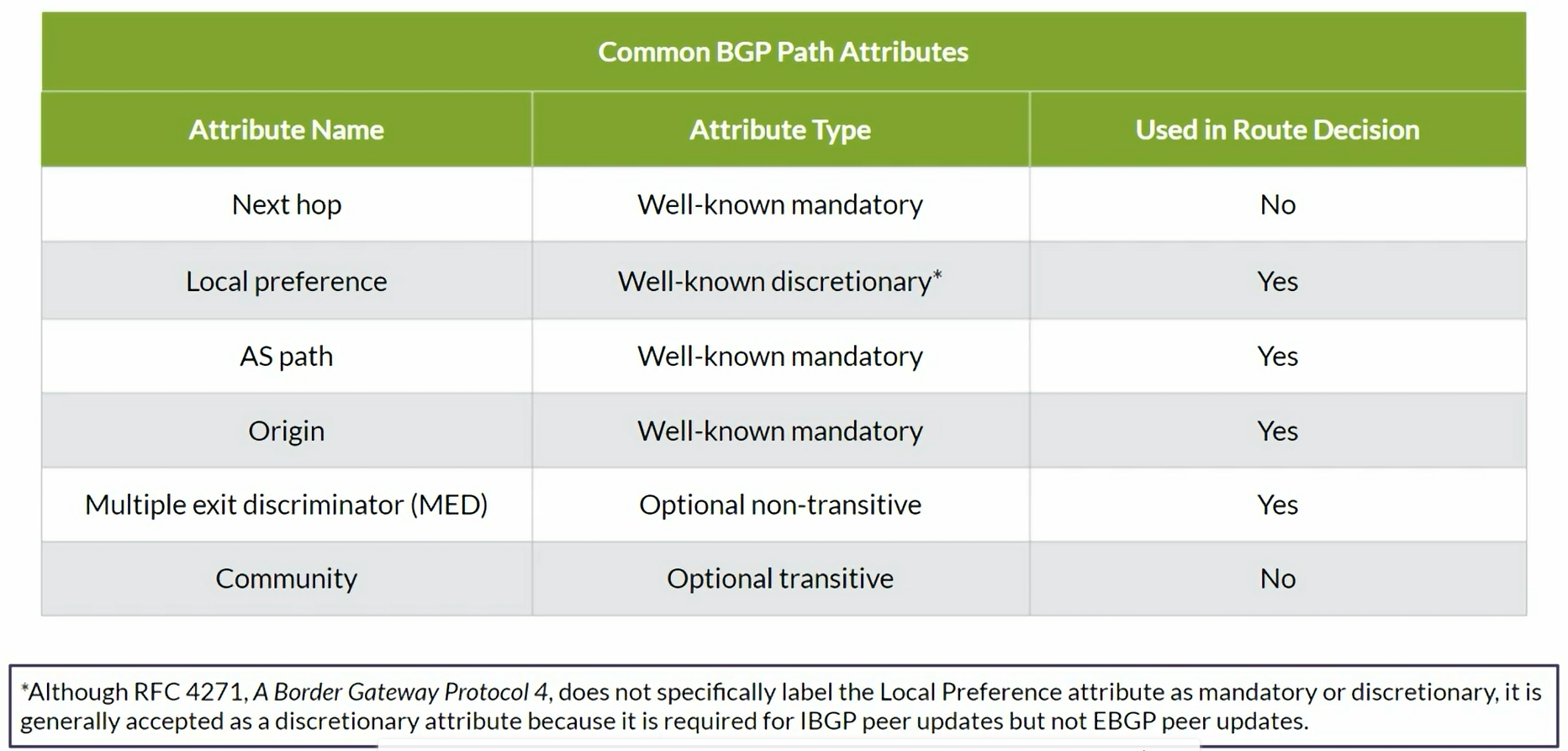
Common BGP Path Attributes
| Attribute Name | Attribute Type |
|---|
| Next Hop | Well-known mandatory |
| Local Preference | Well-known discretionary |
| AS Path | Well-known mandatory |
| Origin | Well-known mandatory |
| Multi Exit Discriminator (MED) | Optional non-transitive |
| Community | Optional transitive |
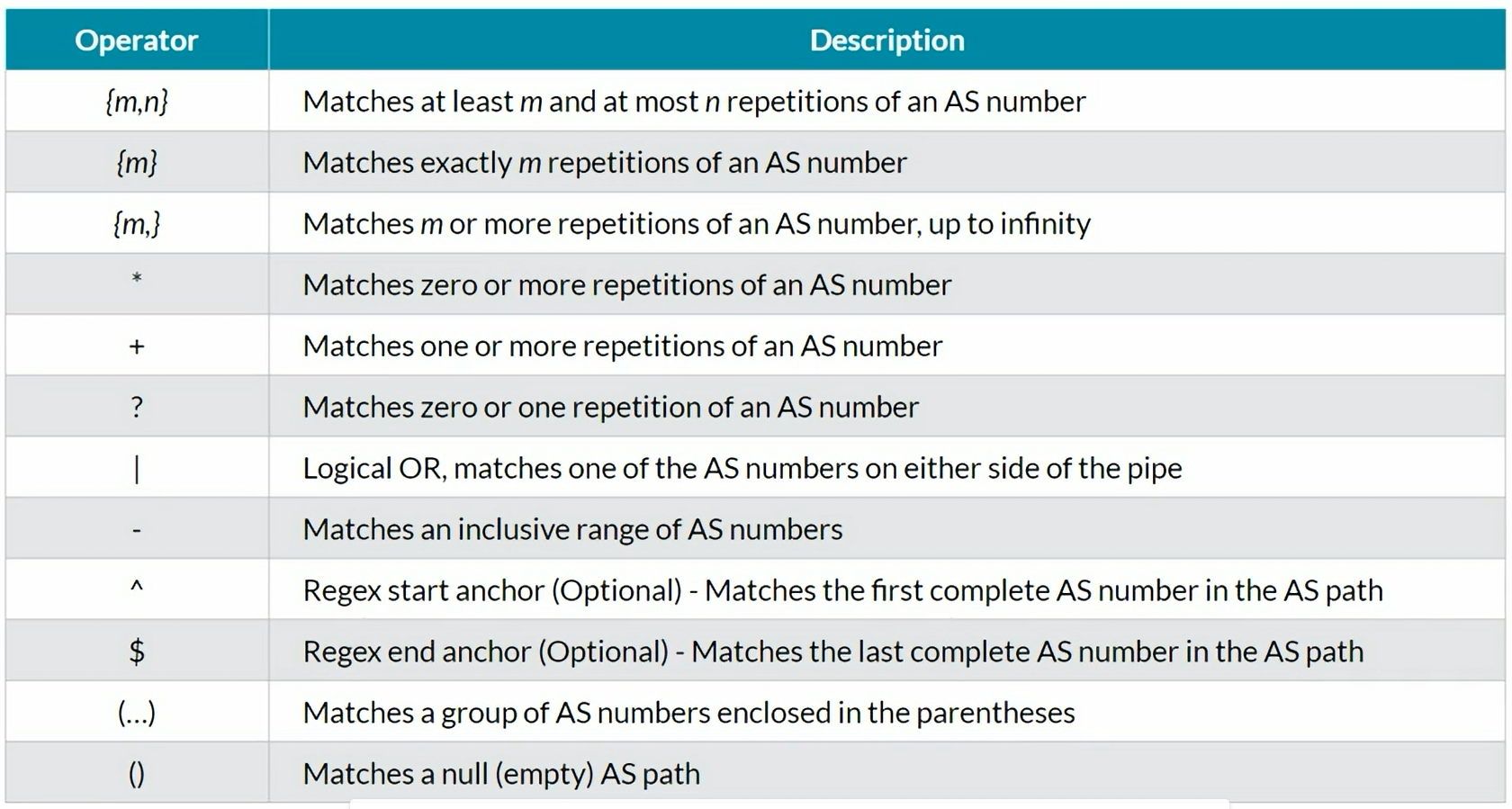
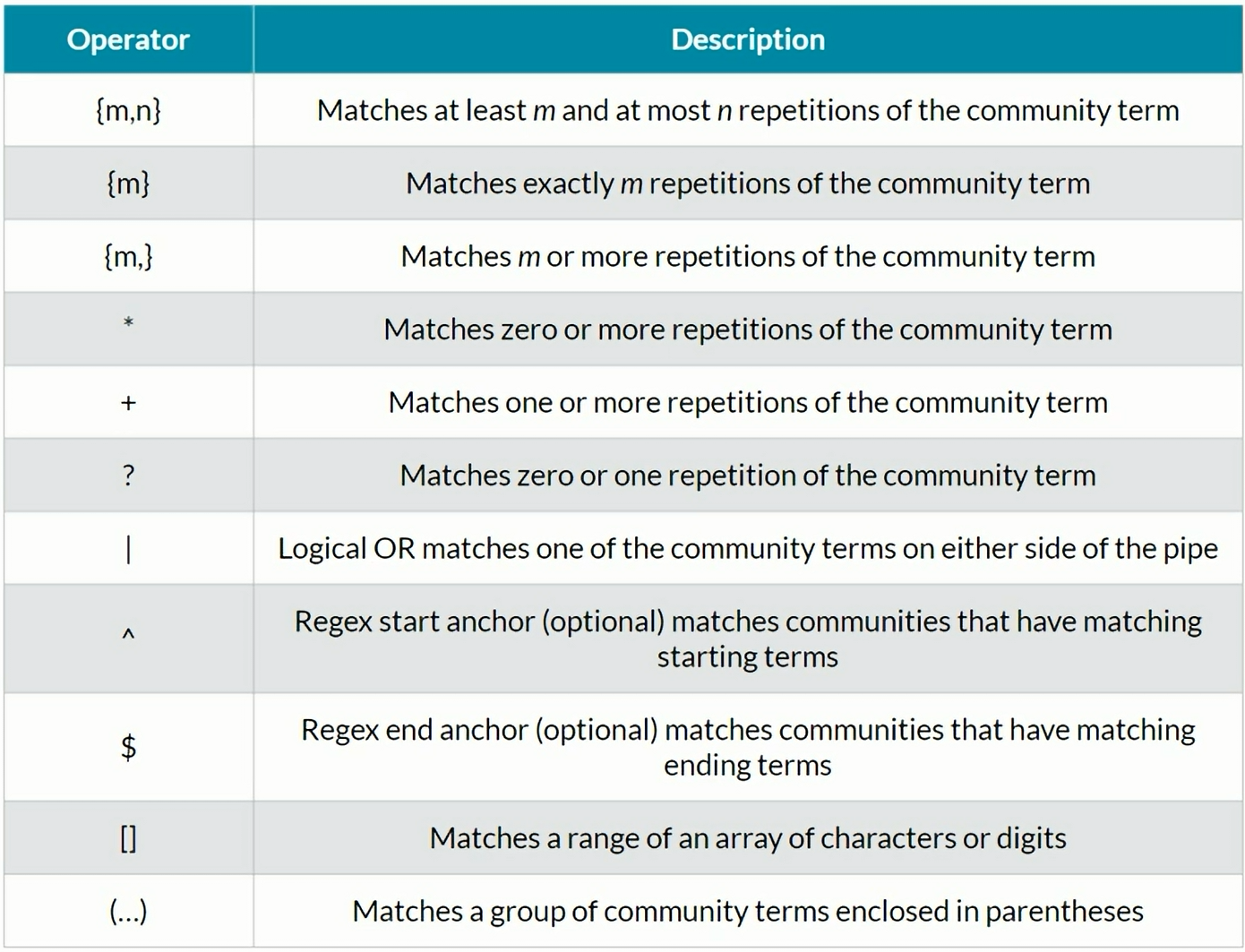
BGP Regex
BGP Well-Known Communities
| Type | Value | Notes |
|---|
| No-export | 0xFFFFFF01 | These routes are nto advertised outside a BGP confederation or AS |
| No-advertise | 0xFFFFFF02 | These routes are not advertised to other BGP peers |
| No-export-subconfed | 0xFFFFFF03 | These routes are advertised to IBGP peers in the same AS but not to members of other confederations |
BGP Communities configuration
1
| set policy-options community <COMMUNITY_NAME> members [ <COMMUNITY-ID> <COMMUNITY-ID> ... ]
|
1
2
3
| set policy-options policy-statement <PS_NAME> term <X> from community <COMMUNITY_NAME>
set policy-options policy-statement <PS_NAME> term <X> then local-preference 200
set policy-options policy-statement <PS_NAME> term <X> then accept
|
1
2
| set protocols bgp group <MY-GROUP> export <PS_NAME>
set protocols bgp group <MY-GROUP> neighbor <X.X.X.X>
|
BGP Communities Regular Expressions
Looking for routes with communities matching a regex in the Routing Table
1
2
3
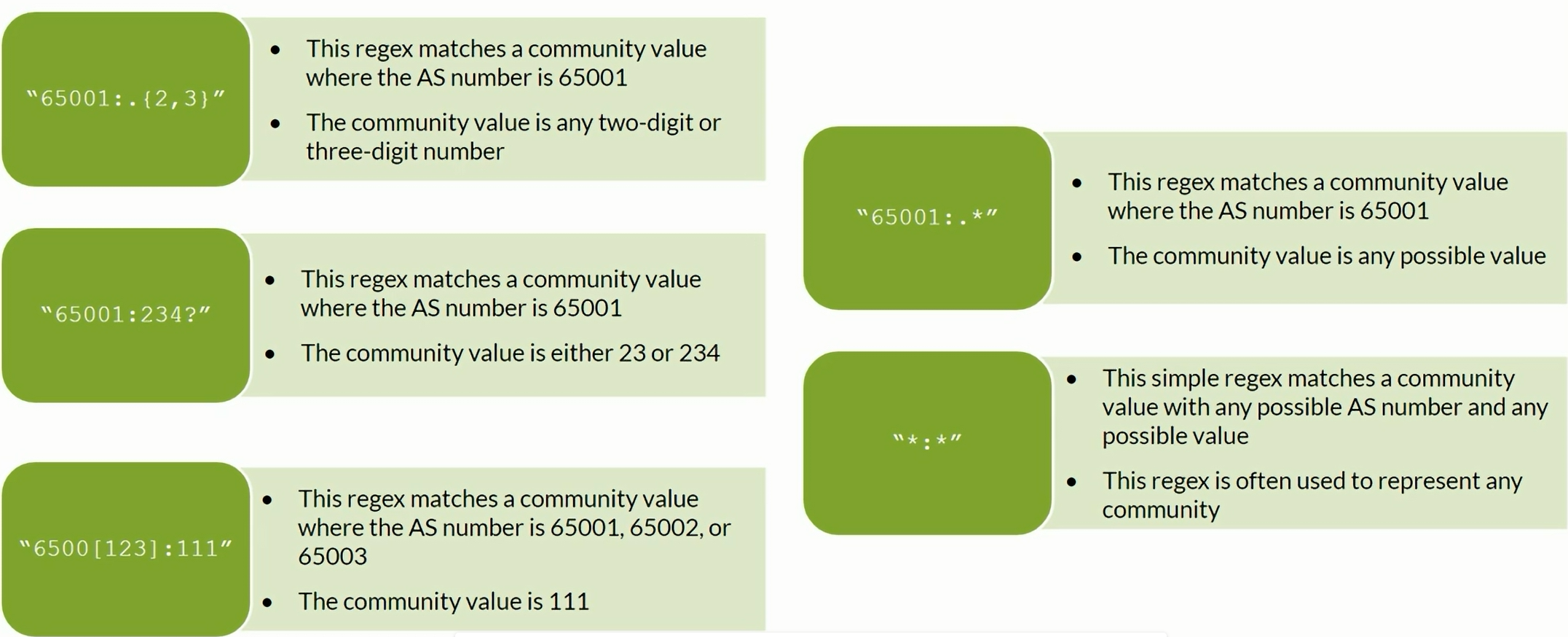
| show route community *:20 terse
show route community *:20 detail
show route community-name <NAME> detail
|
BGP Next-Hop-Self
1
2
3
| set policy-options policy-statement NHS term <X> then next-hop-self
set protocols bgp group <GROUP-NAME> export NHS
|
Advertise only routes generated within the AS to the eBGP peer
1
2
3
4
5
6
| set policy-options as-path null-as "()"
set policy-options policy-statement EXPORT-EBGP term LOCAL-ROUTES from as-path null-as
set policy-options policy-statement EXPORT-EBGP term LOCAL-ROUTES from protocol bgp
set policy-options policy-statement EXPORT-EBGP term LOCAL-ROUTES then accept
set policy-options policy-statement EXPORT-EBGP term LAST then reject
|
1
| set protocols bgp group MY-EXT-GROUP exprt EXPORT-EBGP
|
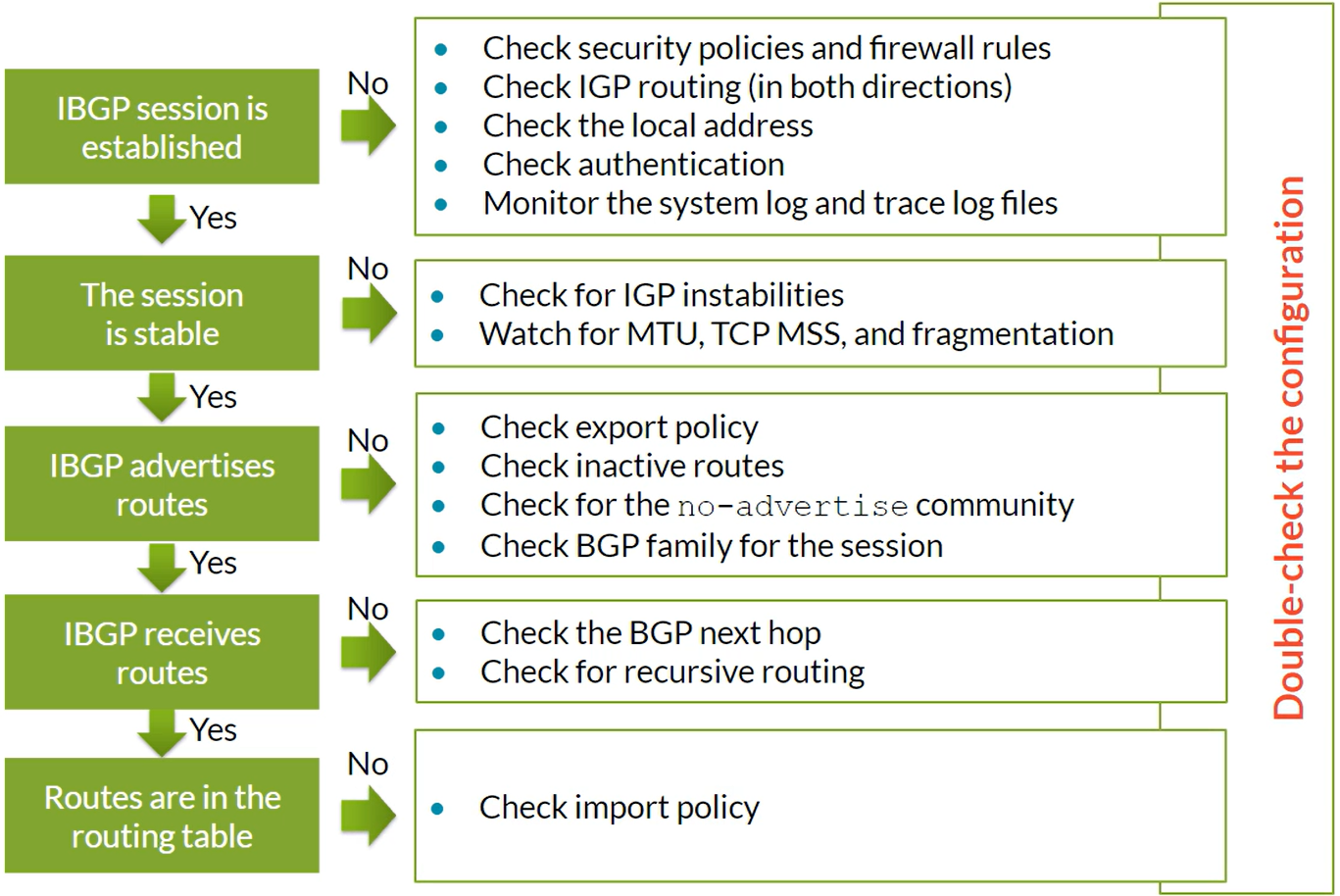
BGP Troubleshooting
iBGP
eBGP
BGP Operational commands
1
2
3
4
5
| show bgp summary | refresh 2
show system connections
show bgp group
show bgp neighbor X.X.X.X
show log messages | match notification
|
1
| monitor traffic interface ge-0/0/4.303 matching "tcp and port 179"
|
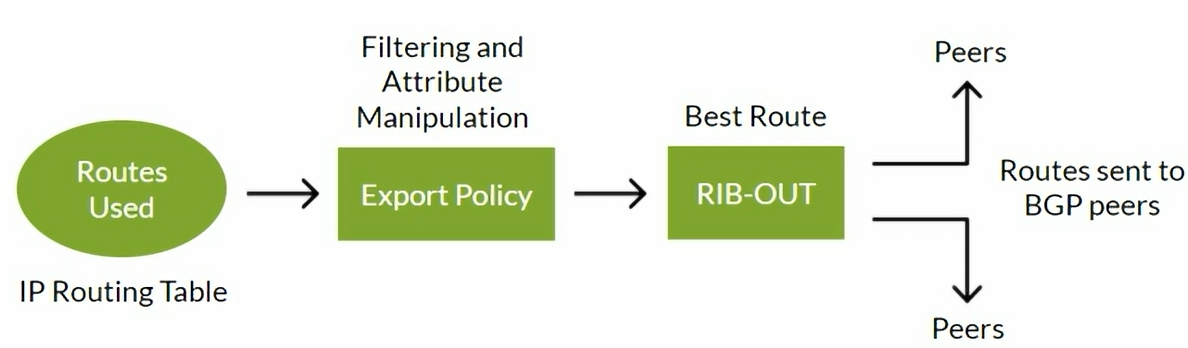
Displays routes being advertised after the export policy is processed
1
| show route advertising-protocol bgp X.X.X.X [extensive]
|
Displays routes received from specific neighor before the import policy except for filtered routes which are hidden.
Use hidden parameter to see the filtered routes.
1
| show route receive-protocol bgp X.X.X.X [hidden]
|
To see the routes after the import policy, look for the in the Routing Table
1
| show route protocol bgp source-gateway X.X.X.X [detail]
|
1
| show route protocol bgp [active-path]
|
1
2
3
4
| show route protocol bgp terse
show route protocol bgp
show route protocol bgp detail
show route protocol bgp extensive
|
BGP Debugging
1
2
3
4
5
6
| set protocols bgp traceoptions file bgp_trace.log size 10m files 2
set protocols bgp traceoptions flag packets detail
set protocols bgp traceoptions flag general
set protocols bgp traceoptions flag open
set protocols bgp traceoptions flag update
set protocols bgp traceoptions flag all
|
BGP Troubleshooting
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| show bgp neighbor X.X.X.X
show log messages | match "open message"
show log messages | match notification | match X.X.X.X
show log bgp_trace.log | match "(BGP SEND)|(BGP RECV)"
show route advertising-protocol bgp X.X.X.X
show route receive-protocol bgp X.X.X.X
show route hidden
show route resolution unresolved
show log bgp_trace.log | match "BGP RECV message type 2"
show system connection inet extensive | find X.X.X.X
ping X.X.X.X source X.X.X.X size 512 do-not-fragment
show interfaces ge-* detail | match "input filter"
show interfaces lo0.0 detail | match "input filter"
show configuration firewall family inter filter blocks-frags
show firewall
|
Enterprise Policies
Summarize BGP routes
1
| set routing-options aggregate route 10.0.0.0/8
|
1
2
3
4
| set policy-options policy-statement EXPORT-EBGP term 1 from protocol aggregate
set policy-options policy-statement EXPORT-EBGP term 1 from route-filter 10.0.0.0/8 exact
set policy-options policy-statement EXPORT-EBGP term 1 then accept
set policy-options policy-statement EXPORT-EBGP term 2 then reject
|
1
2
3
| set protocols bgp group EBGP type external
set protocols bgp group EBGP export EXPORT-EBGP
set protocols bgp group EBGP peer-as 65002
|
BGP prepend AS-path
1
| set routing-options aggregate route 10.0.0.0/8 as-path path 65000
|
1
2
3
4
5
| set policy-options policy-statement GRE-EBGP term 1 from protocol aggregate
set policy-options policy-statement GRE-EBGP term 1 from route-filter 10.0.0.0/8 exact
set policy-options policy-statement GRE-EBGP term 1 then as-path-expand last-as count 5
set policy-options policy-statement GRE-EBGP term 1 then accept
set policy-options policy-statement GRE-EBGP term 2 then reject
|
alternatively:
1
| set policy-options policy-statement GRE-EBGP term 1 then as-path-prepend "65000 65000 65000"
|
1
2
3
| set protocols bgp group EBGP neighbor 172.17.1.37
set protocols bgp group EBGP neighbor 172.17.1.37 export GRE-EBGP
set protocols bgp group EBGP neighbor 172.17.1.37 peer-as 65001
|
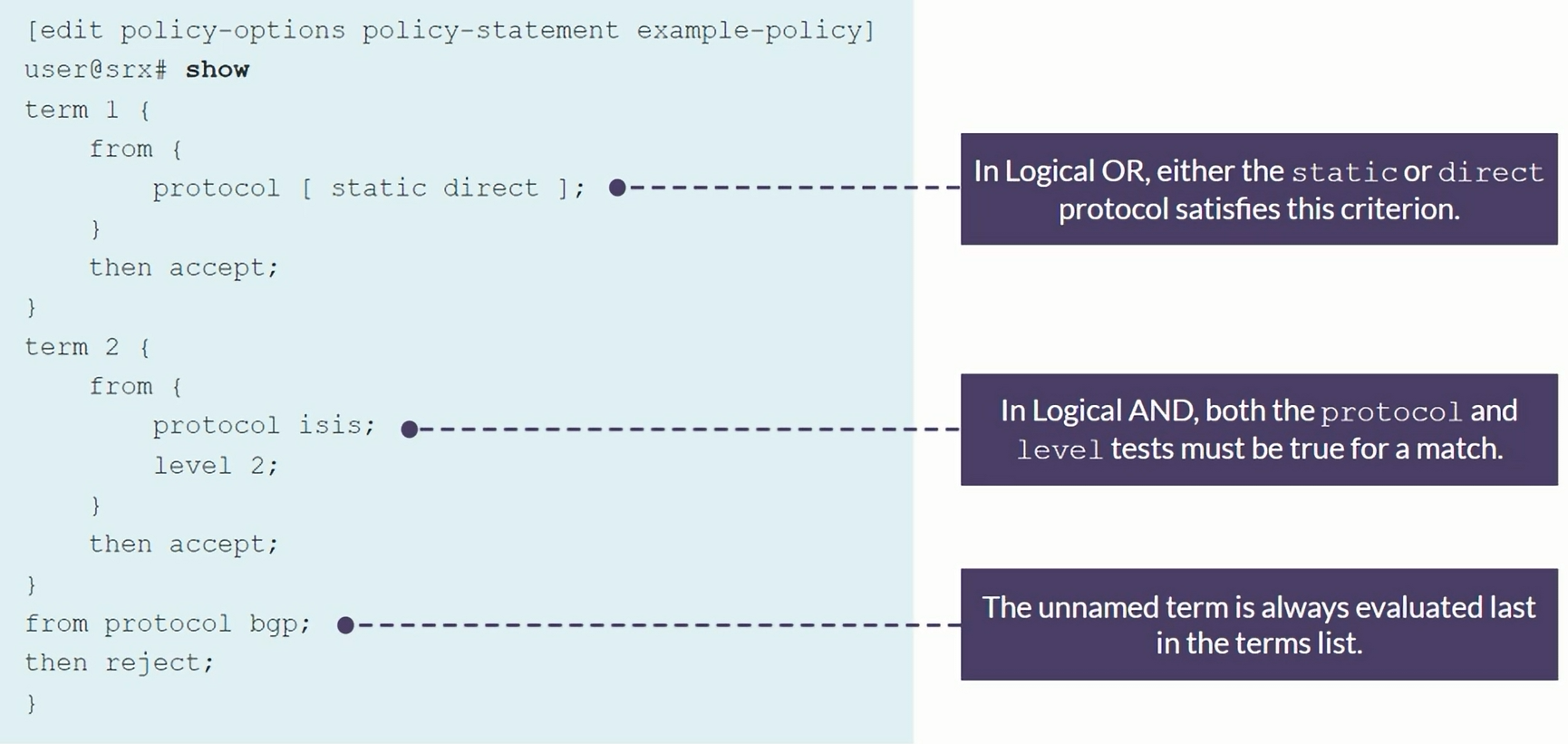
Routing Policy Structure
- You can apply multiple policies in a policy chain
- Evaluates sequentially, from left to right
- A terminating action in a matching term of a policy in the chain stops the processing
- The default policy is always last in a chian
- Applied implicitly
- Is protocol dependent
- Use the
default-action statement to override the protocols default - Always completes with a conclusive action
Prefix Lists
1
2
3
| set policy-options prefix-list RFC1918 10.0.0.0/8
set policy-options prefix-list RFC1918 172.16.0.0/20
set policy-options prefix-list RFC1918 192.168.0.0/16
|
1
2
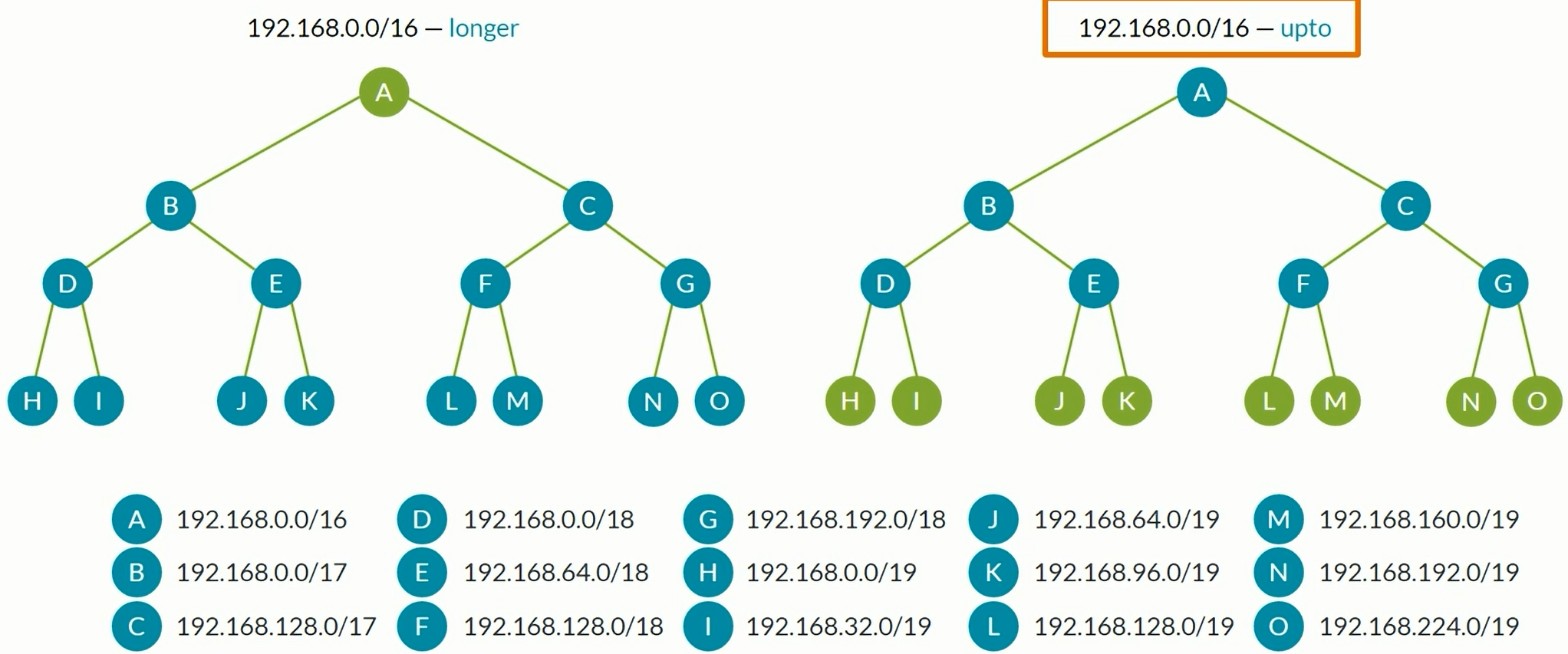
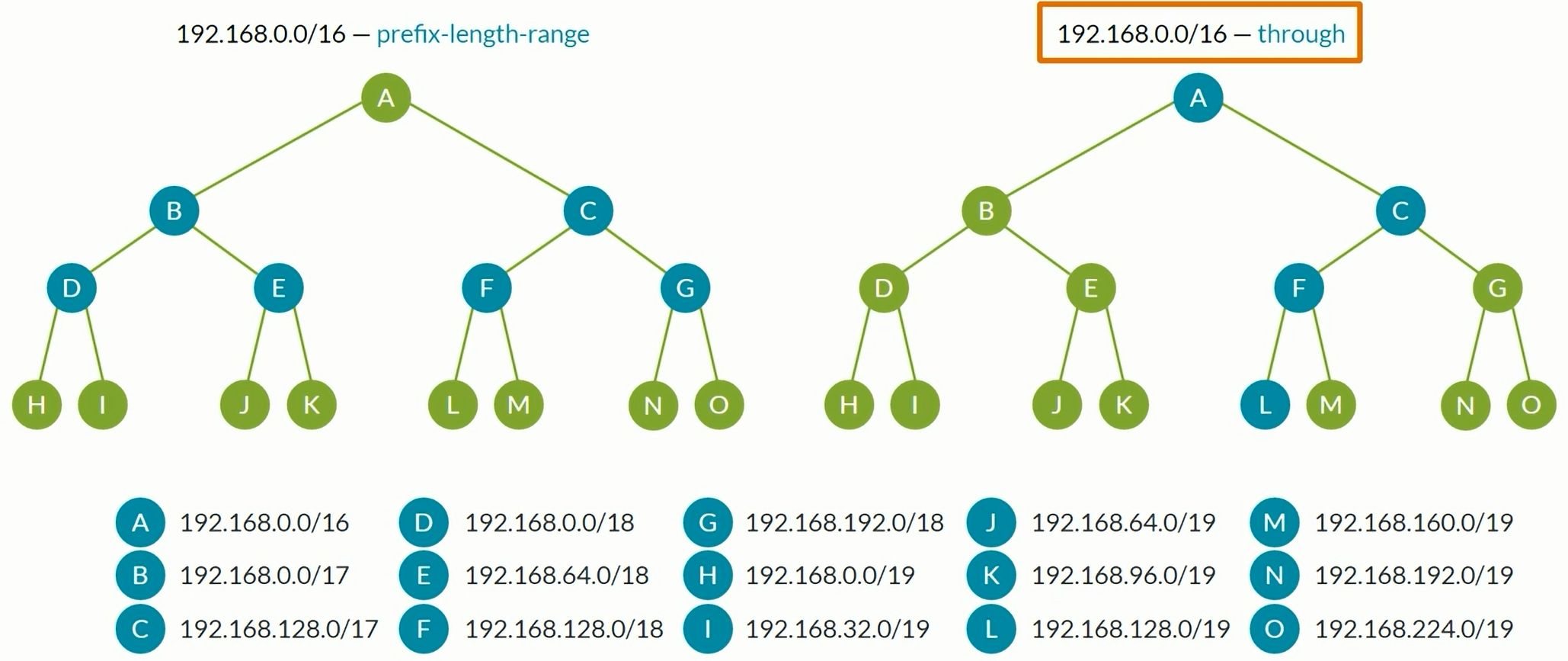
| set policy-options policy-statament REJECT-RFC1918 from prefix-list-filter RFC1918 orlonger
set policy-options policy-statament REJECT-RFC1918 then reject
|
Route Filters
BGP AS-path regex examples
BGP Communitiies regex examples
Routing Policy Troubleshooting
Policy Test Utility
Only evaluates active routes in the Routing Table. Does not support all match conditions. Useful for policies with route-filters. Default action of the test is accept.
1
2
| test policy reject-unwanted-routes 192.168/16
test policy test-statics 172.16.0.1/18
|
Policy Troubleshooting
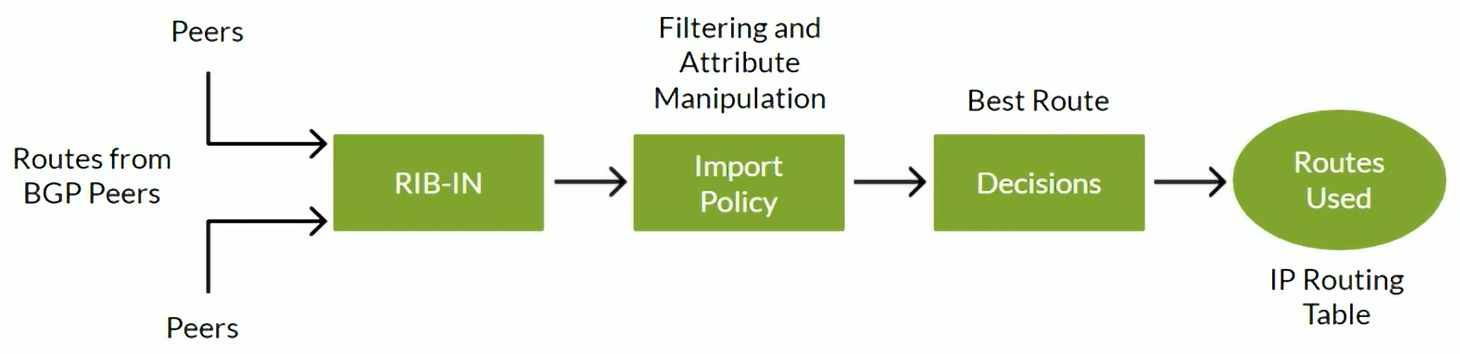
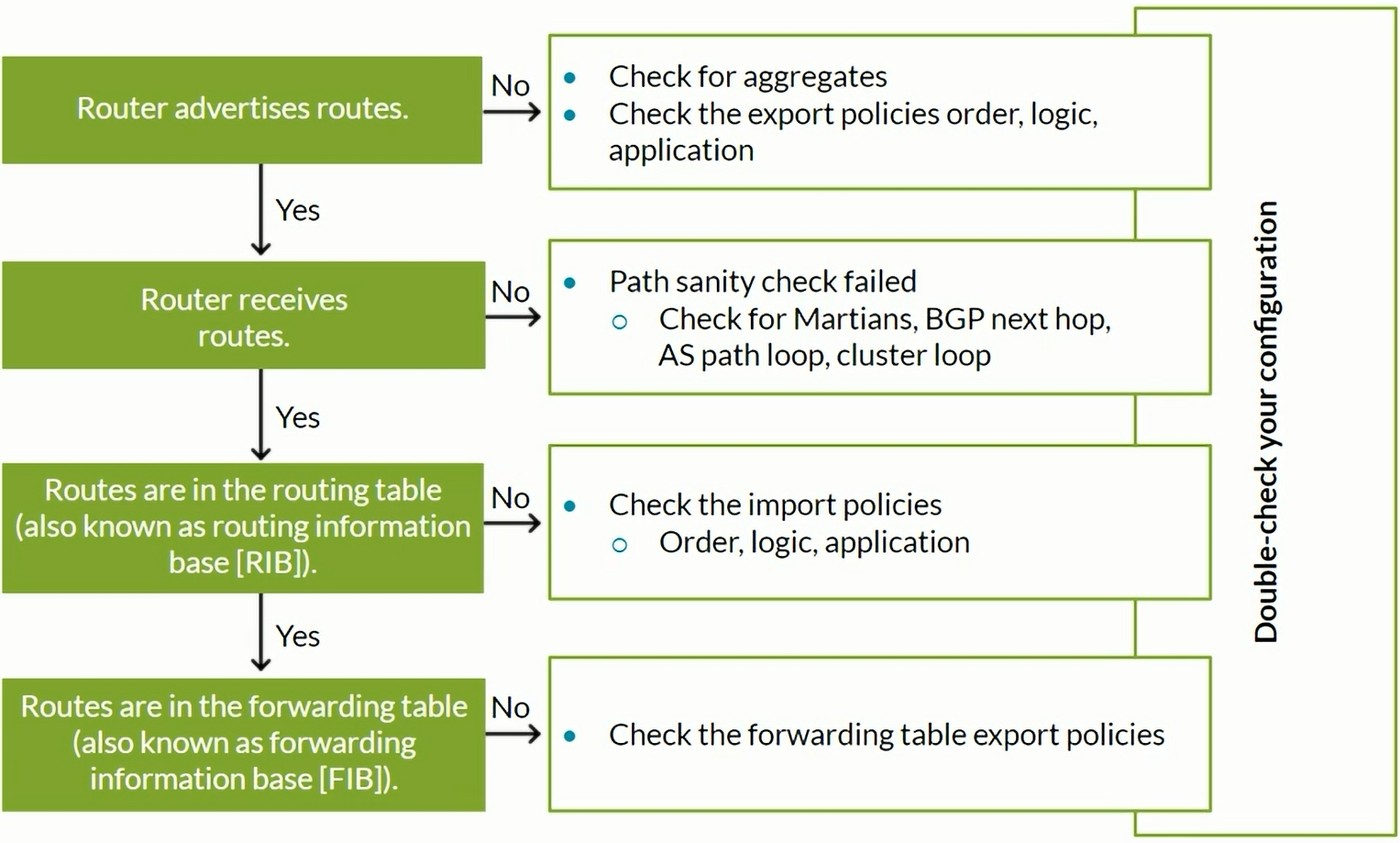
View the BGP routes that are received prior to the filtering of the import policy.
1
| show route receive-protocol bgp X.X.X.X
|
View the BGP routes that have been filtered by the import policy.
1
| show route receive-protocol bgp X.X.X.X hidden
|
View the BGP routes after the import policy processing in the Routing Table.
1
| show route protocol bgp source-gateway X.X.X.X
|
View the BGP routes advertised by the export policy.
1
| show route advertising-protocol bgp X.X.X.X
|
View the OSPF external routes exported by the export policy
1
| show ospf database external
|
Displays the Shorted Path First (SPF) computed routes to the External OSPF subnets
View the OSPF external routes in the Routing Table
1
| show route protocol ospf terse | match "O 150"
|
View the IS-IS external routes exported by the export policy
1
| show isis database router-4.00 detail | match external
|
Displays IS-IS routes in the Routing Table
1
| show route protocol isis terse | match "I 165"
|
View the routes in the Forwardin Table (FIB)
1
| show route forwarding-table destination X.X.X.X/XX
|
Find all BGP routes that traversed AS 50292 or AS 50293
1
| show route protocol bgp aspath-regex ".* (50292|50293)"
|
Use community regex filters to limit operational command output
1
2
| show route protocol bgp community ".*:[678]0"
show route 200.200/16 detail | match communities
|
View all configured policies
View Import and Export policies attached to a BGP neighbor
1
| show bgp neighbor X.X.X.X | match "(export) | (import)"
|
Policy roubleshooting Use Case
- Do not accept the
any:777 or any:888 communities
1
2
| show route receive-protocol bgp X.X.X.X community "*:(777)|(888)"
show route protocol bgp community "*:(777)|(888)"
|
- Replace all incoming communities with
65000:neighbor_AS
1
2
| show route protocol bgp source-gateway X.X.X.X community-name as100-comm
show route protocol bgp community-name no-export terse
|
- Mark routes originating in any autonomous system (AS) other than the neighboring AS with the
no-export community
Incorrect configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 1 from community DROP-COMM
set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 1 then reject
set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 2 from as-path AS100
set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 2 then community set AS100-COMM <--- Error: does not have a terminating action, which passes processing to the next term
set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 3 then community set NO-EXPORT <--- Error: Overwrites all previously set communities with the new community, no-export
set policy-options as-path AS100 "100"
set policy-options community AS100-COMM members 65000:100
set policy-options community DROP-COMMM members [ *:777 *:888 ] <--- Error: this is a logical AND, not a logical OR
set policy-options community NO-EXPORT members no-export
|
IMPORTANT: If the policy does not explicilty accept or reject the route, the next policy is processed.
Correct configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 1 from community [ DROP-COMM-1 DROP-COMM-2 ] <--- Correct: Logical OR
set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 1 then reject
set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 2 from as-path AS100
set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 2 then community set AS100-COMM
set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 2 then accept <--- Correct: terminating Action
set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 3 then community set NO-EXPORT
set policy-options policy-statement ENT-IMPORT-FILTER term 3 then community add AS100-COMM <--- Correct: adding Community
set policy-options as-path AS100 "100"
set policy-options community AS100-COMM members 65000:100
set policy-options community DROP-COMMM-1 members *:777
set policy-options community DROP-COMMM-2 members *:888
set policy-options community NO-EXPORT members no-export
|
1
2
3
| show route protocol bgp source-gateway X.X.X.X hidden terse
show route 10.1.100/24 detail | match "(communities)|(as path)"
show route 10.3.100/24 detail | match "(communities)|(as path)"
|
Multicast
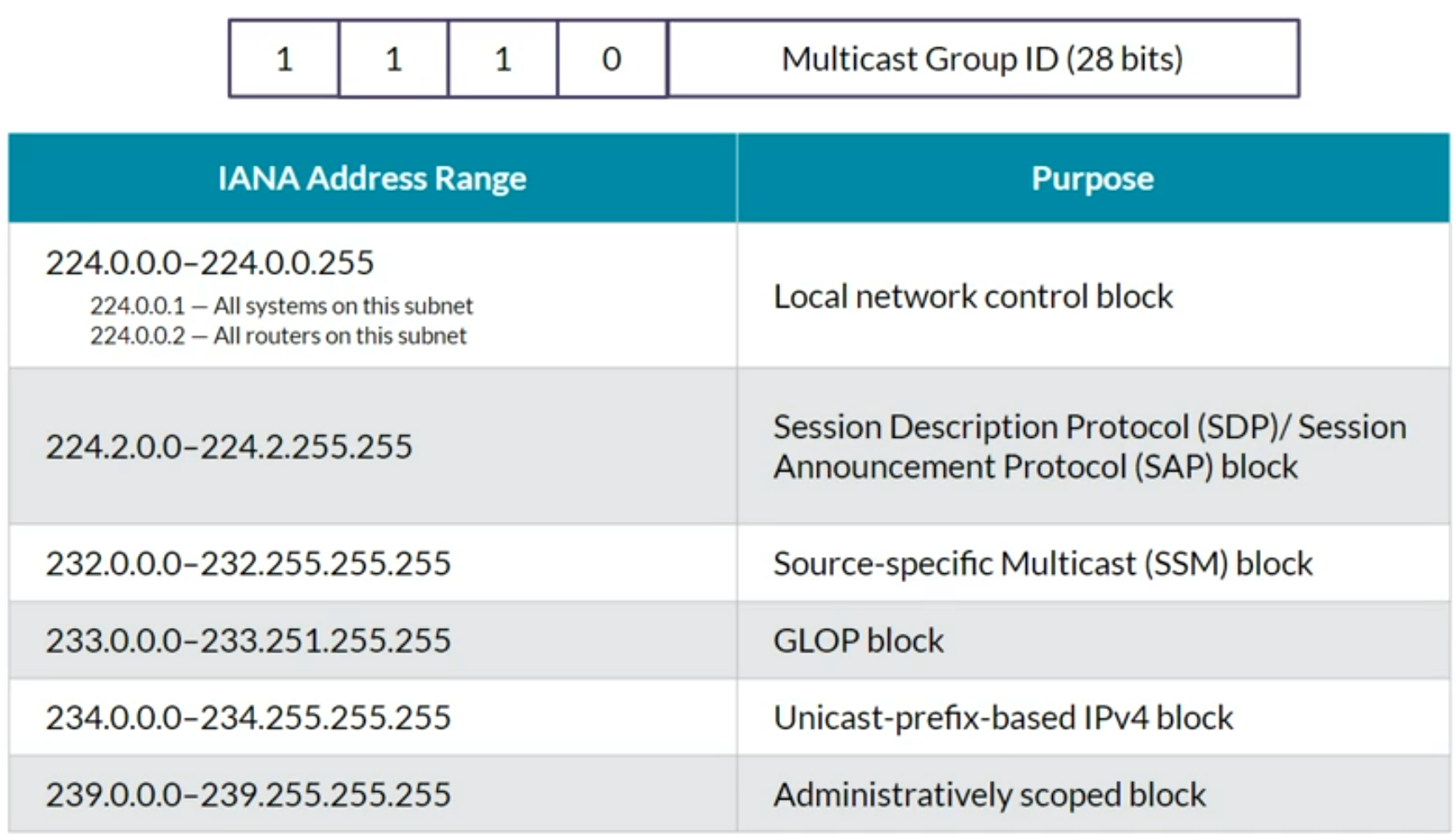
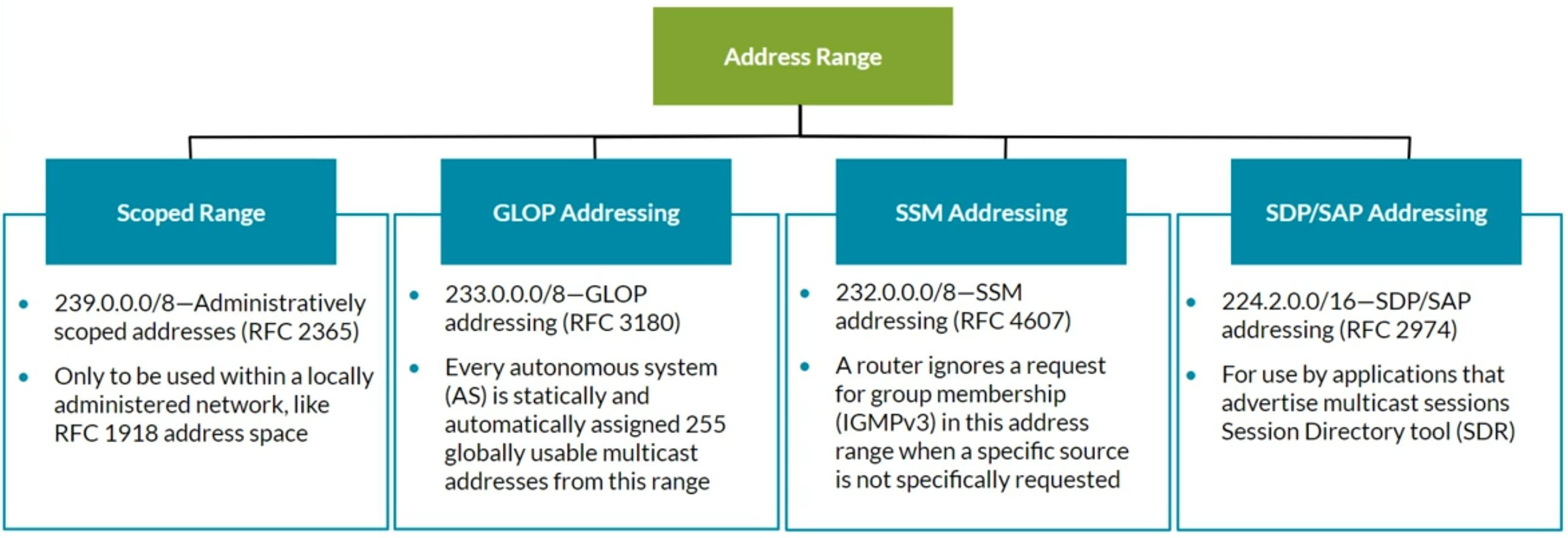
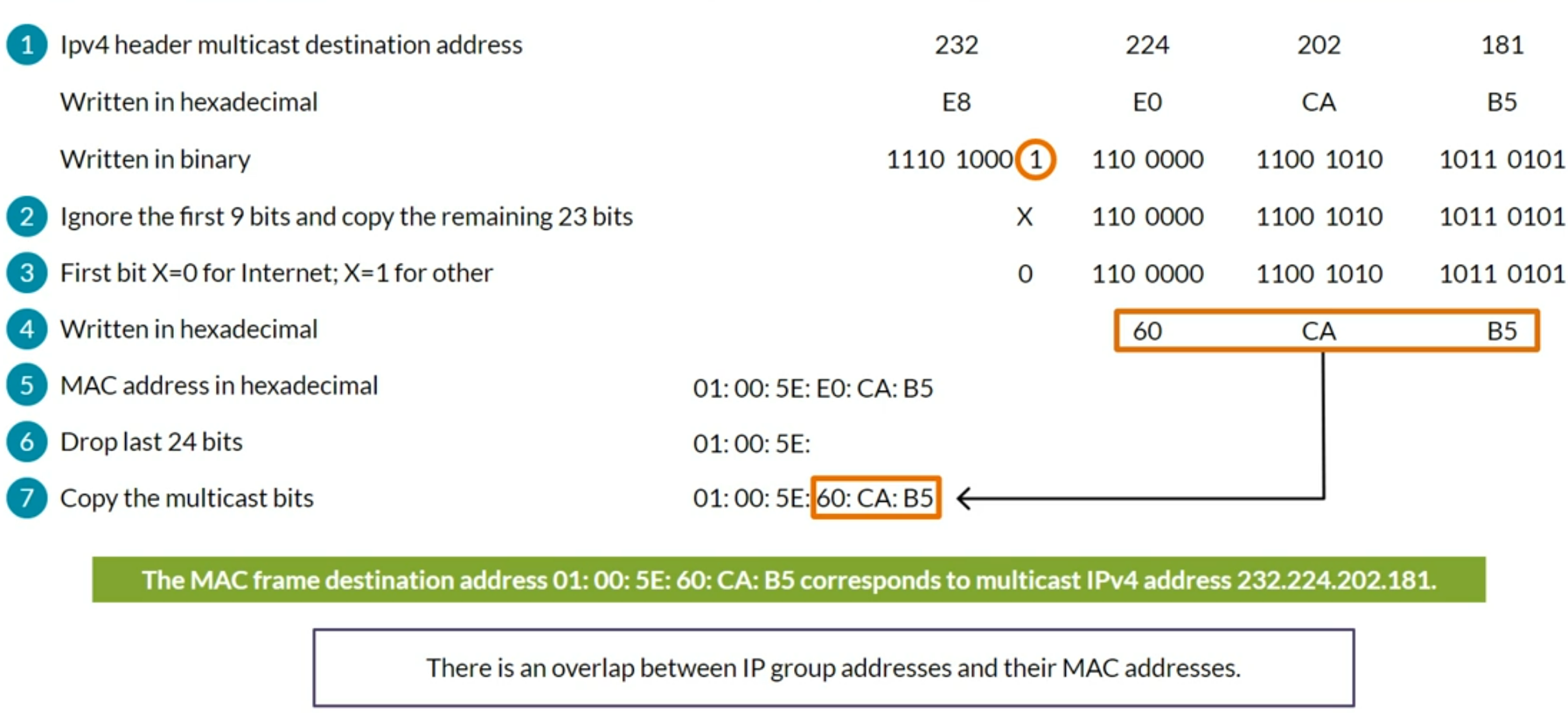
Multicast IP & Ethernet addressing
RPF Check
1
| show multicast rpf X.X.X.X
|
Multicast Routing Tables
inet.0- Default table used for RPF check lookups
inet.1- Forwarding cache for successful RPF-checked traffic
inet.2- Alsternate table for RPF check lookups
- Multicast topology independent from unicast topology
- Use of RIB groups required
IGMP verification commands
1
2
3
| show igmp interface
show igmp group
show igmp statistics
|
Traceoptions
1
2
3
| set protocol igmp traceoptions file trace-igmp.log
set protocol igmp traceoptions flag packets detail
set protocol igmp traceoptions flag general detail
|
1
| monitor start trace-igmp.log
|
PIM verification commands
1
2
3
| show pim interfaces
show pim rps extensive
show pim join extensive
|
1
| show multicast route extensive
|
Configuring IGMP
1
2
| set protocols igmp interface ge-0/0/8 version 2
set protocols igmp interface ge-0/0/8 immediate-leave
|
1
2
| clear igmp statistics
clear igmp membership all
|
Configuring PIM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| set protocols pim interface all mode sparse
set protocols pim interface fxp0.0 disable
or
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/4 mode sparse
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/8 mode sparse
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/1 mode sparse
set protocols pim interface lo0 mode sparse
|
Static RP configuration on the RP
1
| set protocols pim rp local address 192.168.121.1 [group-ranges 224/4]
|
Static RP configuration on all other (non-RP) Routers
1
| set protocols pim rp static address 192.168.121.1
|
Auto RP configuration
Configuration on RP-candidate and Mapping Agent Routers configuration:
1
| set protocols pim rp local address 10.1.1.1
|
- Auto-RP mapping agent role: Performs election of RPs
1
| set protocols pim rp auto-rp mapping
|
- Dense mode flooding for announce/discovery groups
1
2
| set protocols pim dense-groups 224.0.1.39
set protocols pim dense-groups 224.0.1.40
|
- Interface sparse-dense mode
1
2
| set protocols pim interface all mode sparse-dense
set protocols pim interface fxp0.0 disable
|
Configuration on all other Routers:
- Auto-RP discovery role: Listen to election results
1
| set protocols pim rp auto-rp discovery
|
- Dense mode flooding for announce/discovery groups
1
2
| set protocols pim dense-groups 224.0.1.39
set protocols pim dense-groups 224.0.1.40
|
- Interface sparse-dense mode
1
2
| set protocols pim interface all mode sparse-dense
set protocols pim interface fxp0.0 disable
|
BSR configuration
Configuration on RP and BSR Routers:
1
| set protocols pim rp local address 10.1.1.1
|
- Bootstrap candidacy, higher priority value to become boostrap router
1
| set protocols pim rp bootstrap priority 200
|
1
2
| set protocols pim interface all mode sparse
set protocols pim interface fxp0.0 disable
|
Configuration on all other Routers:
1
2
| set protocols pim interface all mode sparse
set protocols pim interface fxp0.0 disable
|
Configuration to keep traffic on the Share Path
1
| set protocols pim spt-threshold infinity RPT-ALWAYS-POLICY
|
1
2
3
4
| set policy-options policy-statement RPT-ALWAYS-POLICY term 1 from route-filter 224.7.7.7/32 exact
set policy-options policy-statement RPT-ALWAYS-POLICY term 1 from source-address-filter 10.1.1.1/32 exact
set policy-options policy-statement RPT-ALWAYS-POLICY term 1 then accept
set policy-options policy-statement RPT-ALWAYS-POLICY term 2 then reject
|
Load balance PIM Joins on ECMP
1
| set protocols pim join-load-balance
|
PIM Join/Prune timeout
1
2
3
4
5
| set protocols pim join-prune-timeout 230
set protocols pim reset-tracking-bit
set protocols pim propagation-delay 500
set protocols pim override-interval 2000
|
Monitoring and Verifying PIM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| show pim interfaces
show pim neighbors [detail]
show pim statistics
show pim join [extensive]
show pim source [detail]
show pim rps [extensive]
show pim bootstrap
show multicast usage
show multicast route extensive
show multicast next-hops
show multicast rpf X.X.X.X (IP SRC of the Multicast traffic)
show route table inet.1
|
1
| mtrace from-source group 224.7.7.7 ttl 20 source 10.0.107.1
|
1
| ping 225.1.2.3 ttl 10 interface ge-1/0/4.12 bypass-routing
|
Disable Routers to respond to multicast pings
1
| set system no-multicast-echo
|
IGMP static joins do not respond to pings requests. Enabling SA (Session Announcement Protocol) listening on Routers action as the receiver:
1
| set protocols sap listen 225.1.2.3
|
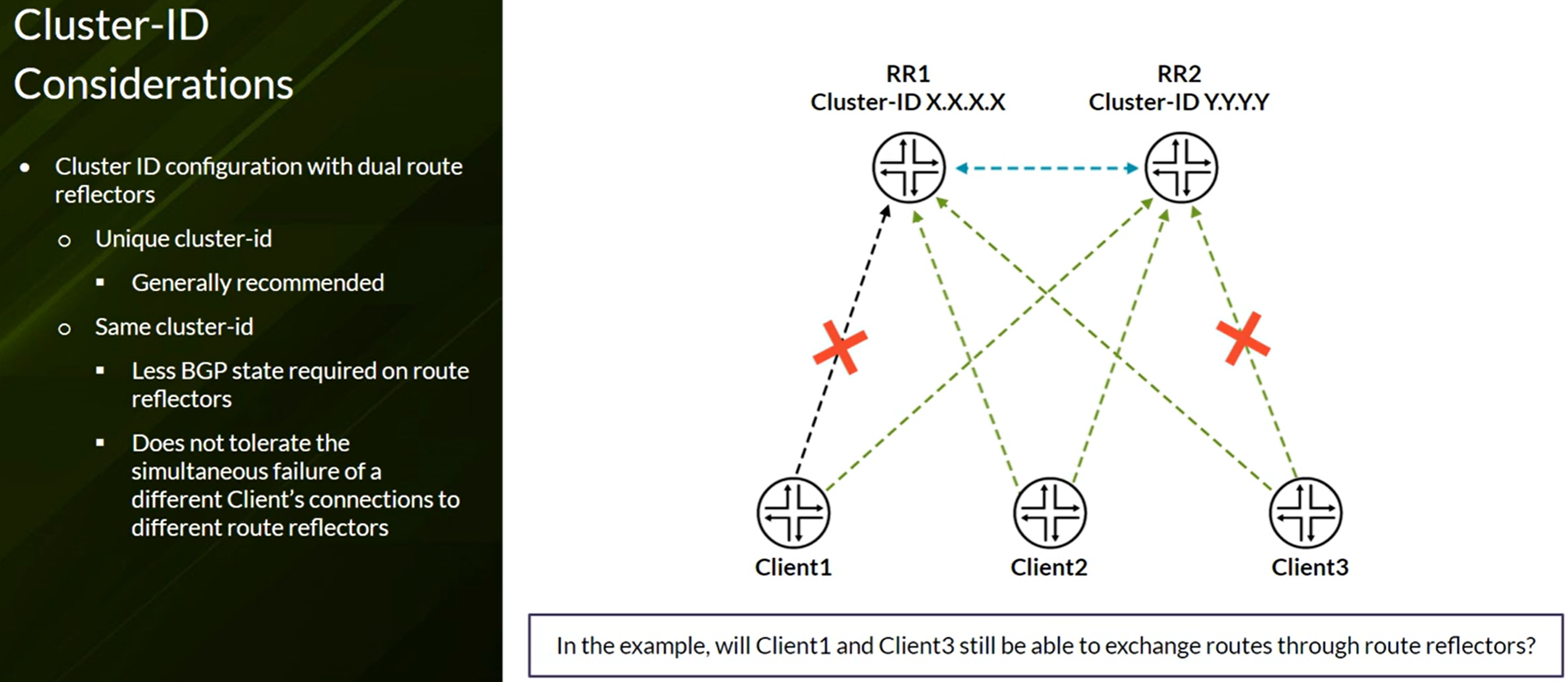
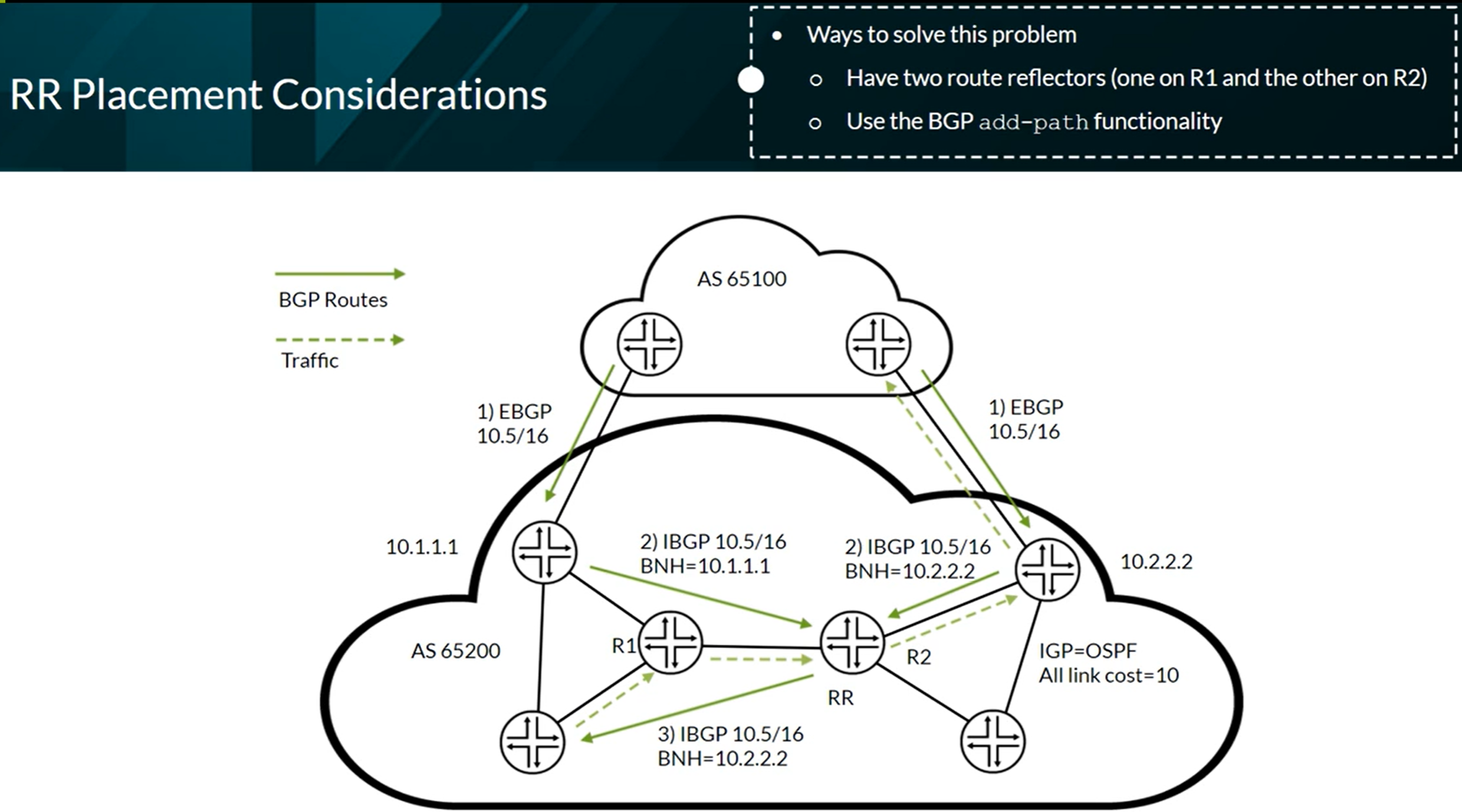
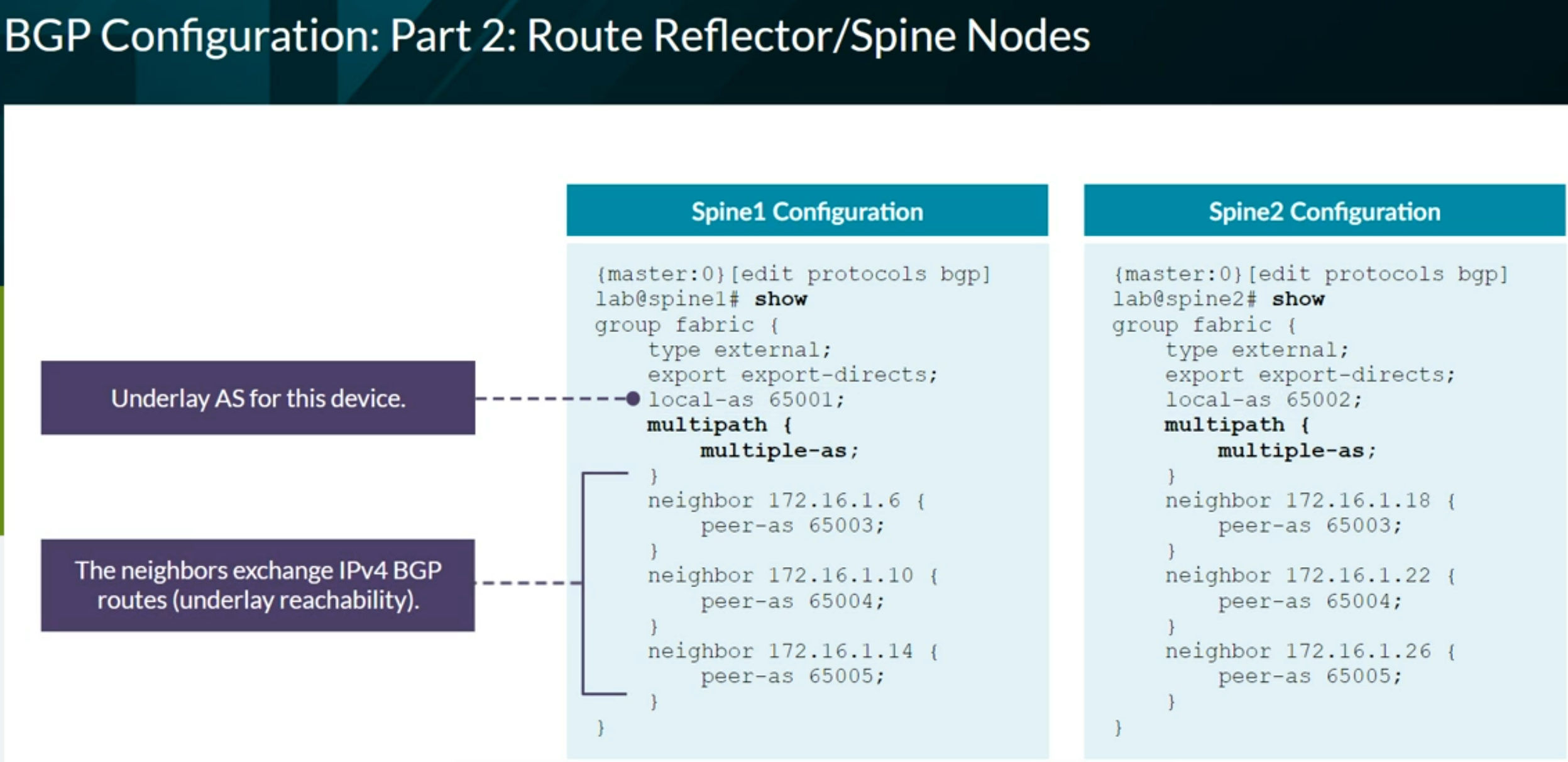
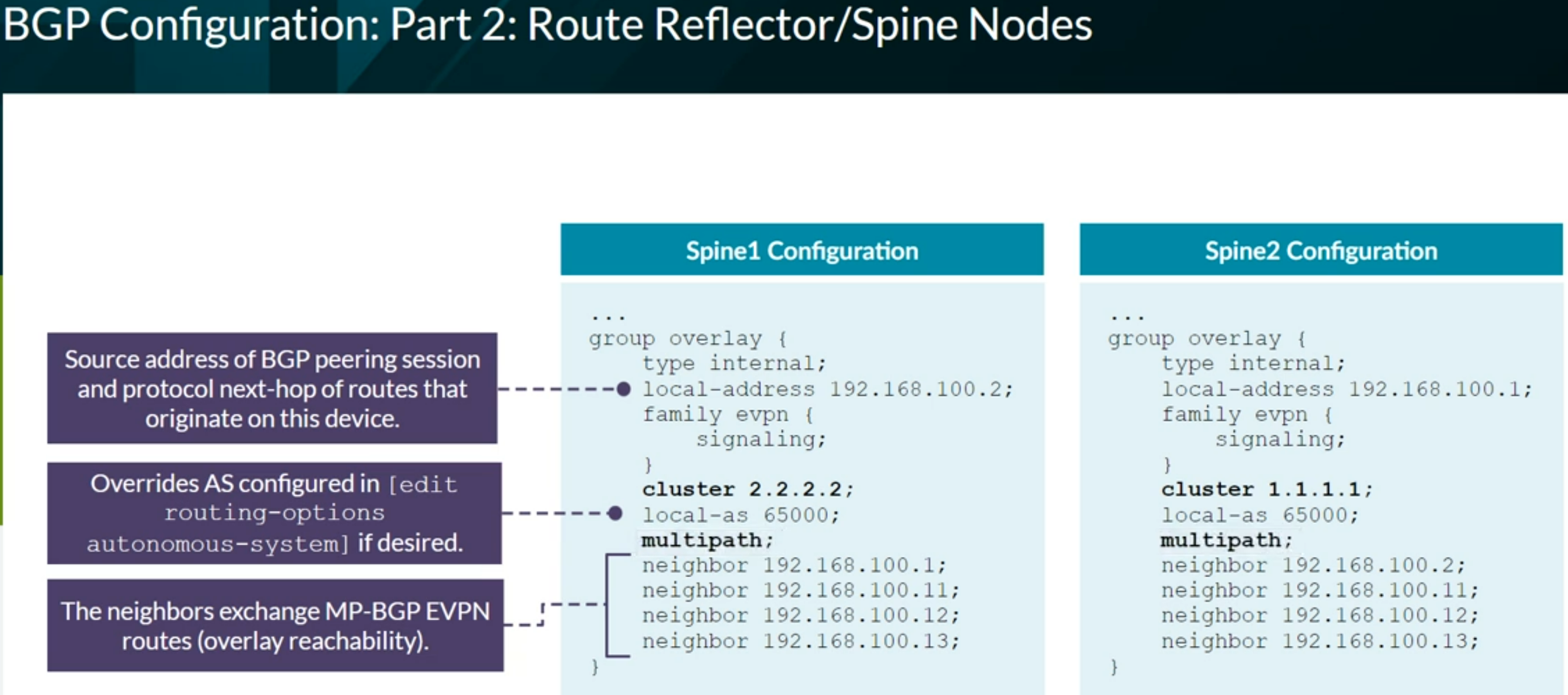
BGP Route Reflection
Route Reflector new attributes:
- Cluster list
- Originator ID
To configure BGP Route Reflector, use the cluster configuration line:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| set protocols bgp group INT-PEERS type internal
set protocols bgp group INT-PEERS local-address 172.16.1.1
set protocols bgp group INT-PEERS cluster 172.16.1.1 <<<<<<-------
set protocols bgp group INT-PEERS neighbor 172.16.2.2
set protocols bgp group INT-PEERS neighbor 172.16.3.3
set protocols bgp group INT-PEERS neighbor 172.16.4.4
|
One solution is the use of the BGP feature path-selection always-compare-med. Another solution is the add-path command to advertise all the routes and not only the active one.
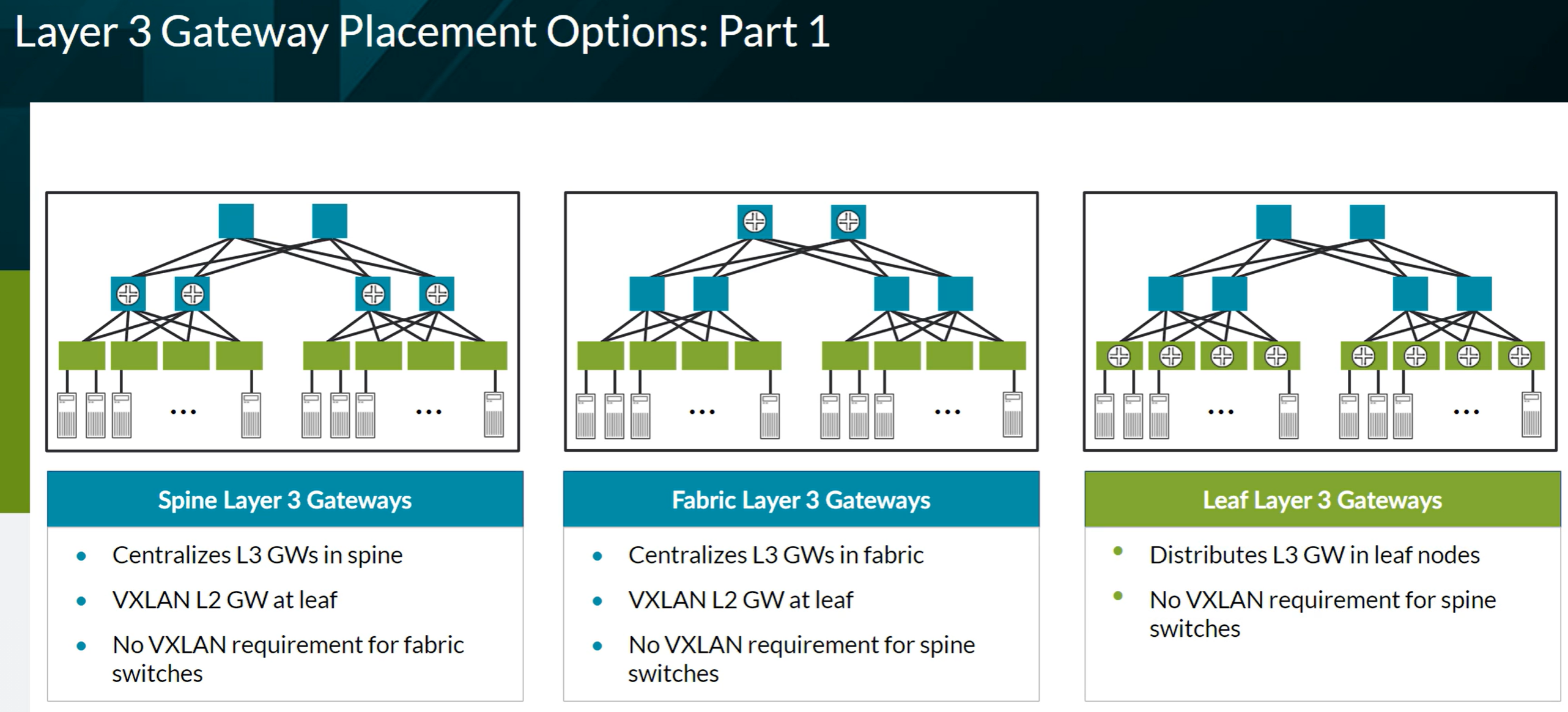
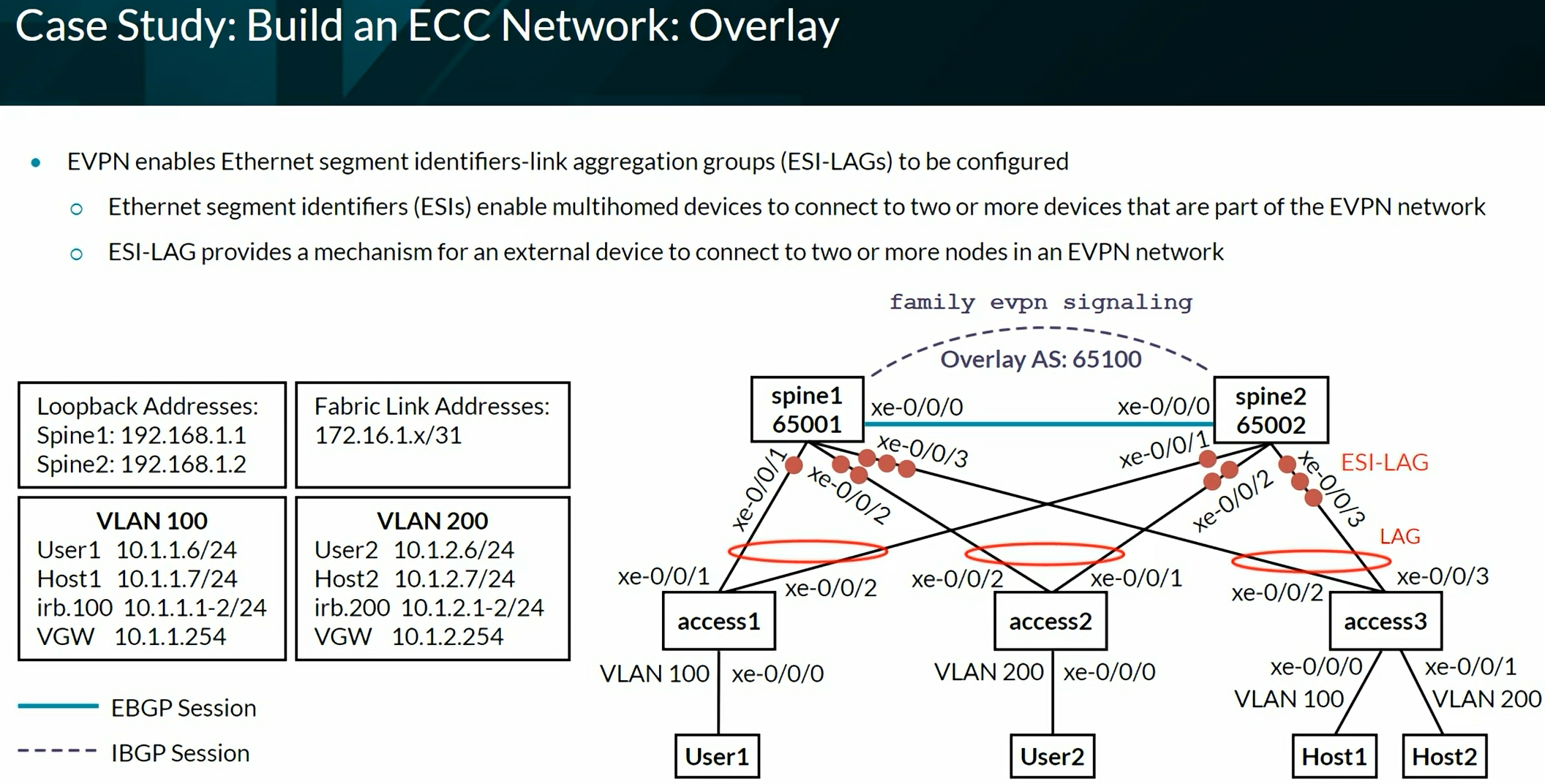
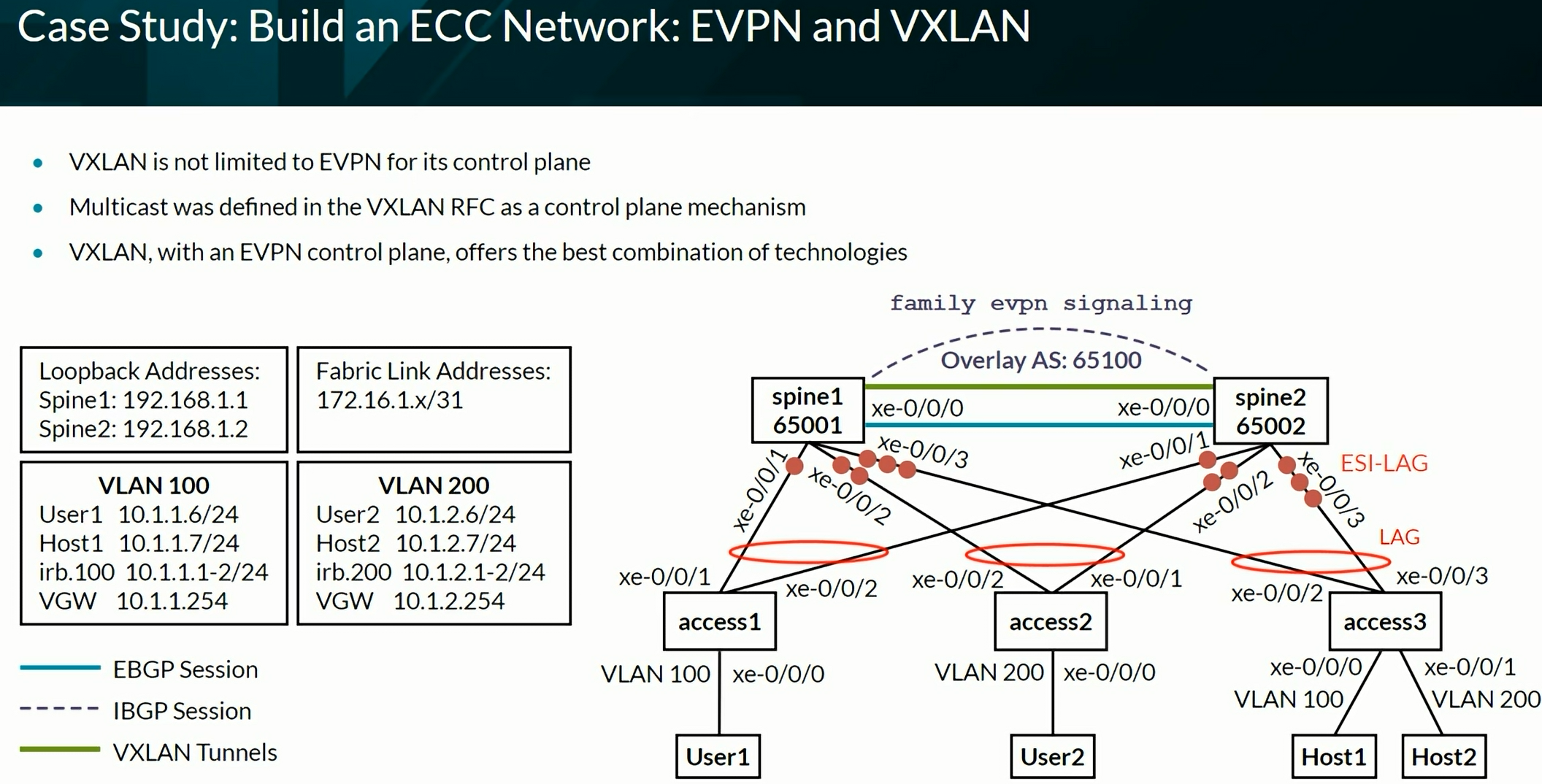
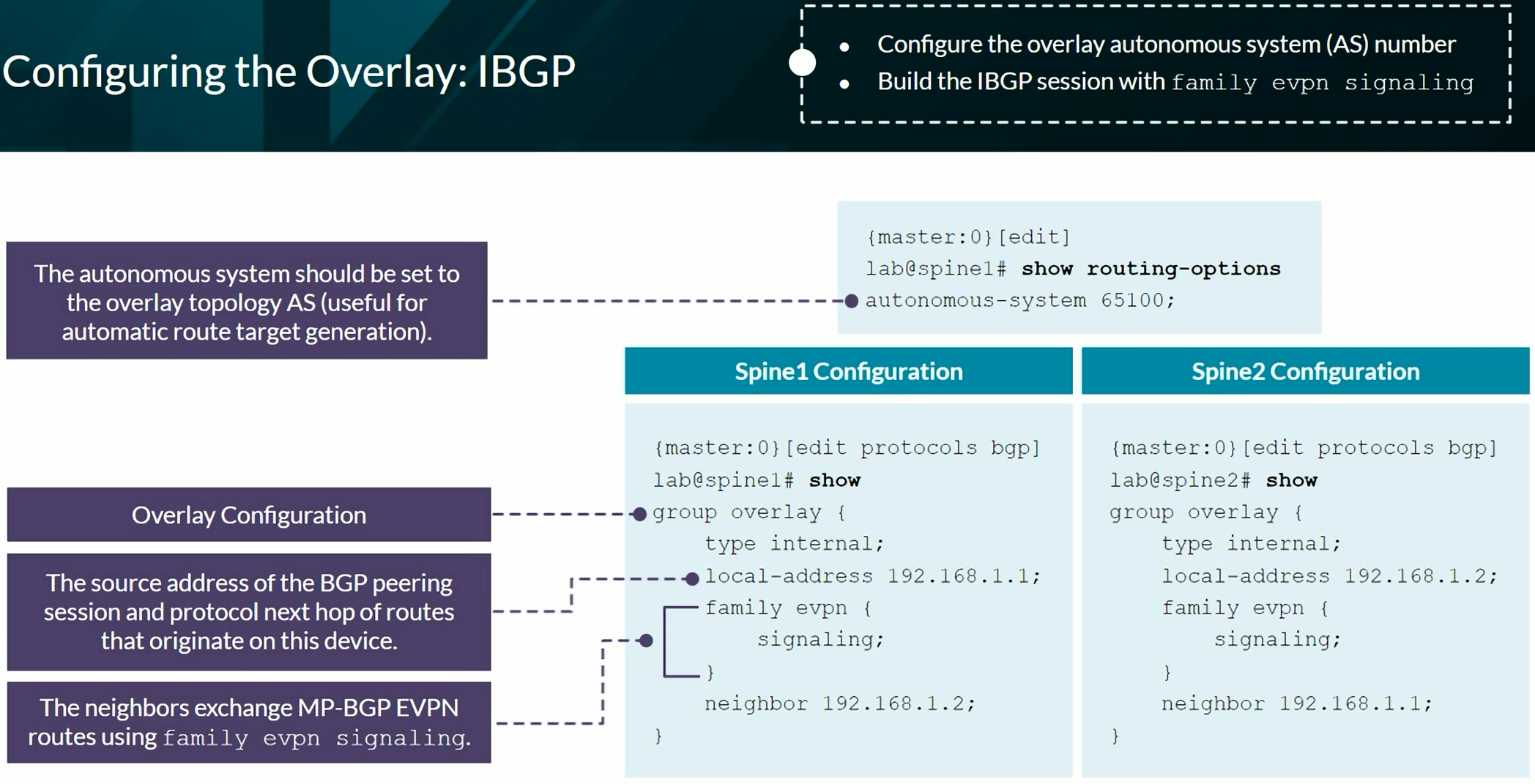
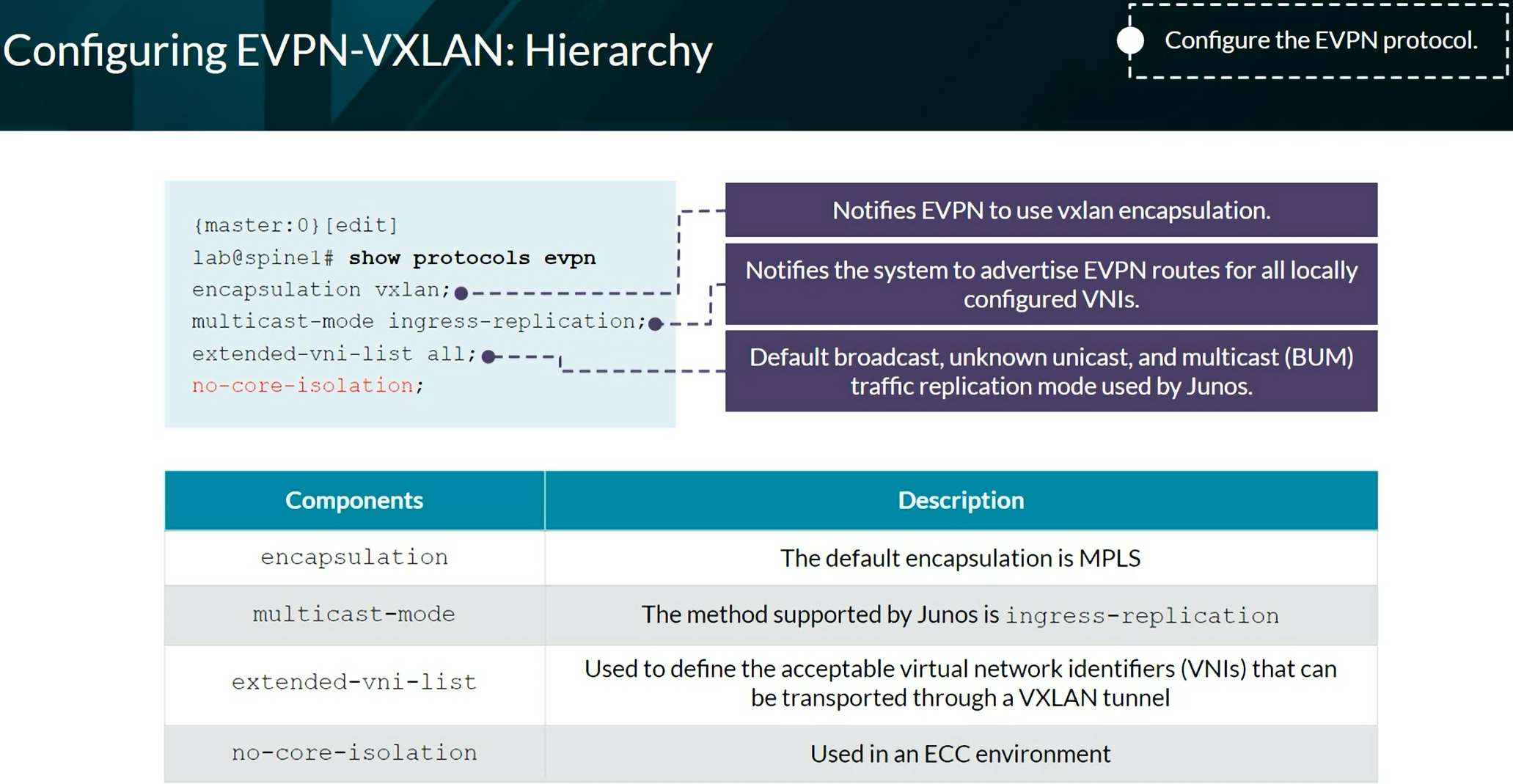
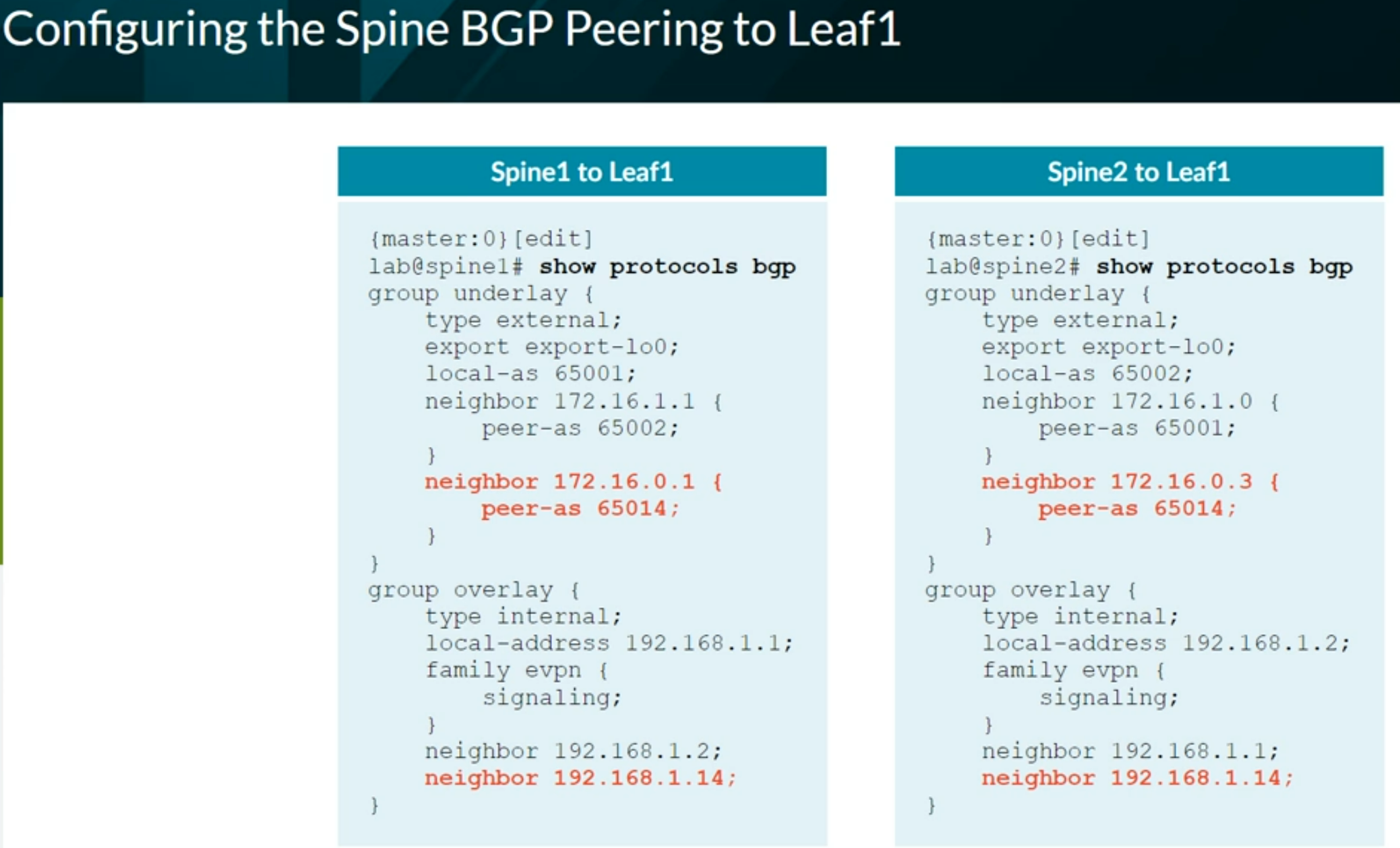
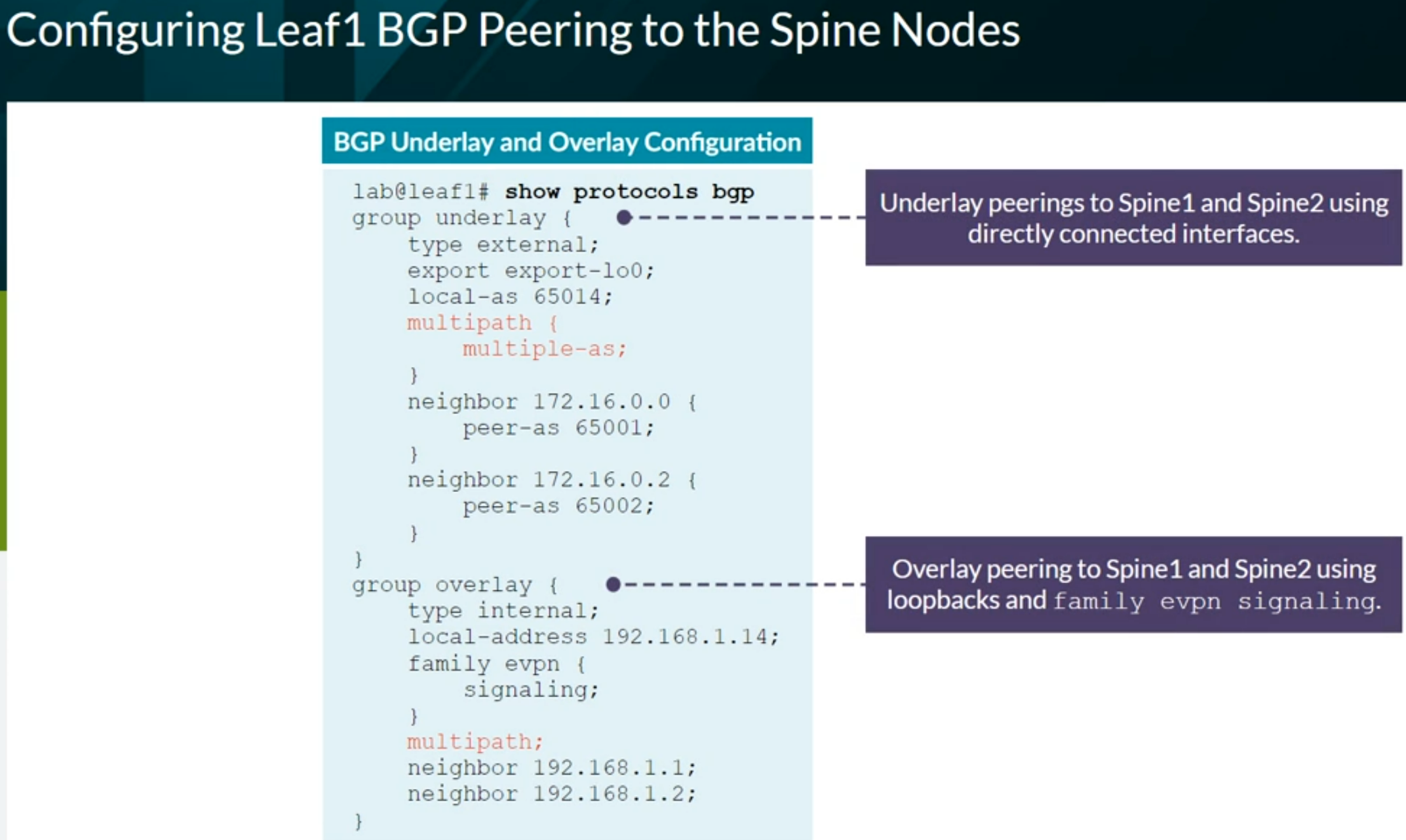
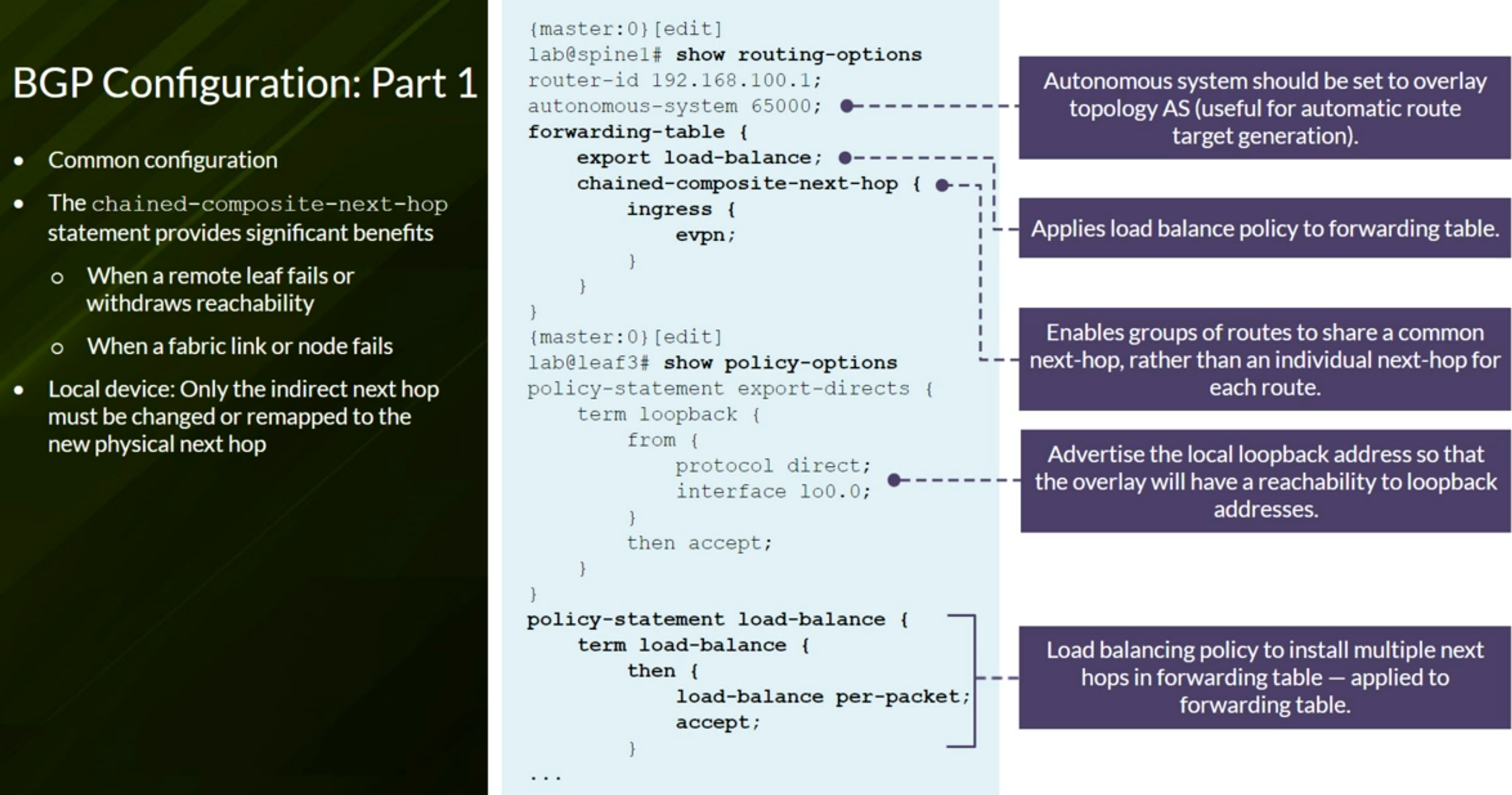
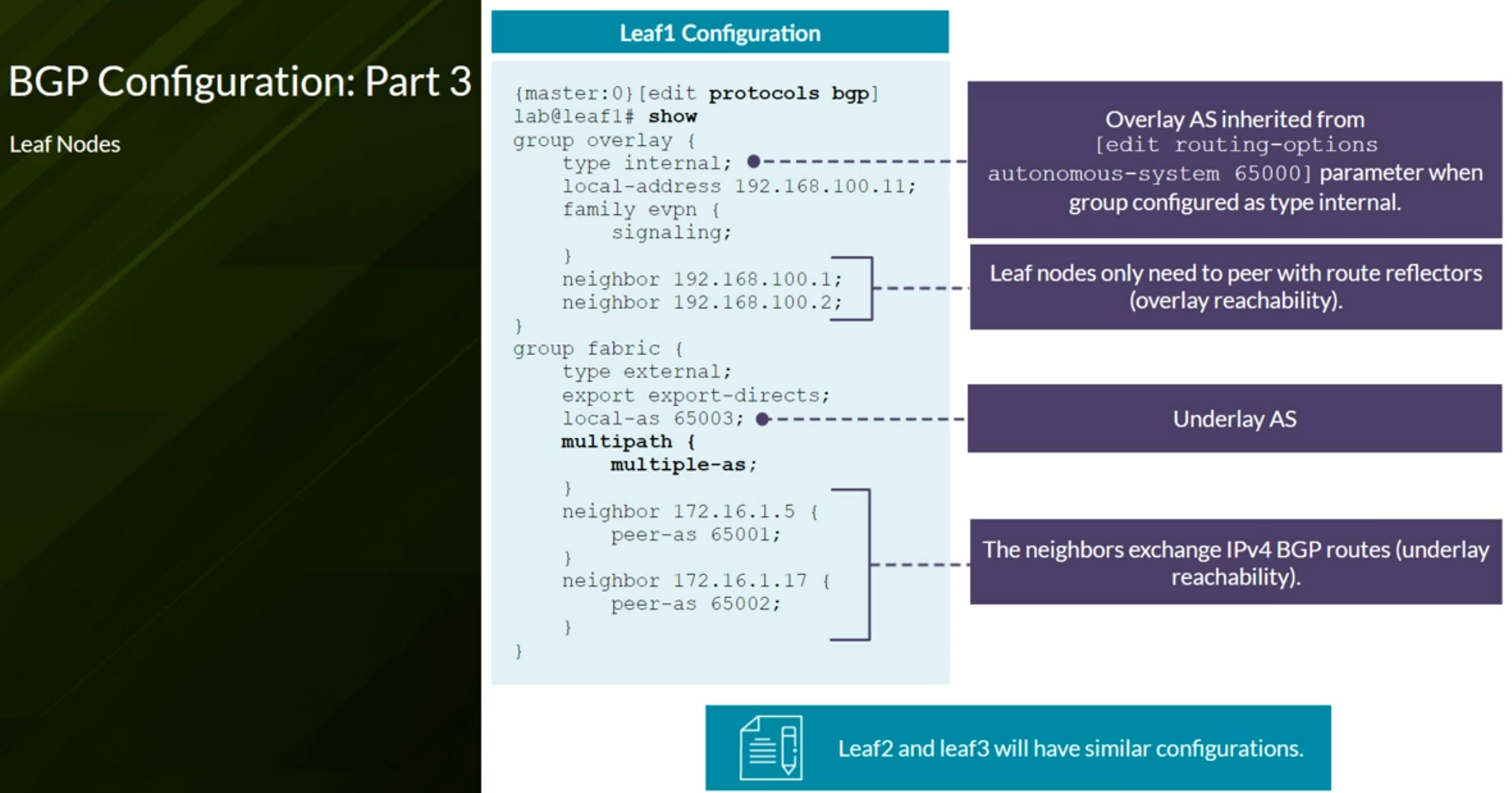
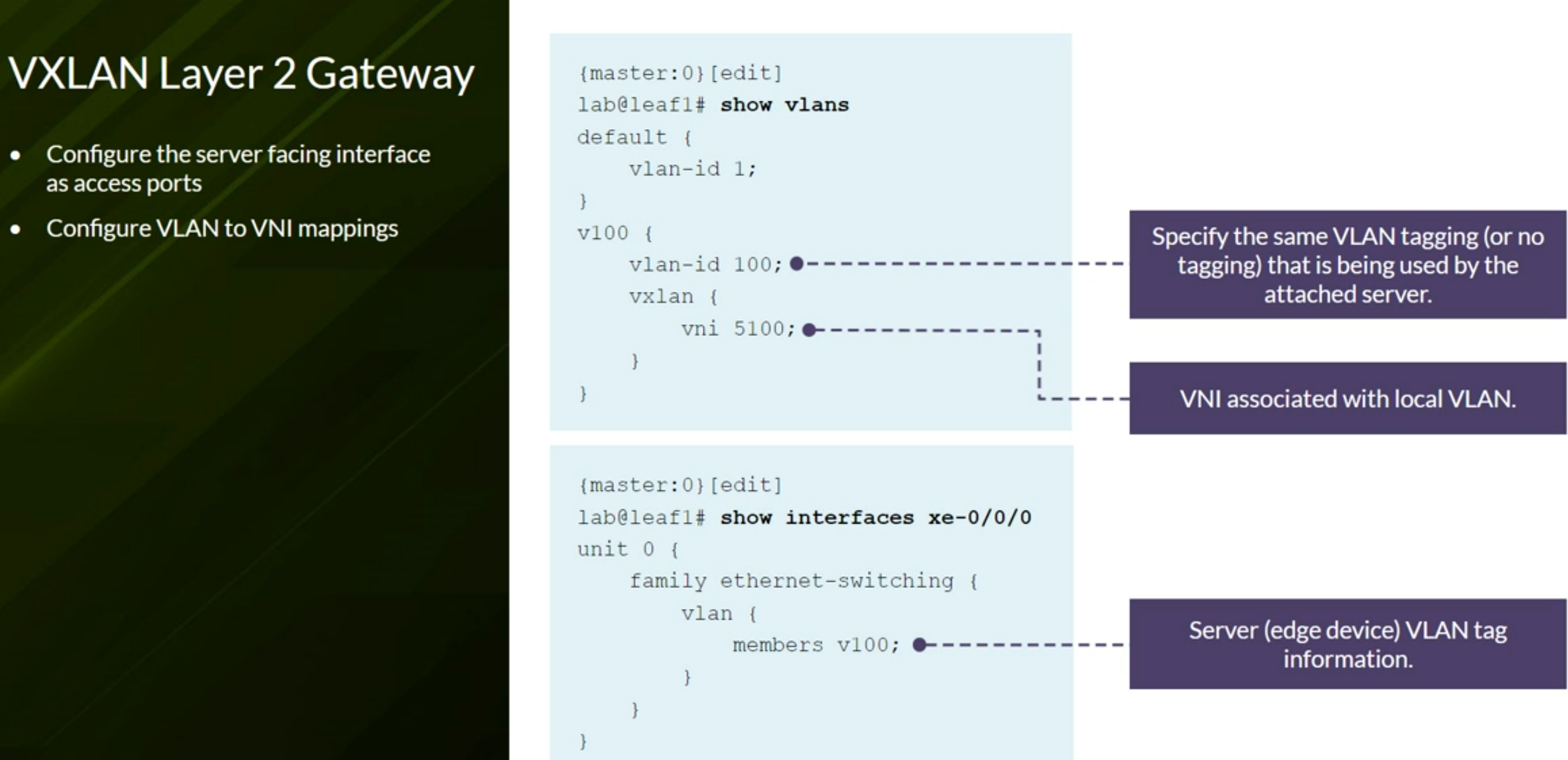
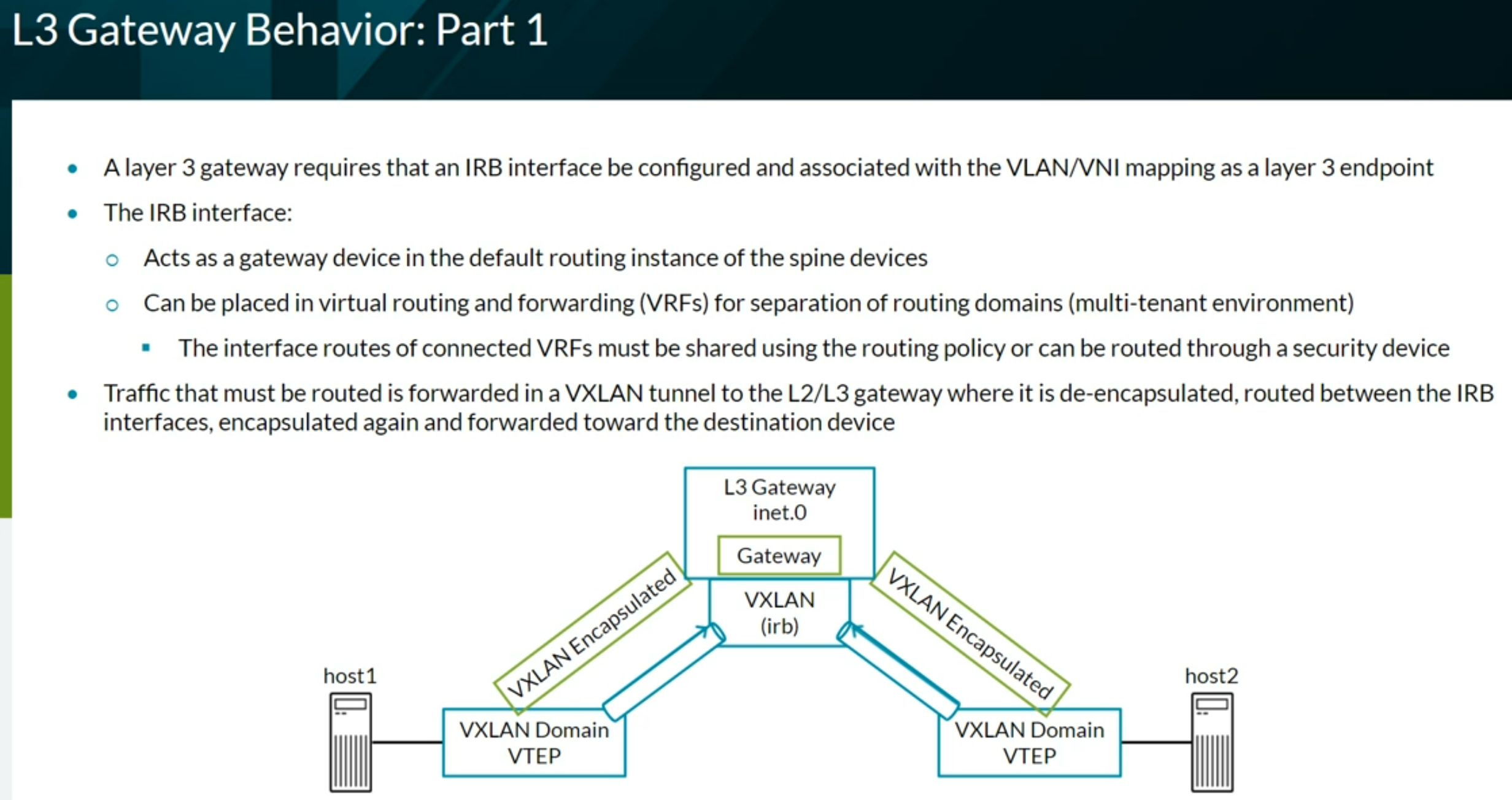
VXLAN BGP EVPN
- EVPN
- AFI (Address Family Indicator): 25 Layer VPN
- SAFI (Subsequent Address Family Indicator): 70 EVPN
- Configuration on Junos OS:
family evpn signaling
EVPN instanve (EVI) = Virtual Switch = MAC VRF
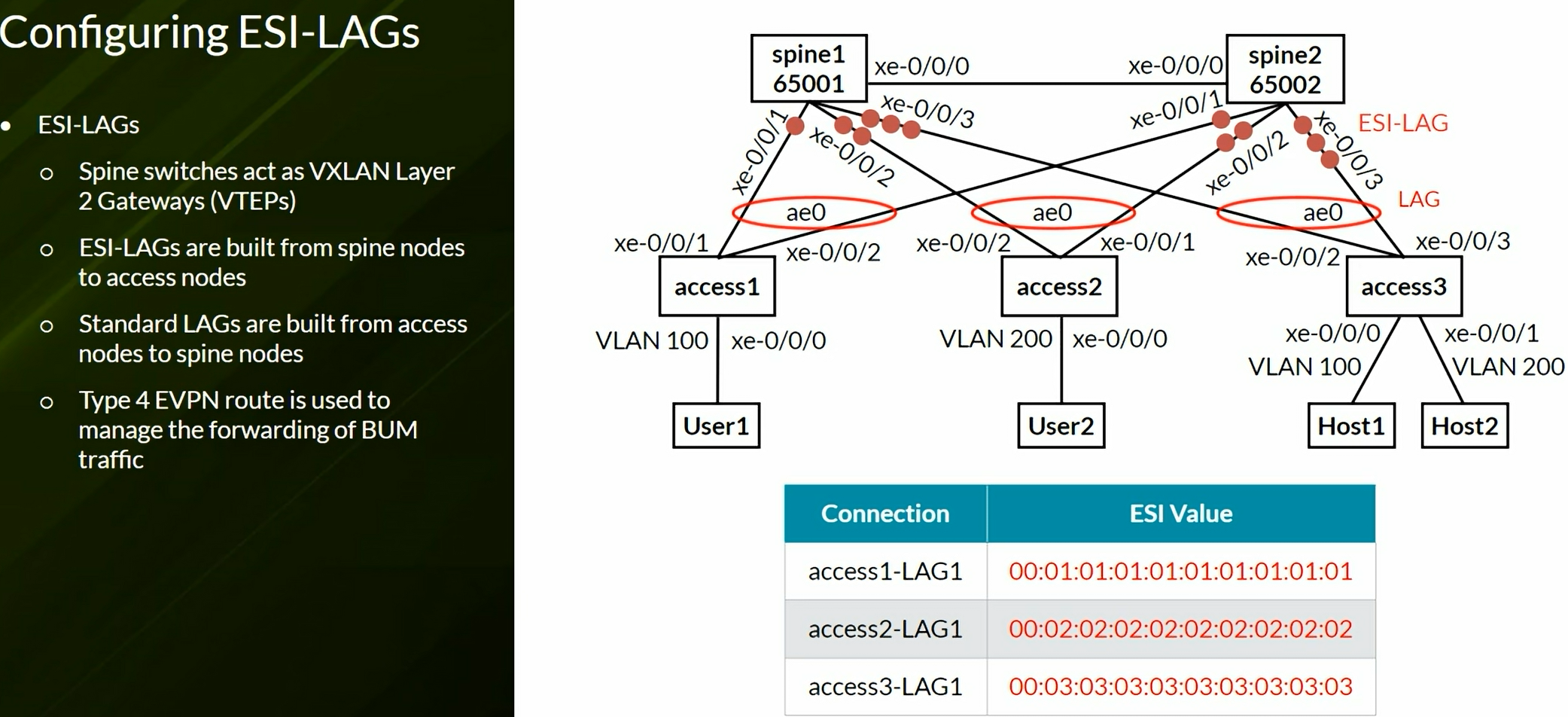
ESI - Ethernet Segment Identifier
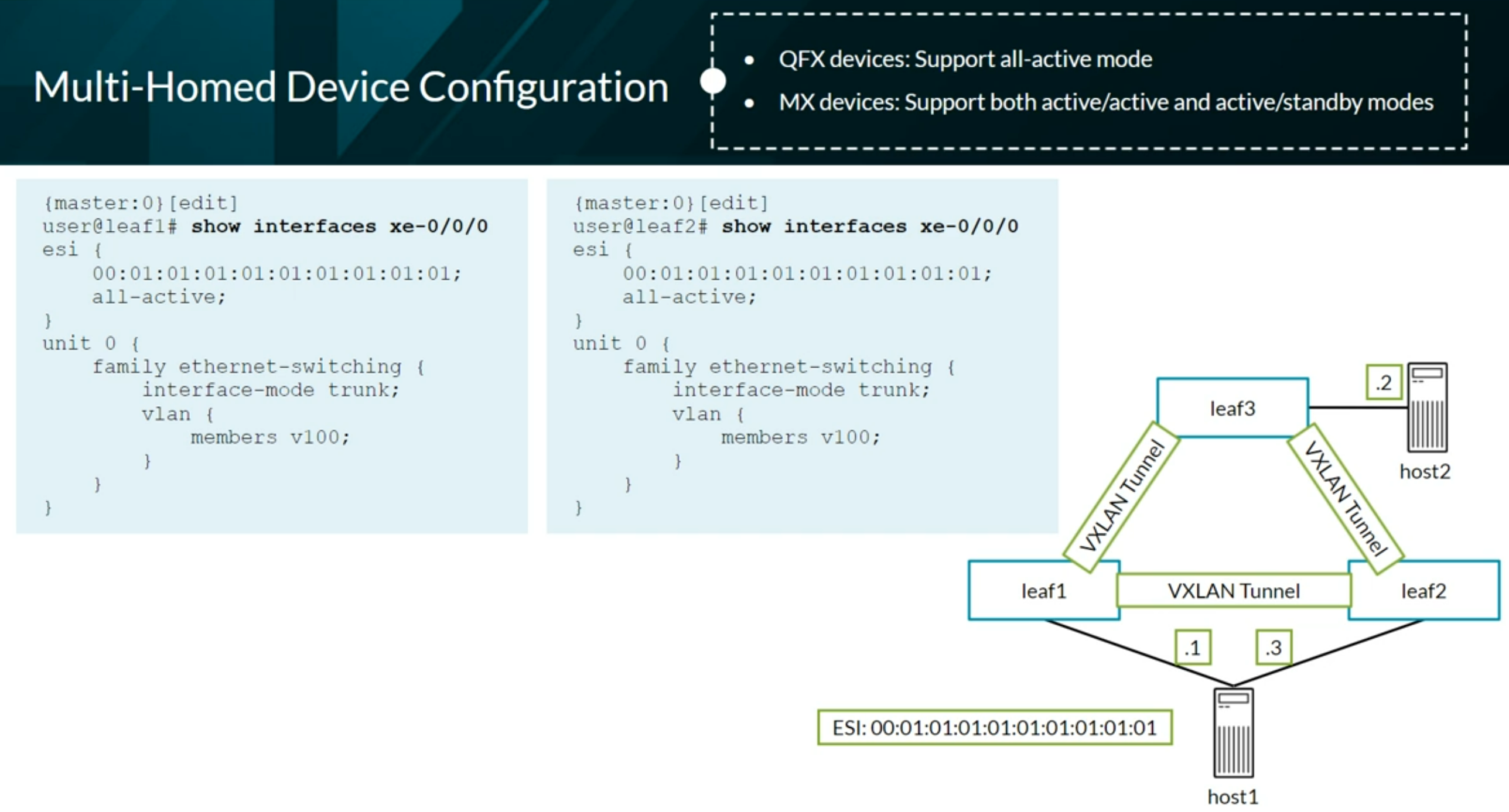
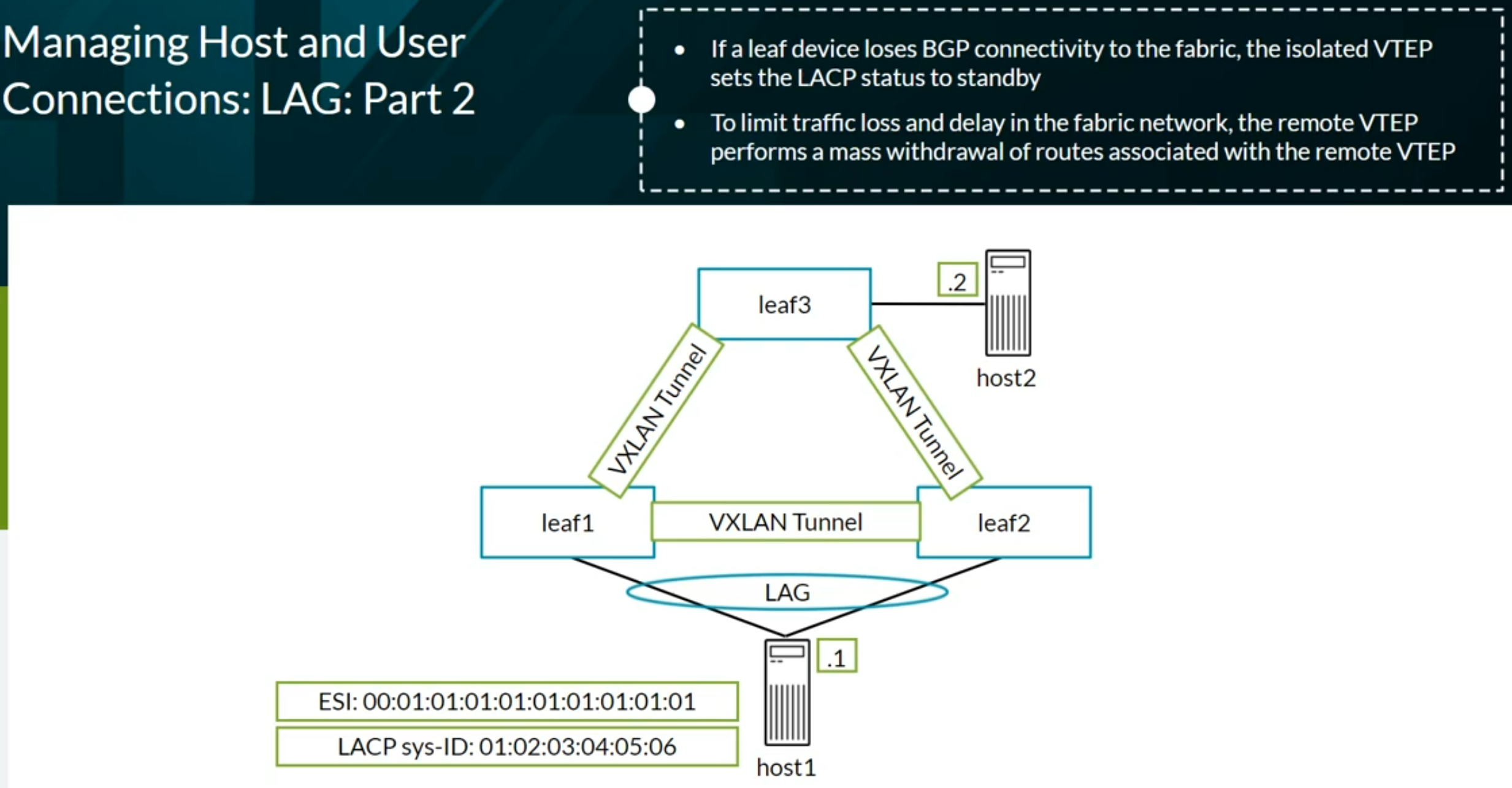
- Multihomed devices must be assigned a unique, 10-octet ESI that starts with 00
- Single-homed sites use reserved ESI of 0 (0x00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00)
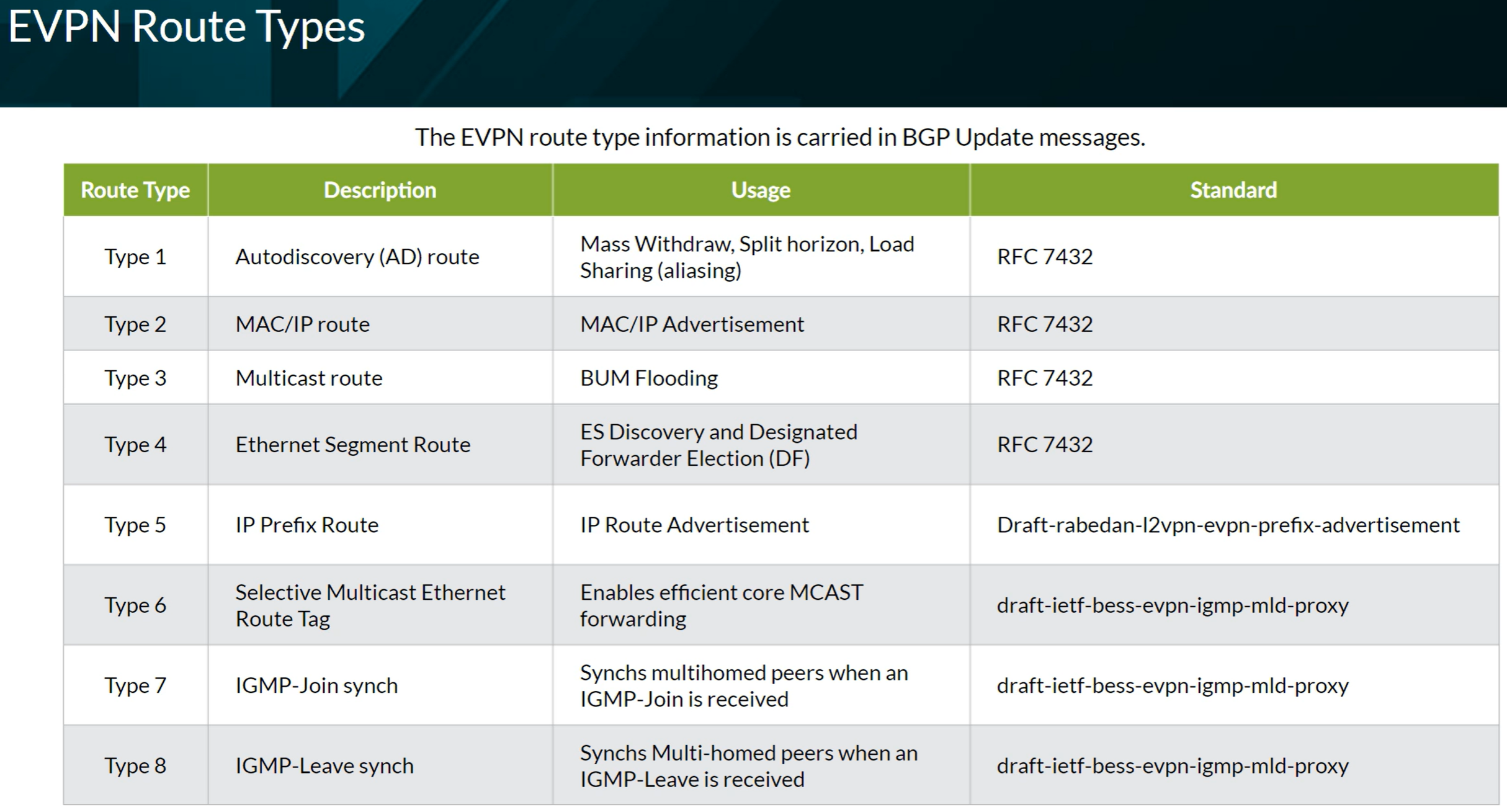
EVPN Route Types
Types 1 to 5 refer to Unicast traffic. Types 6 to 8 refer to Multicast traffic. Types 9 to 11 refer to Broadcast traffic.
Routing Tables
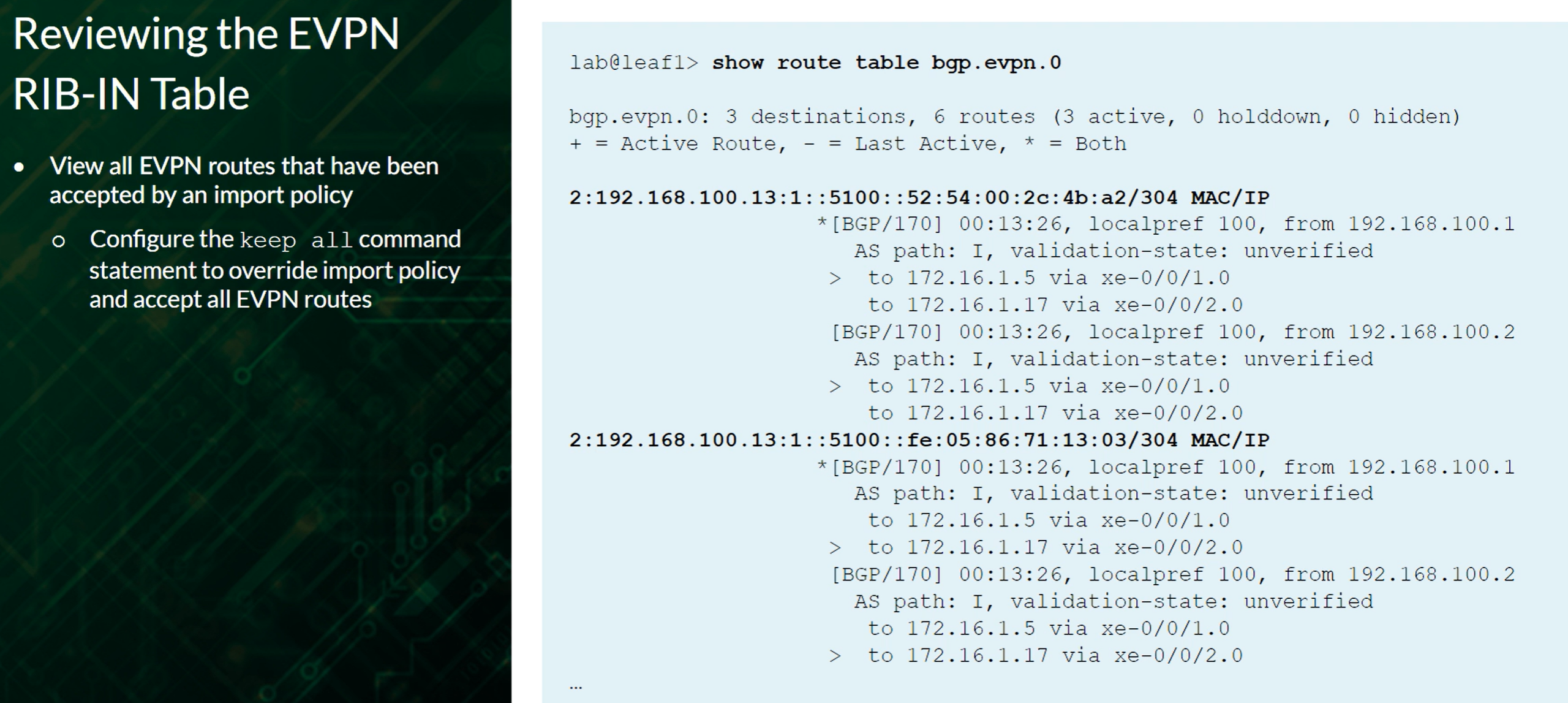
inet.3 - MPLS VPN routing tablevxlan.inet.0 - BGP EVPN routing tablebgp.evpn.0 - BGP EVPN routing table. Contains the EVPN routes received from remote BGP peersdefault-switch.evpn.0
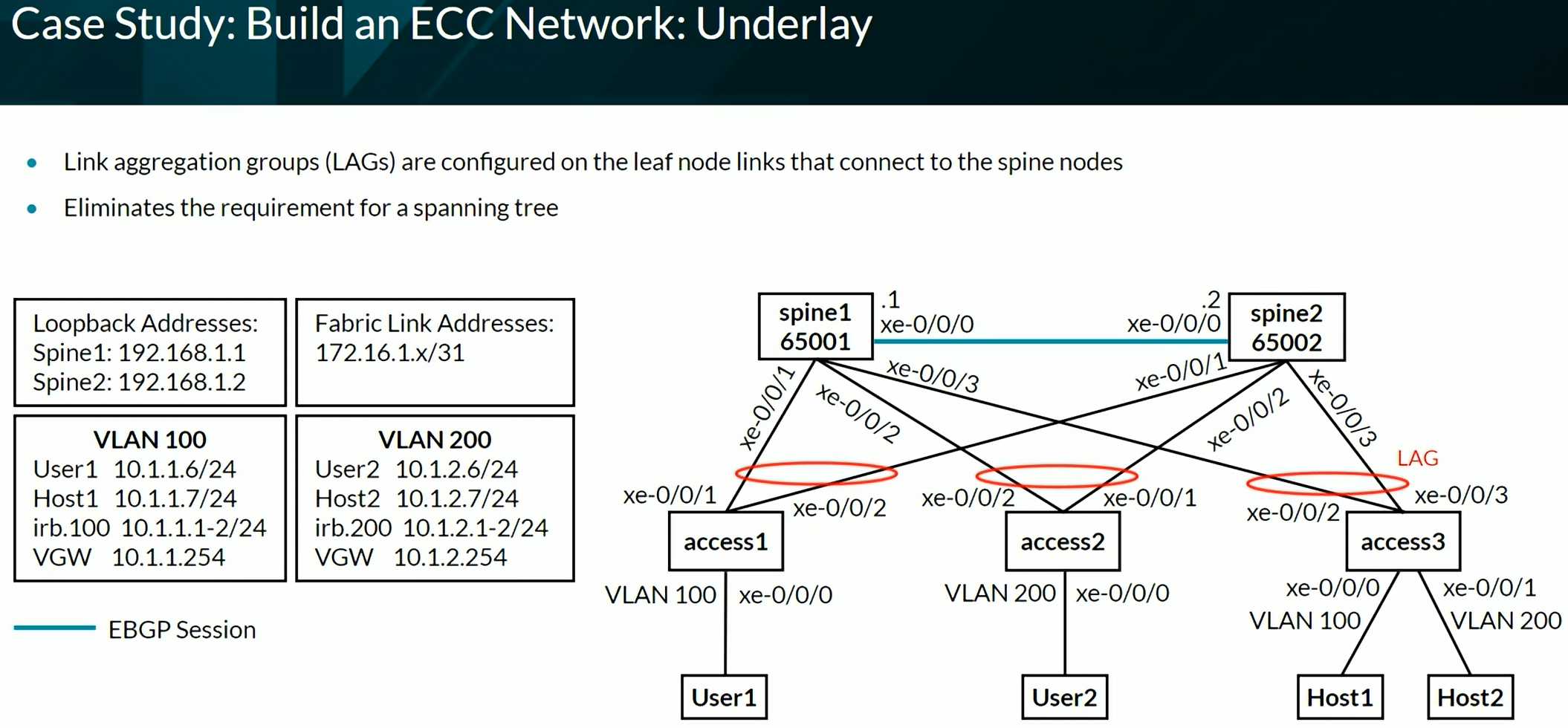
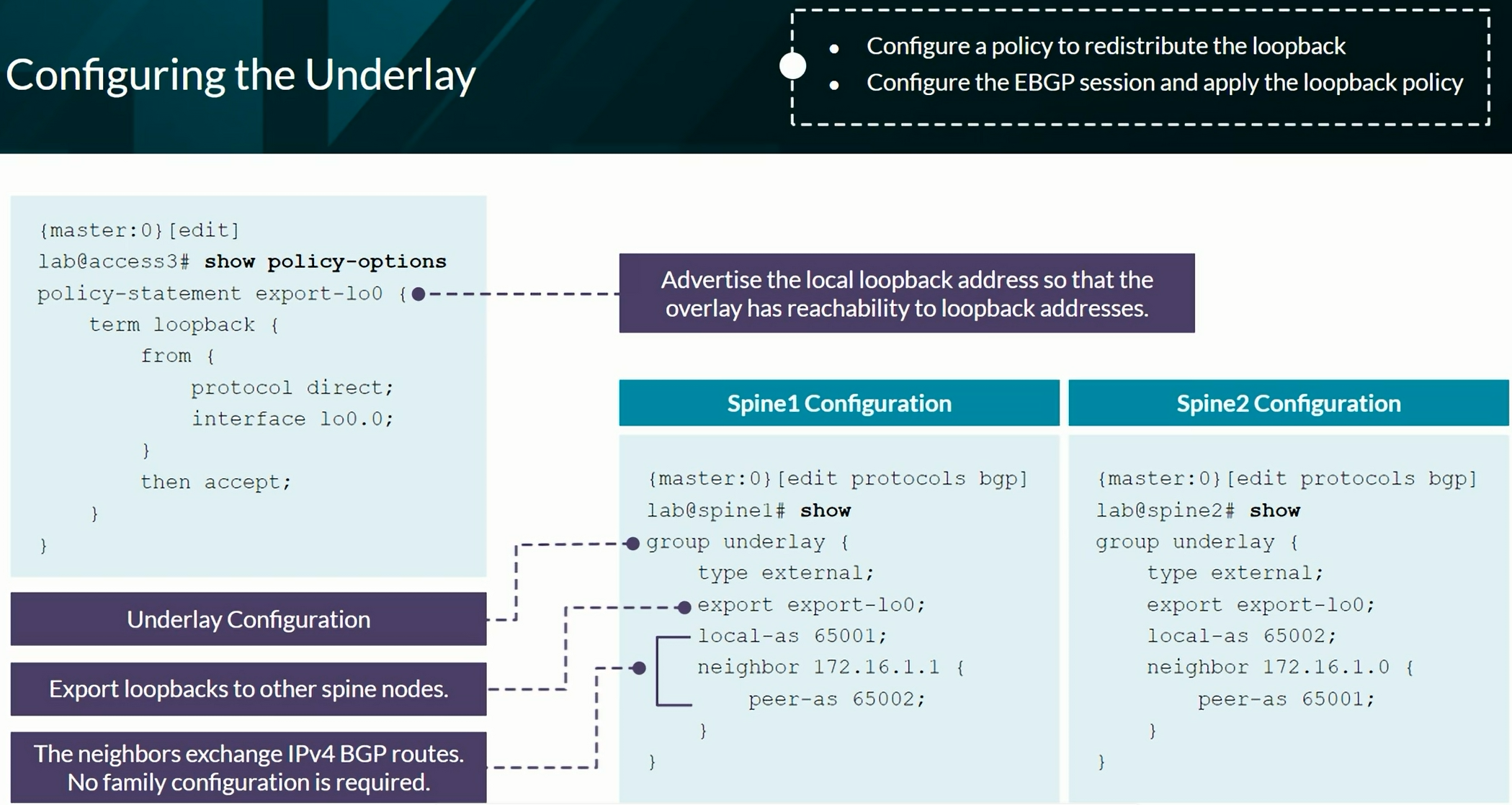
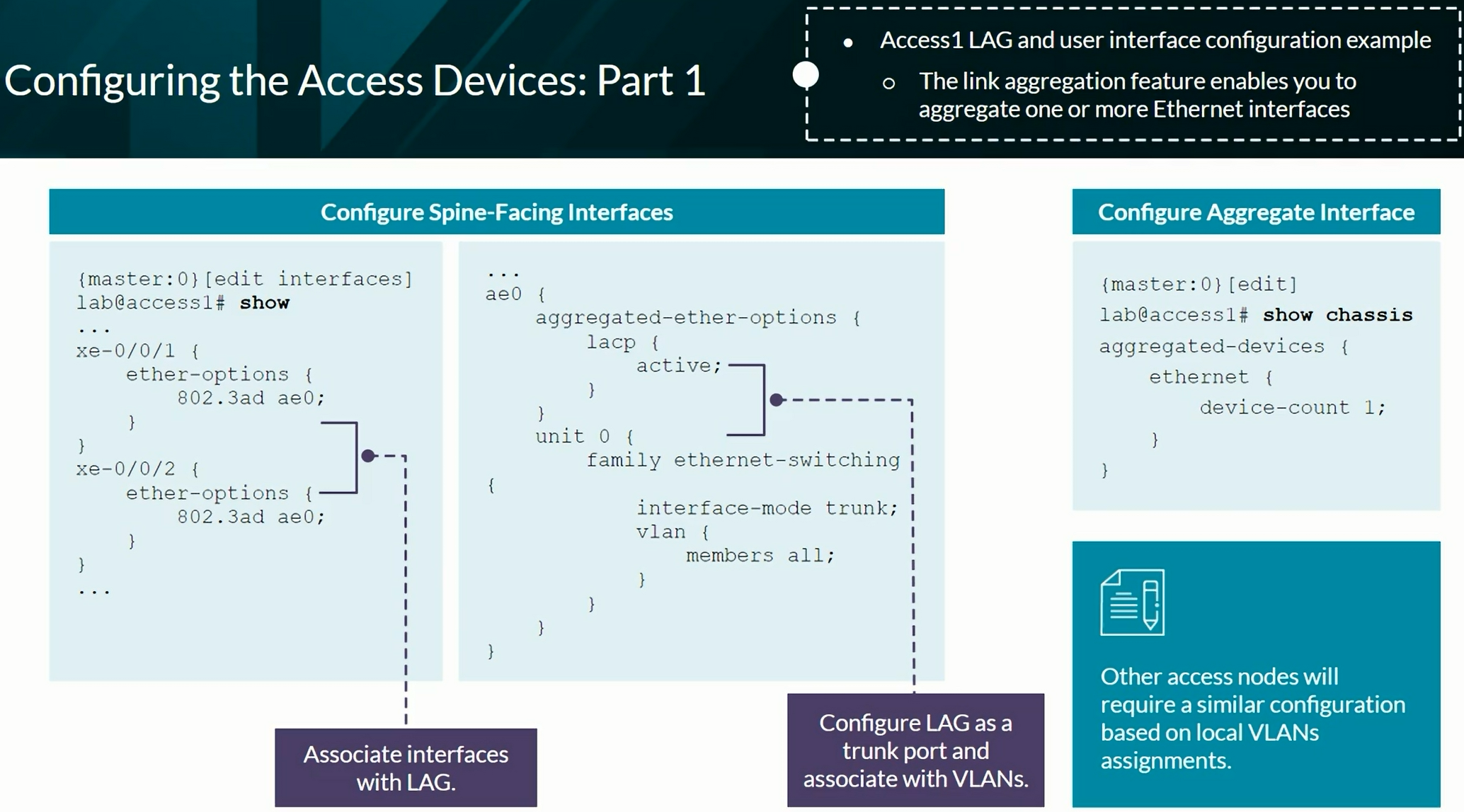
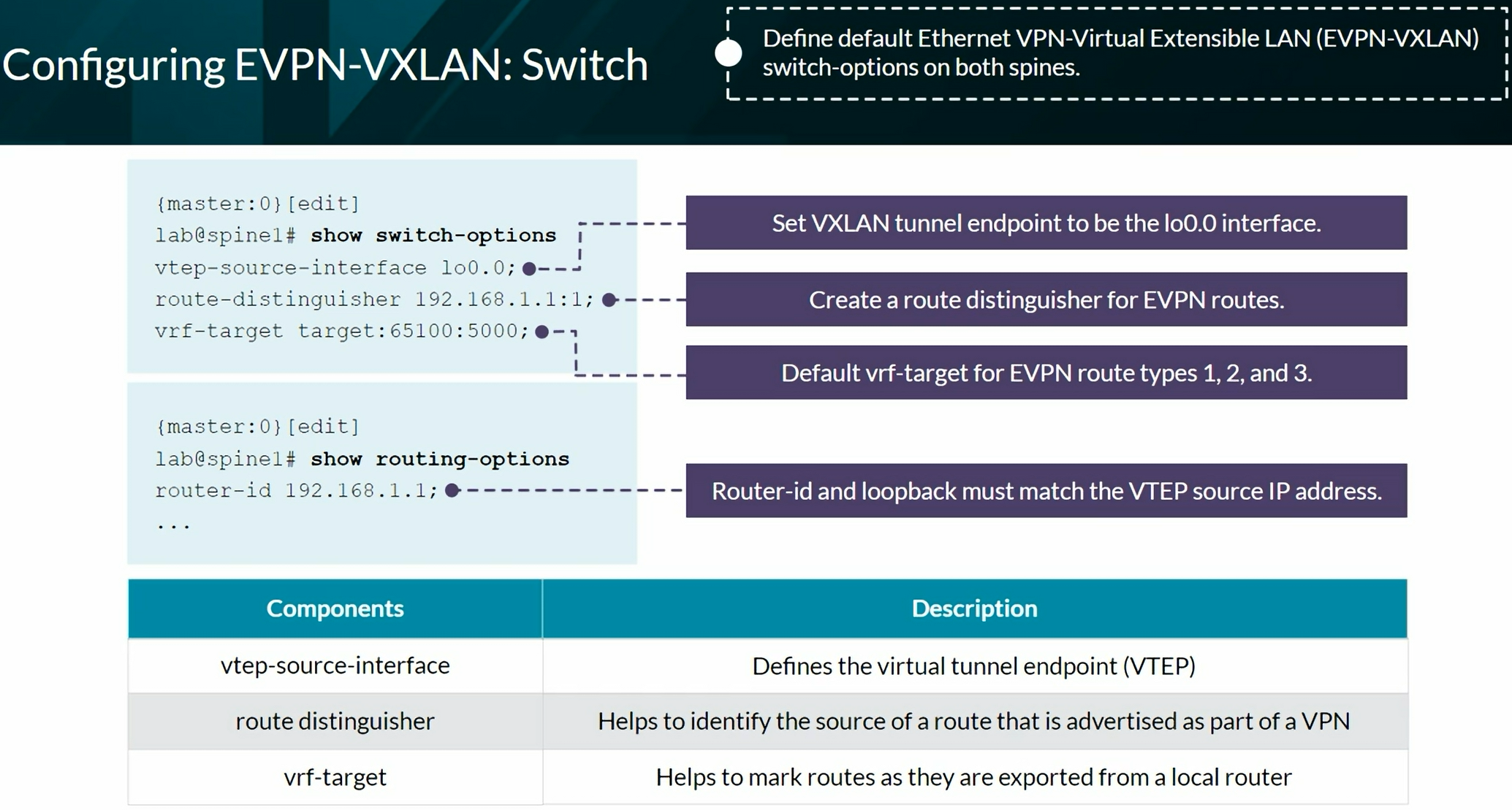
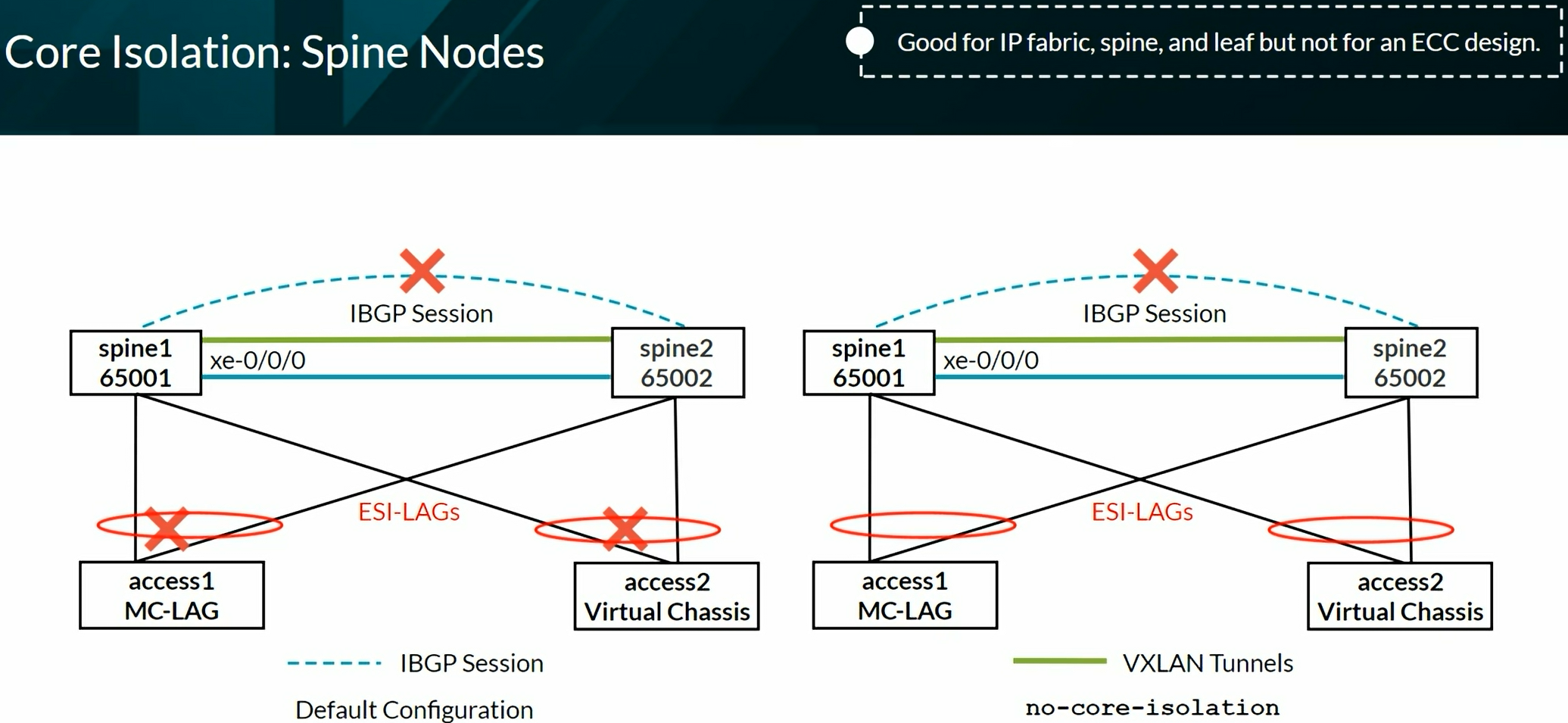
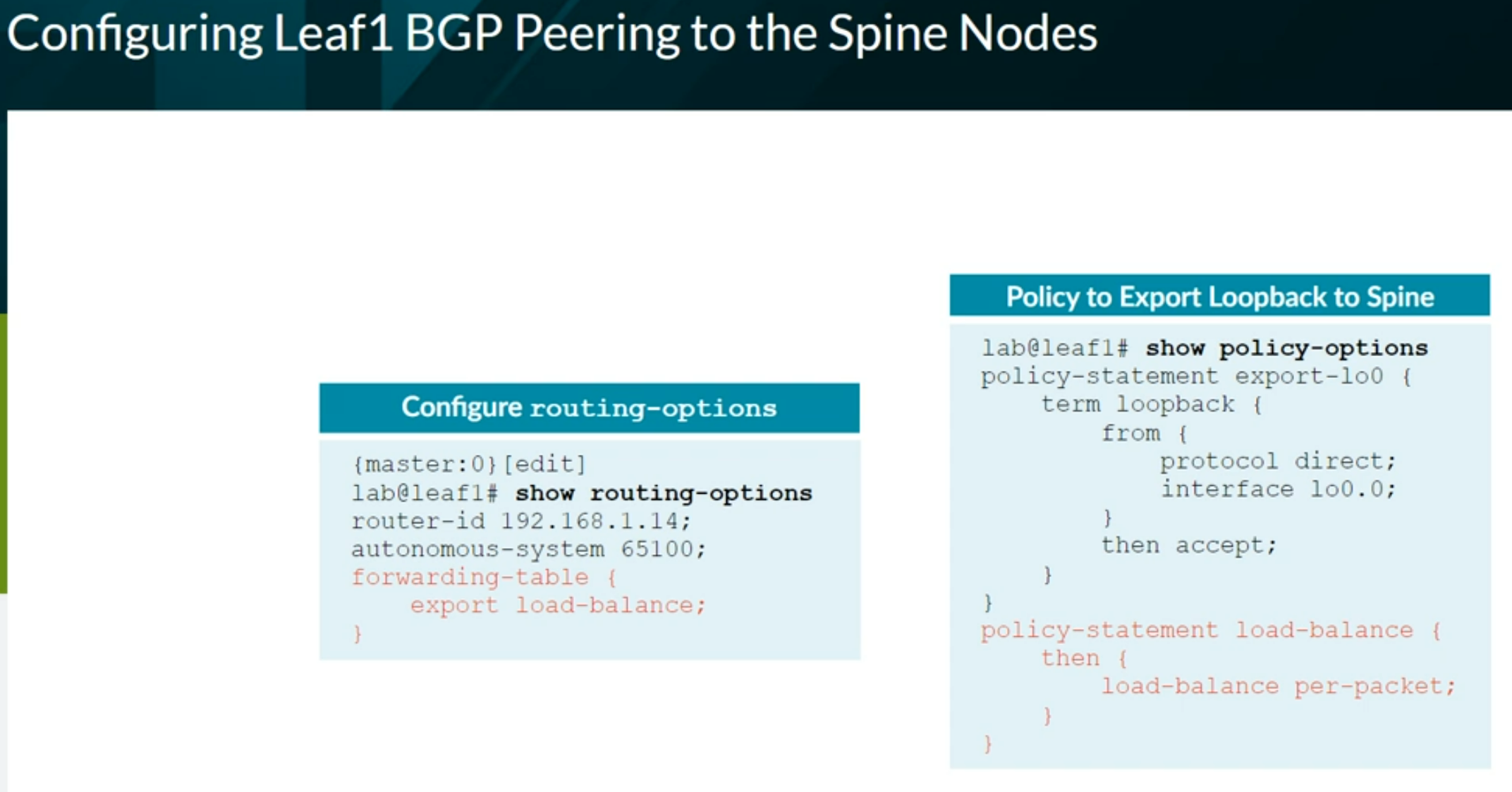
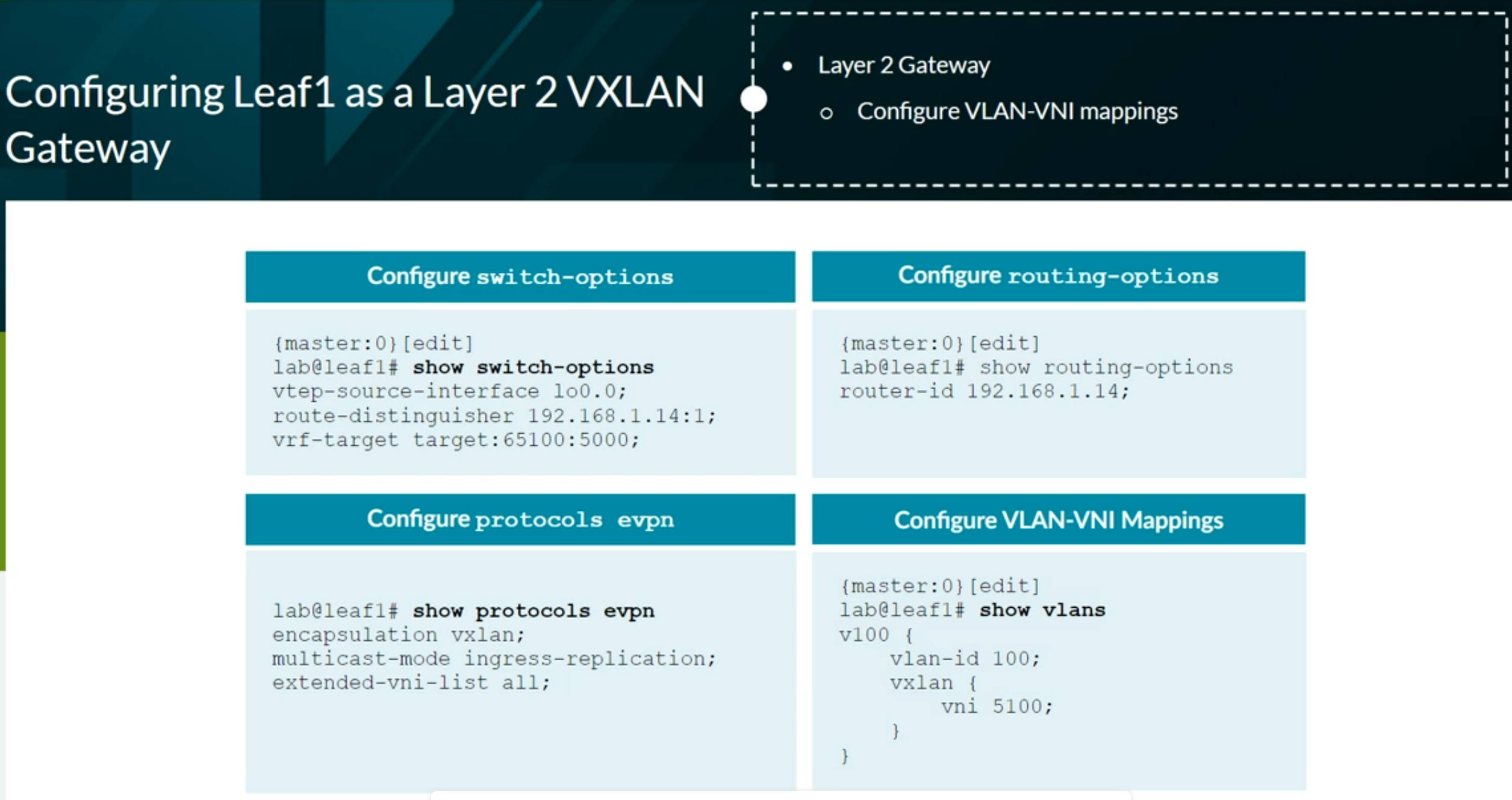
Configuring VXLAN BGP EVPN (ECC - Evolved Campus Core design)
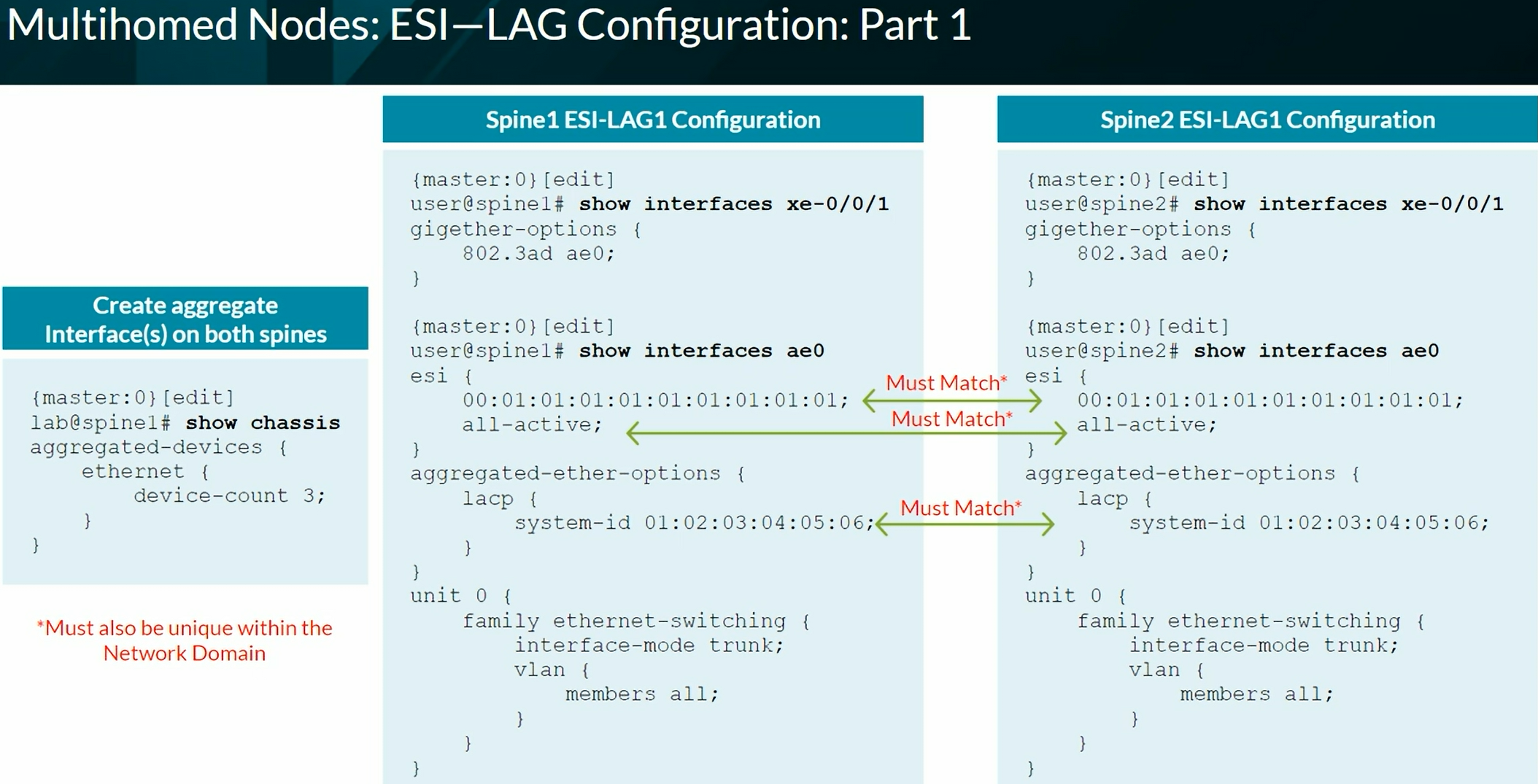
Configures the device to automatically create an End System Identifier (ESI ID) based on the LACP system ID.
1
| set interfaces ae0 esi auto-derive lacp
|
Verification commands
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| show lacp interfaces
show interfaces ae0 detail
show bgp summary
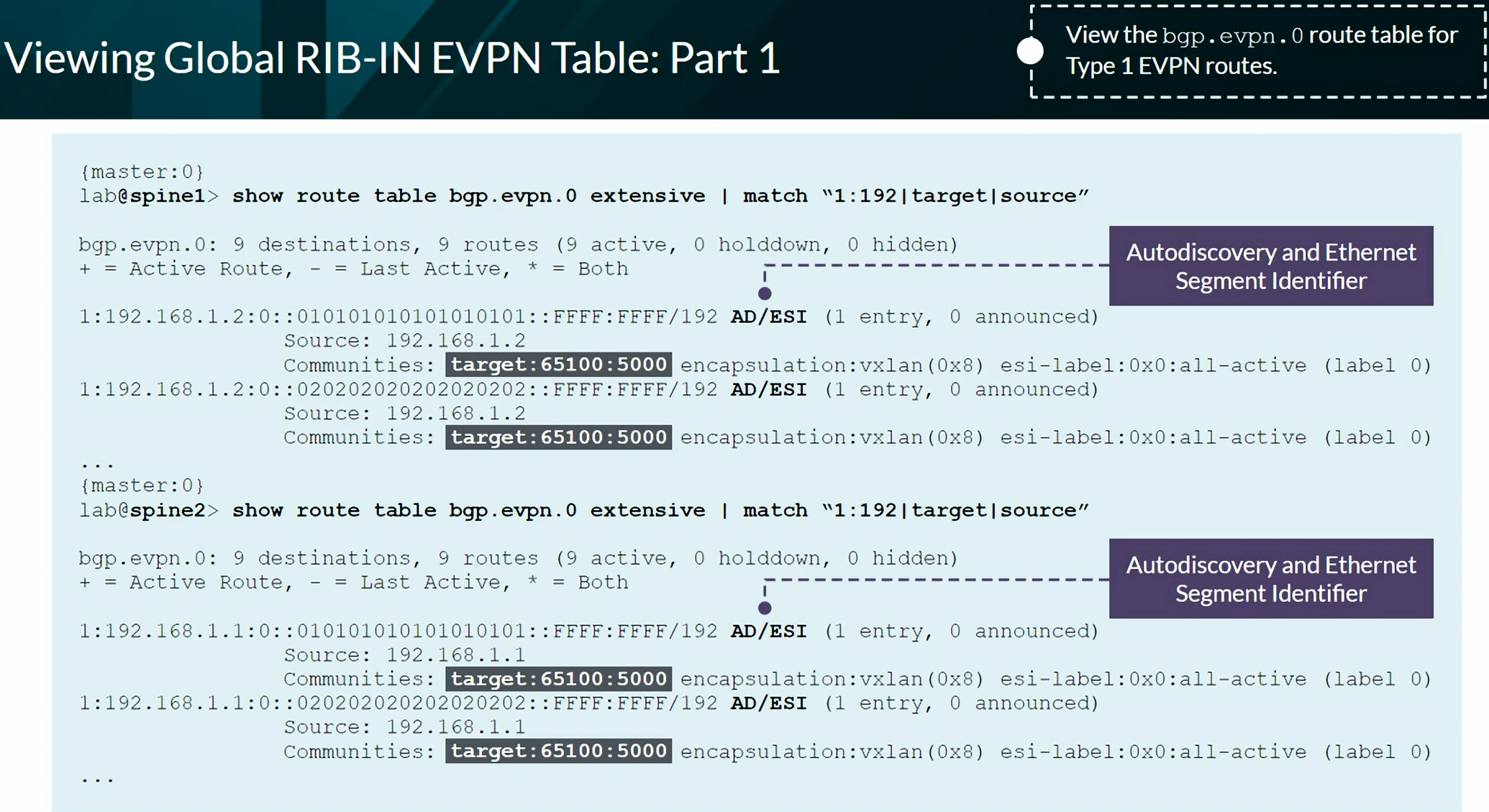
show route table bgp.evpn.0 extensive
show interfaces vtep
show ethernet-switching vxlan-tunnel-end-point
show ethernet-switching vxlan-tunnel-end-point remote
show krp indirect-next-hop
|
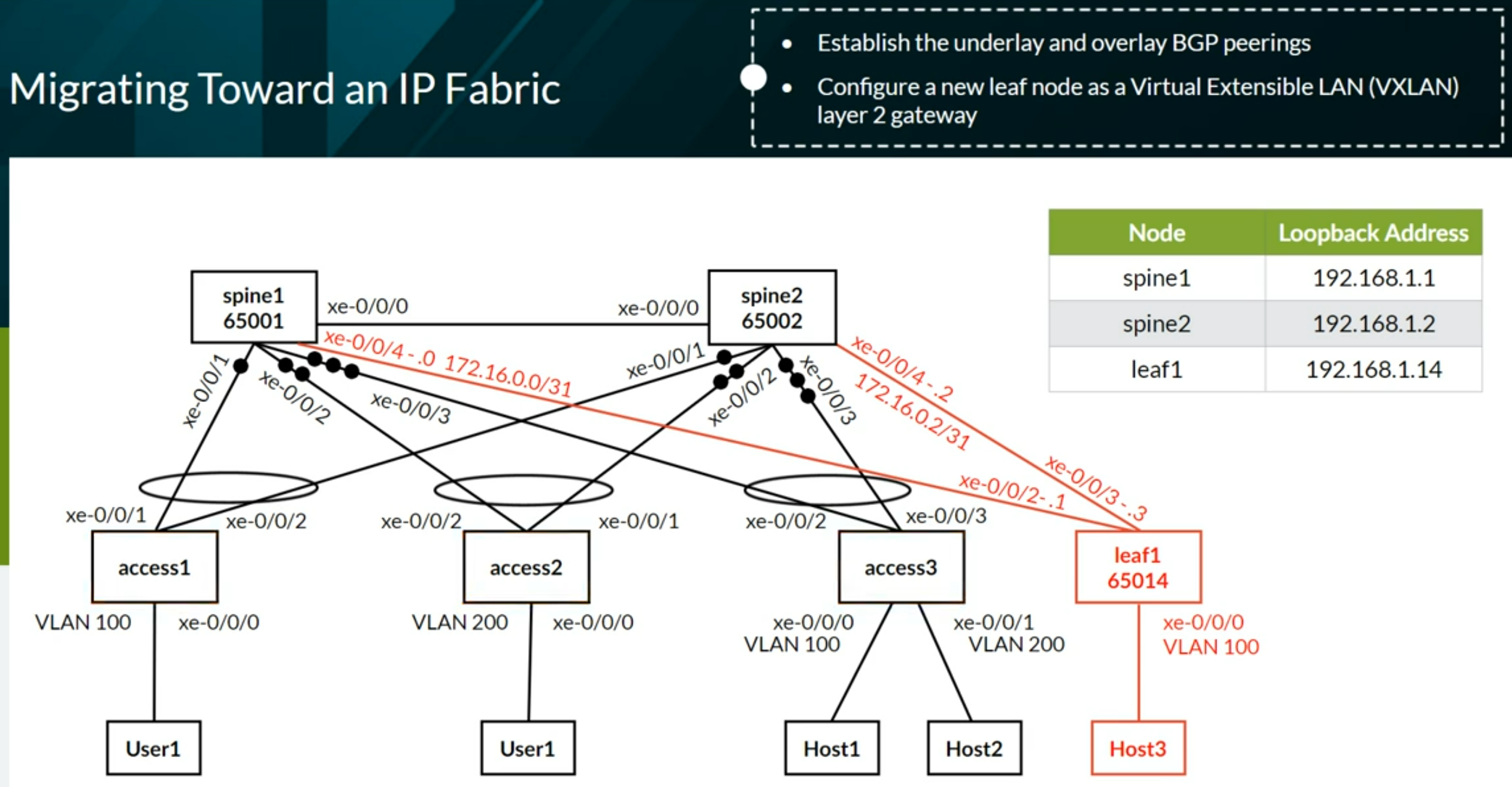
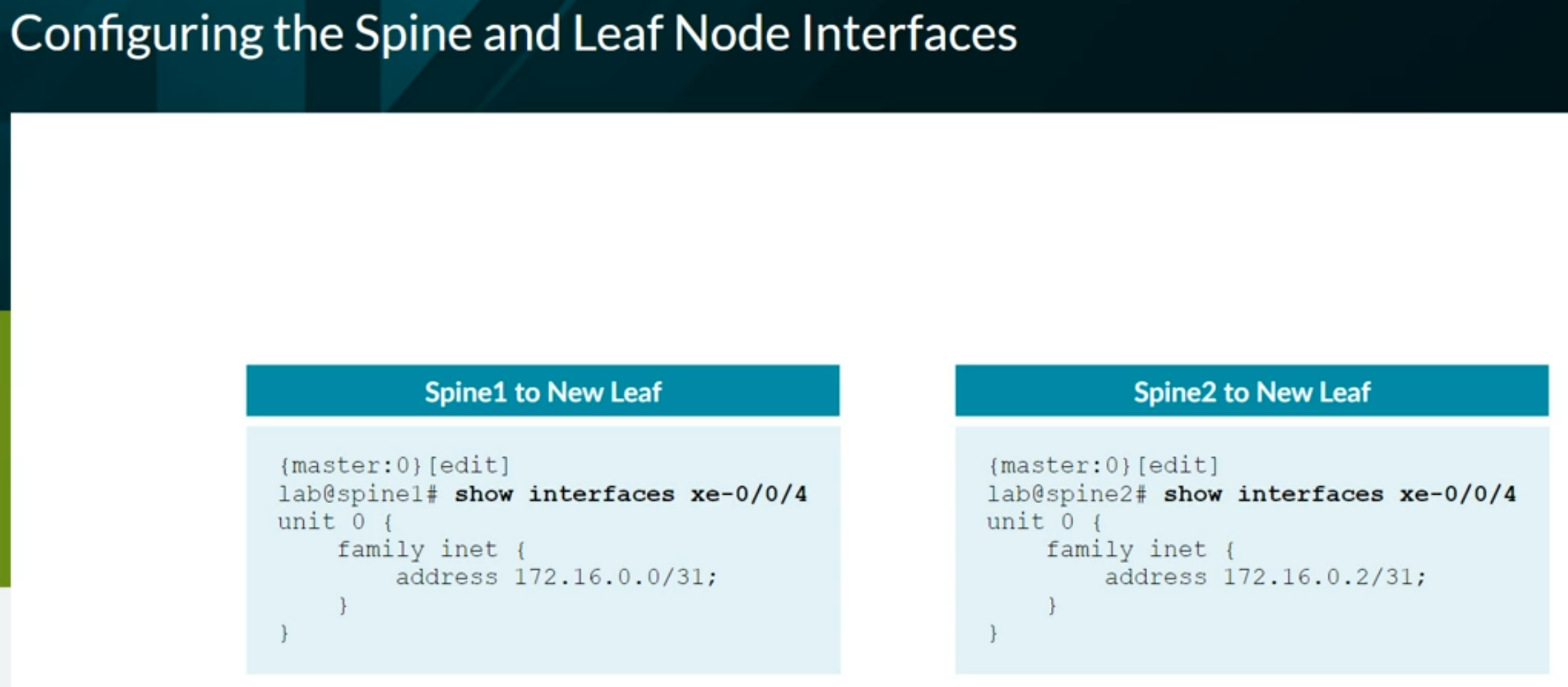
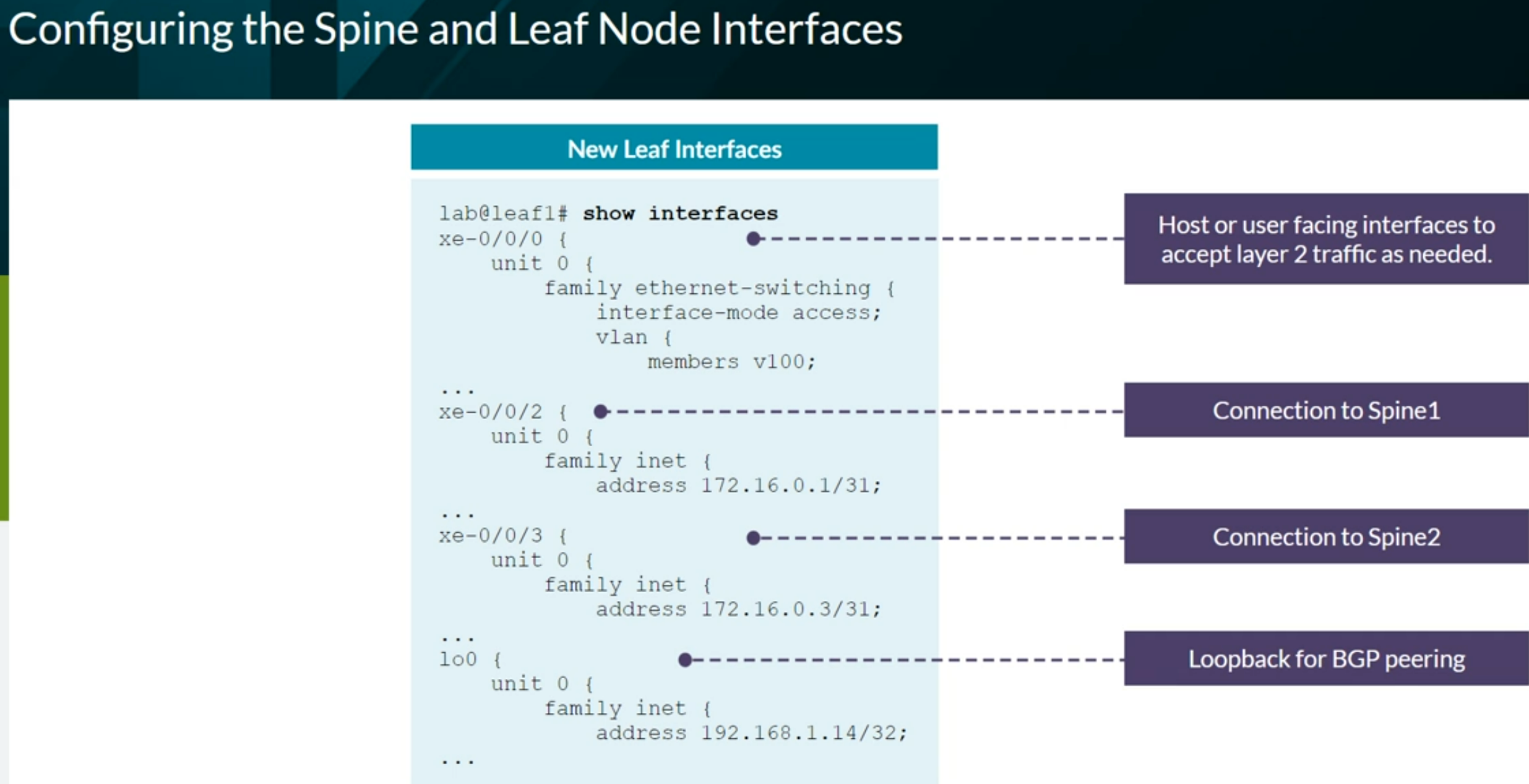
Configuring VXLAN BGP EVPN (IP Fabric) Brownfield from ECC
Configuring VXLAN BGP EVPN (IP Fabric) Greenfield
Configuring Full Fabric
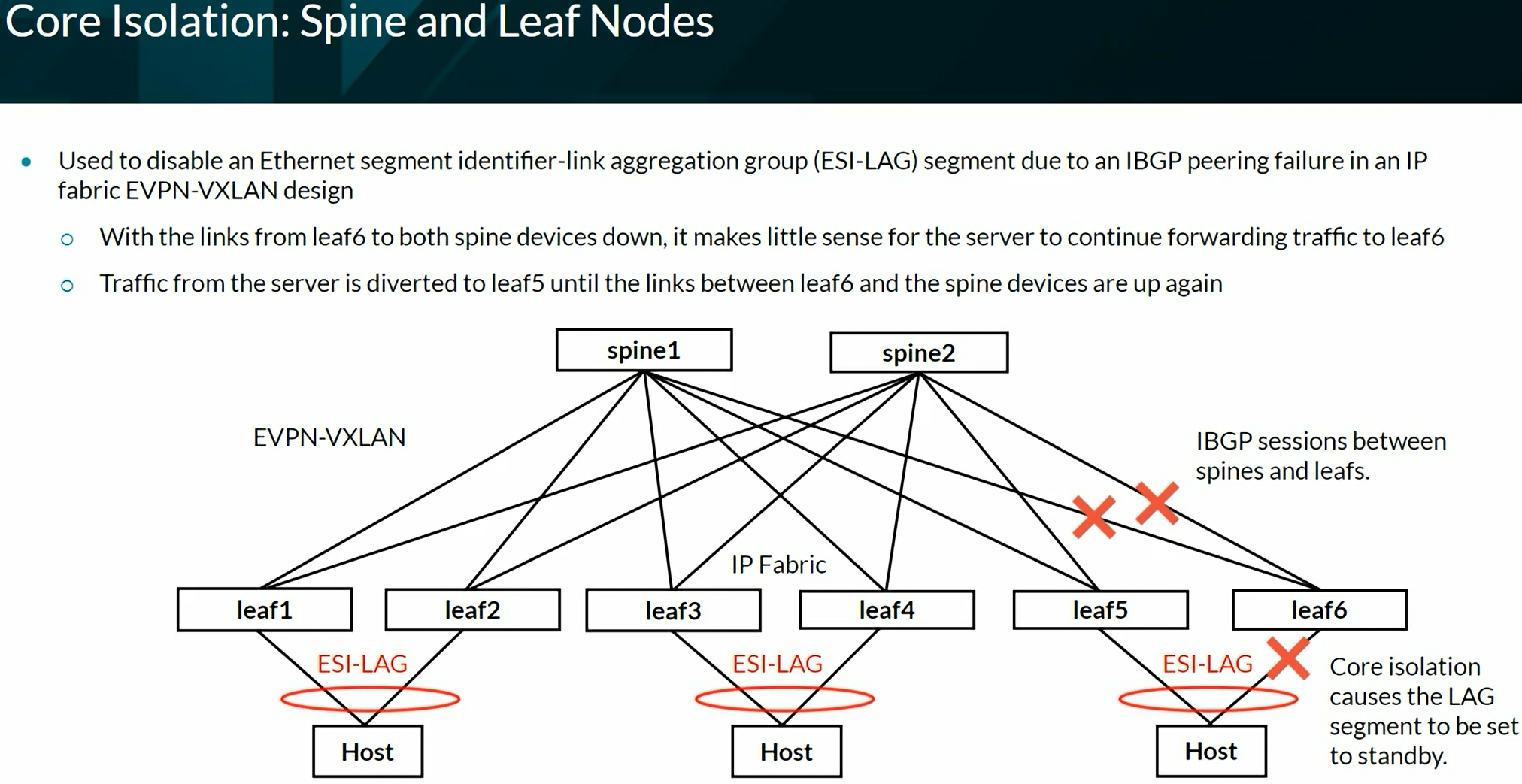
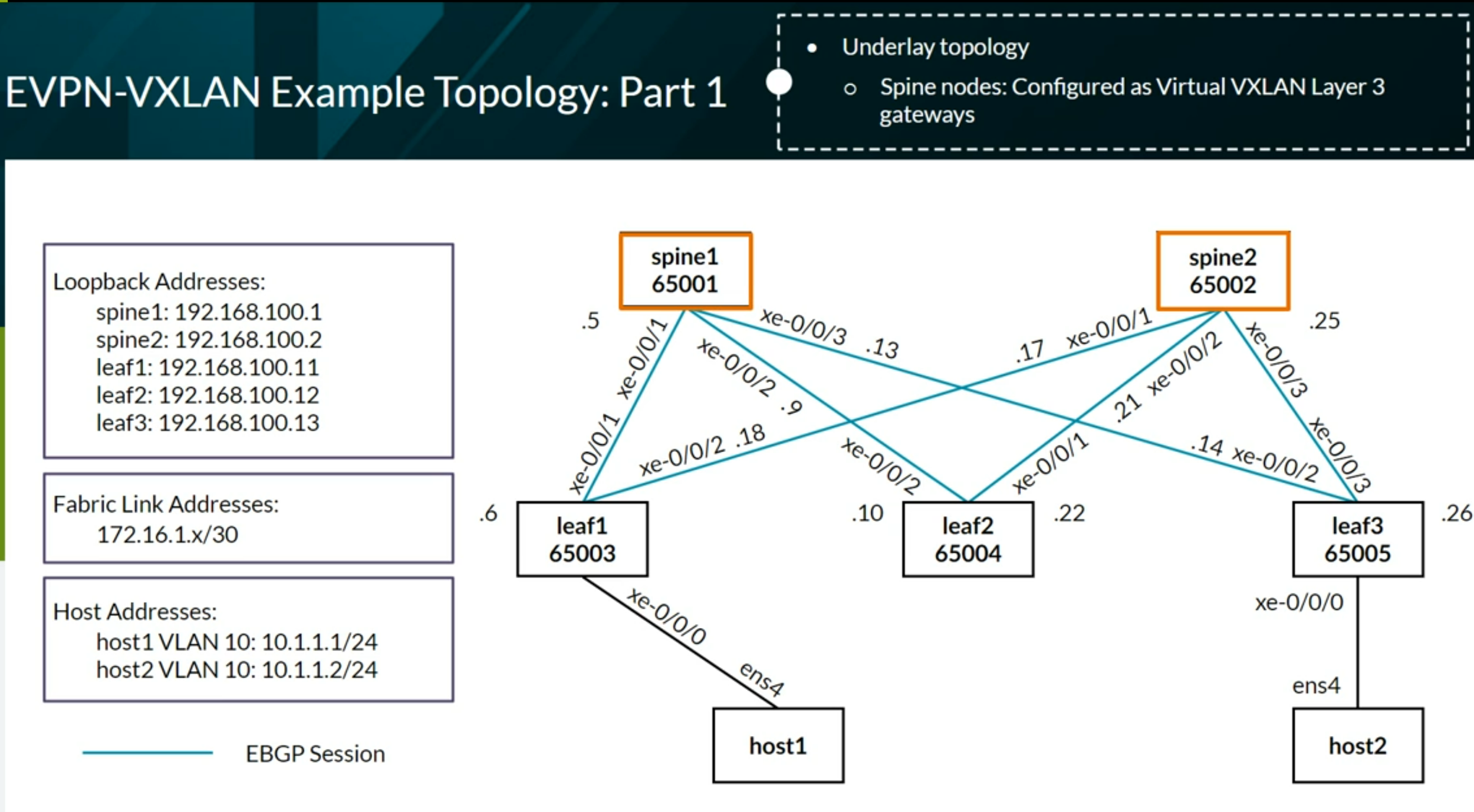
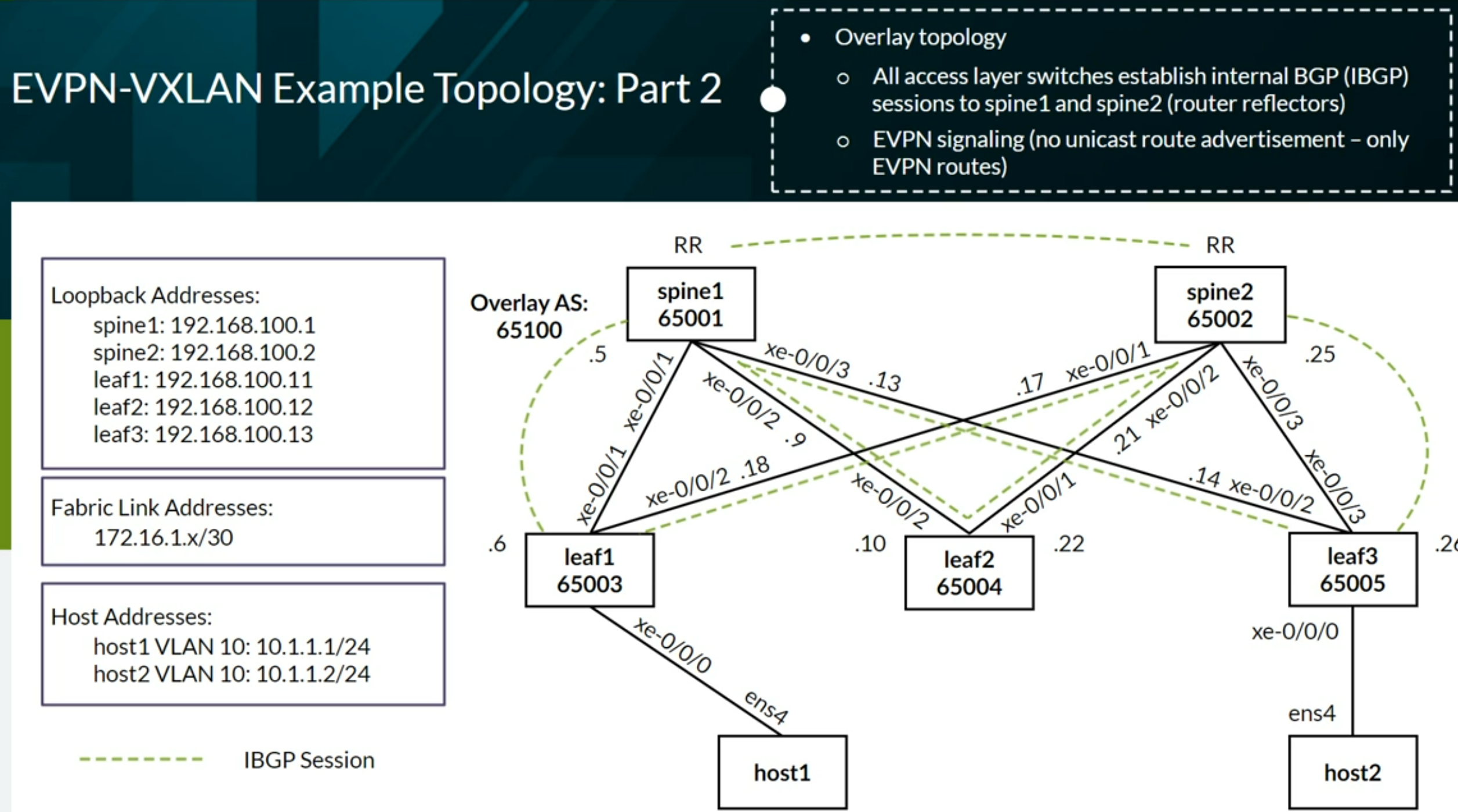
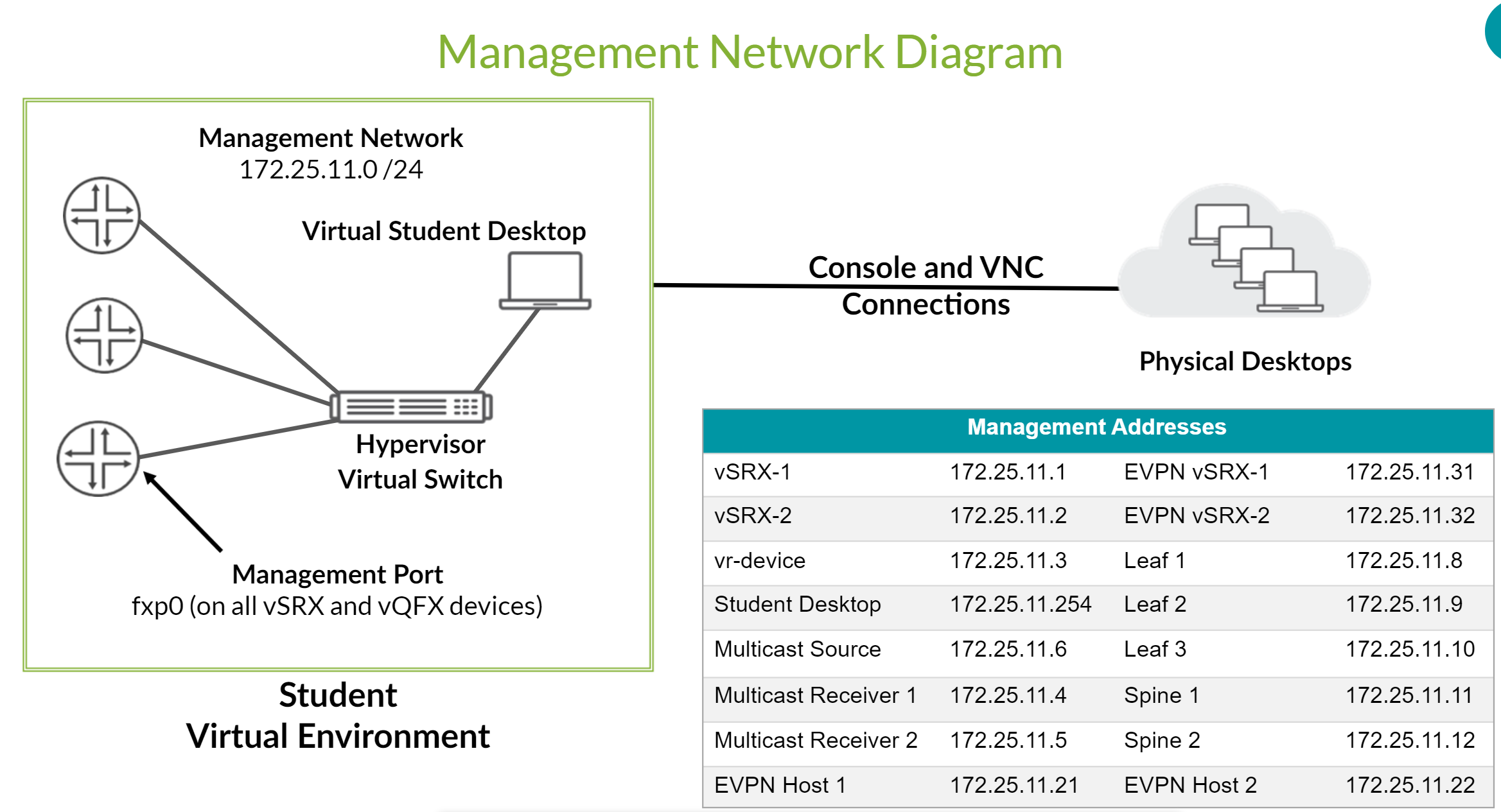
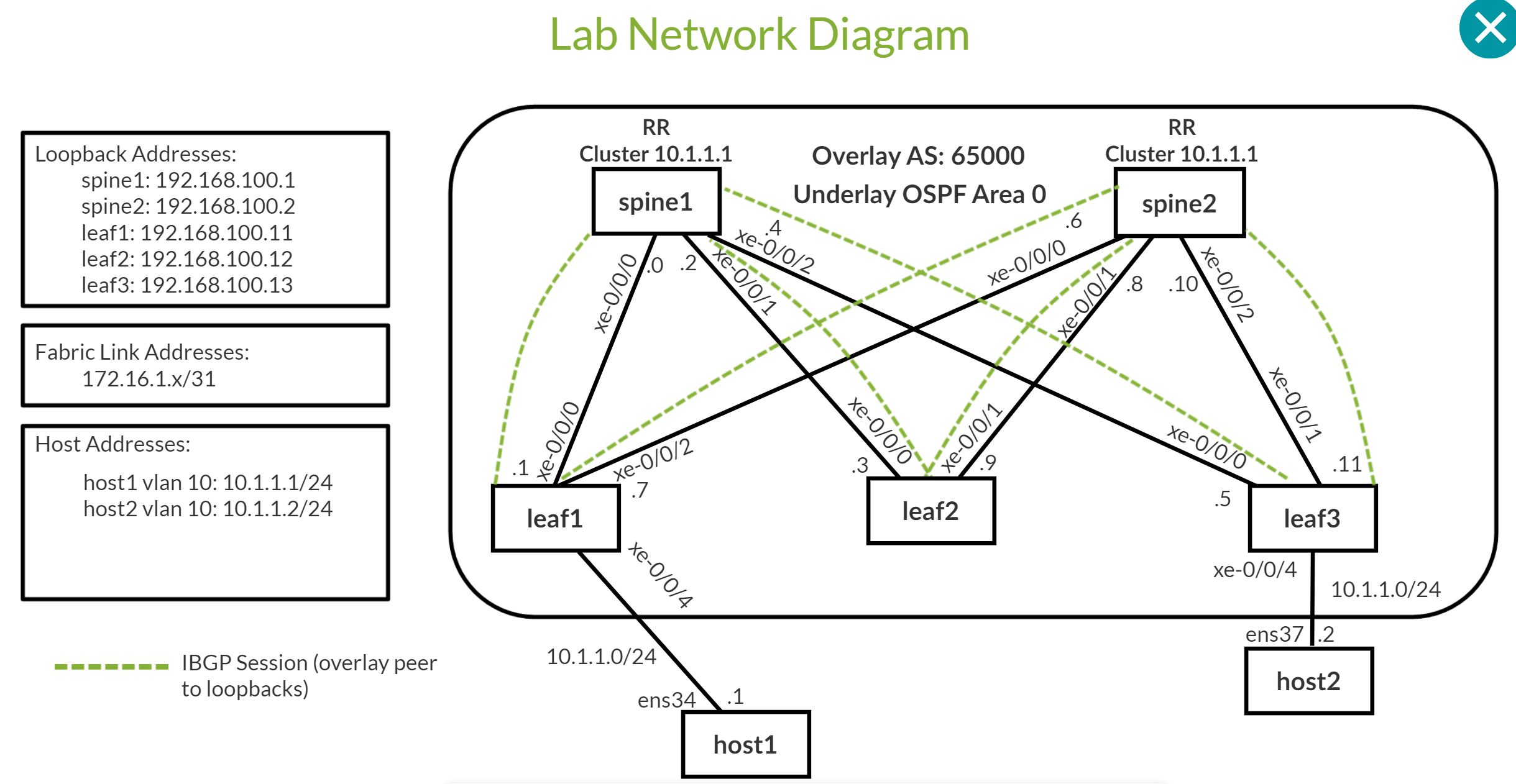
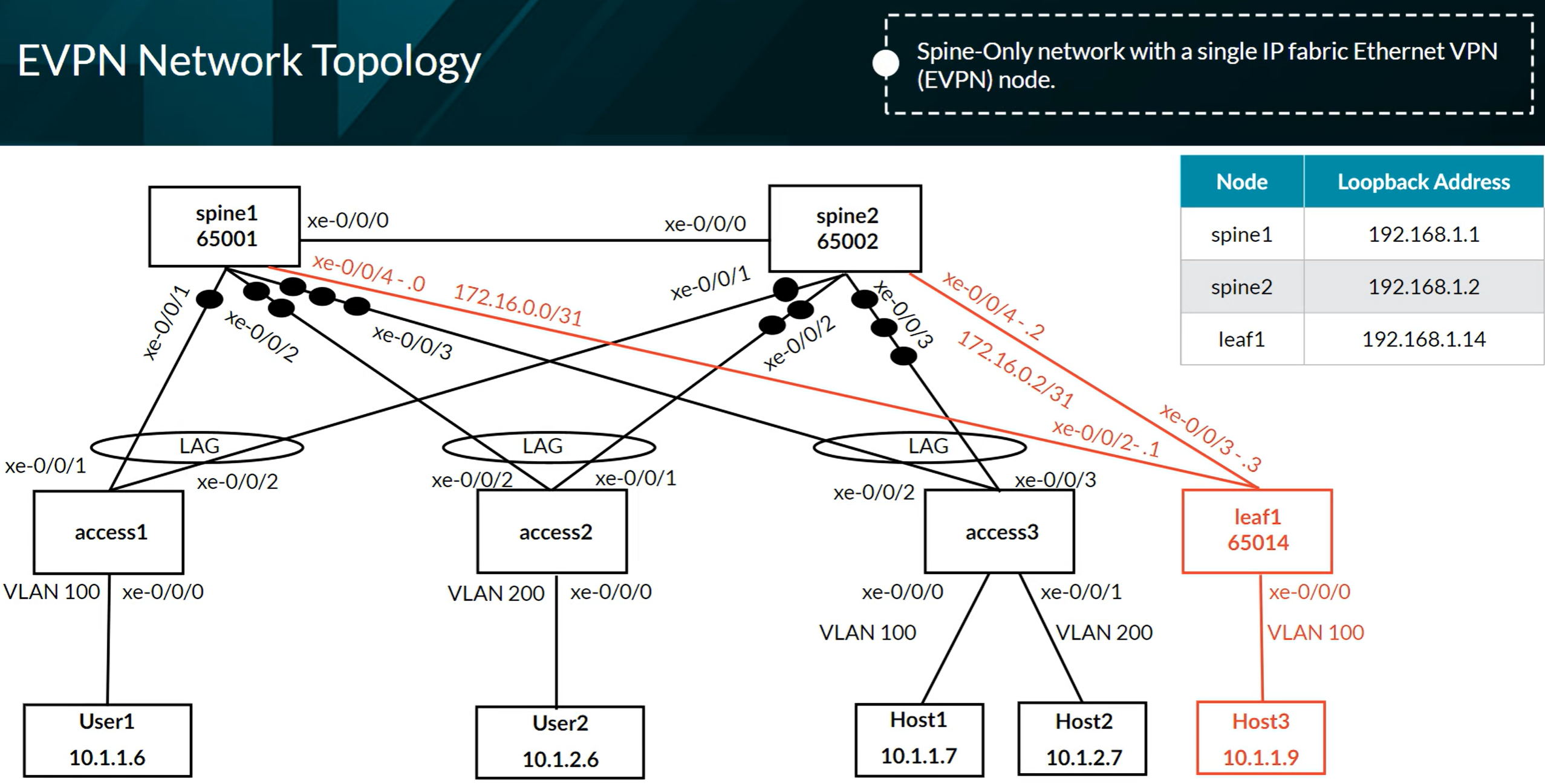
VXLAN EVPN Lab Network
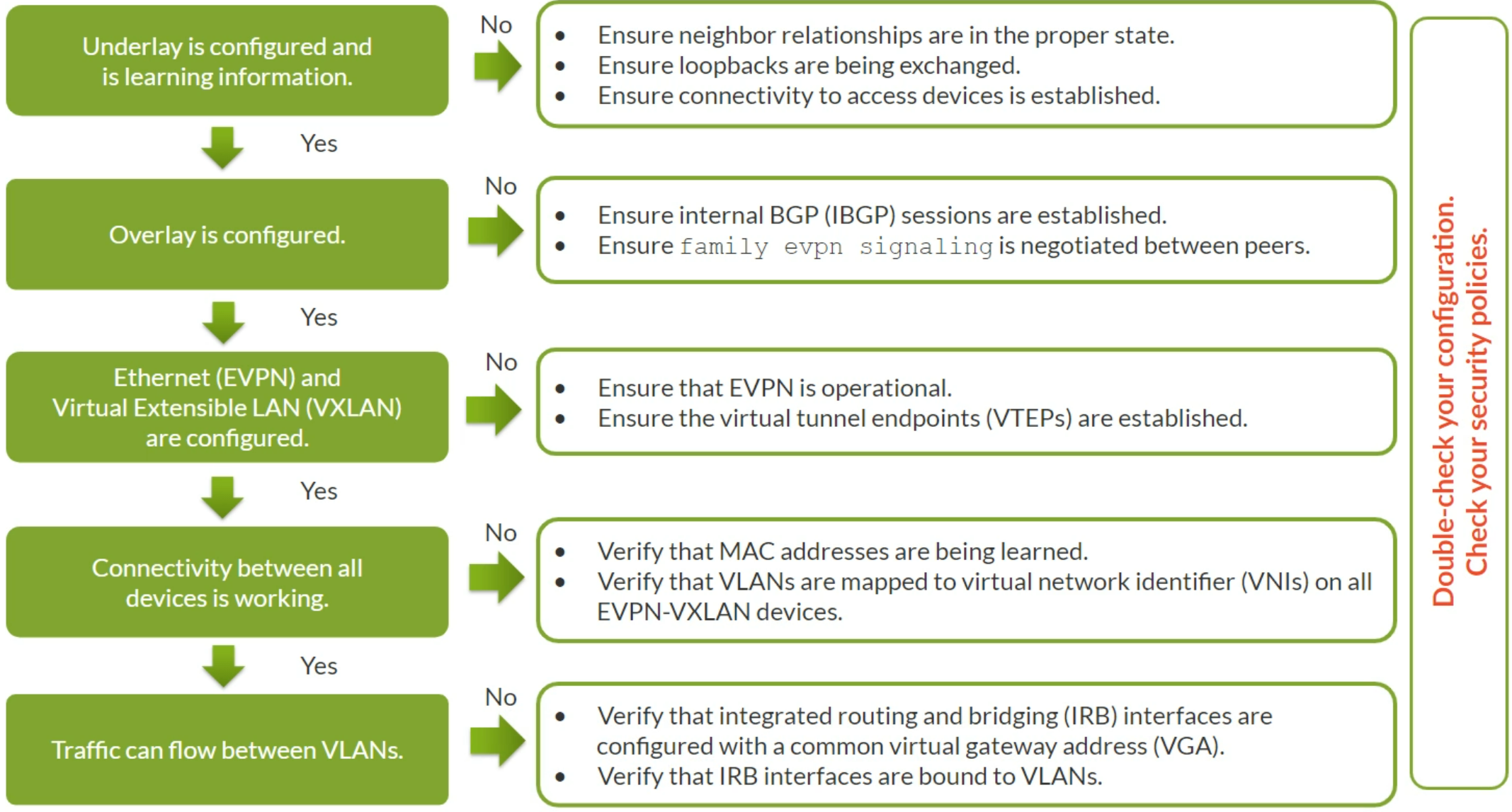
Verifying and Troubleshooting EVPN-VXLAN Architecture
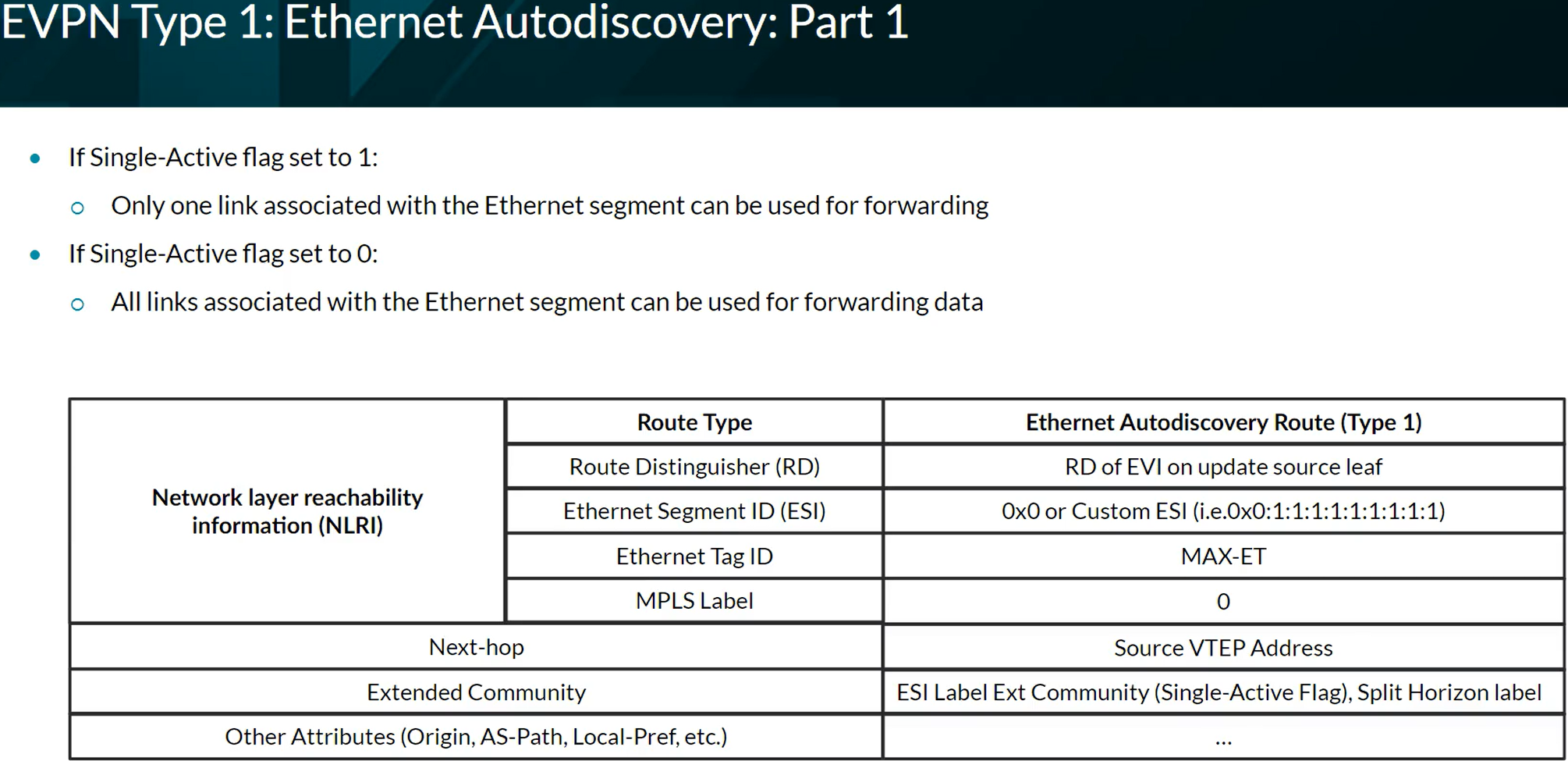
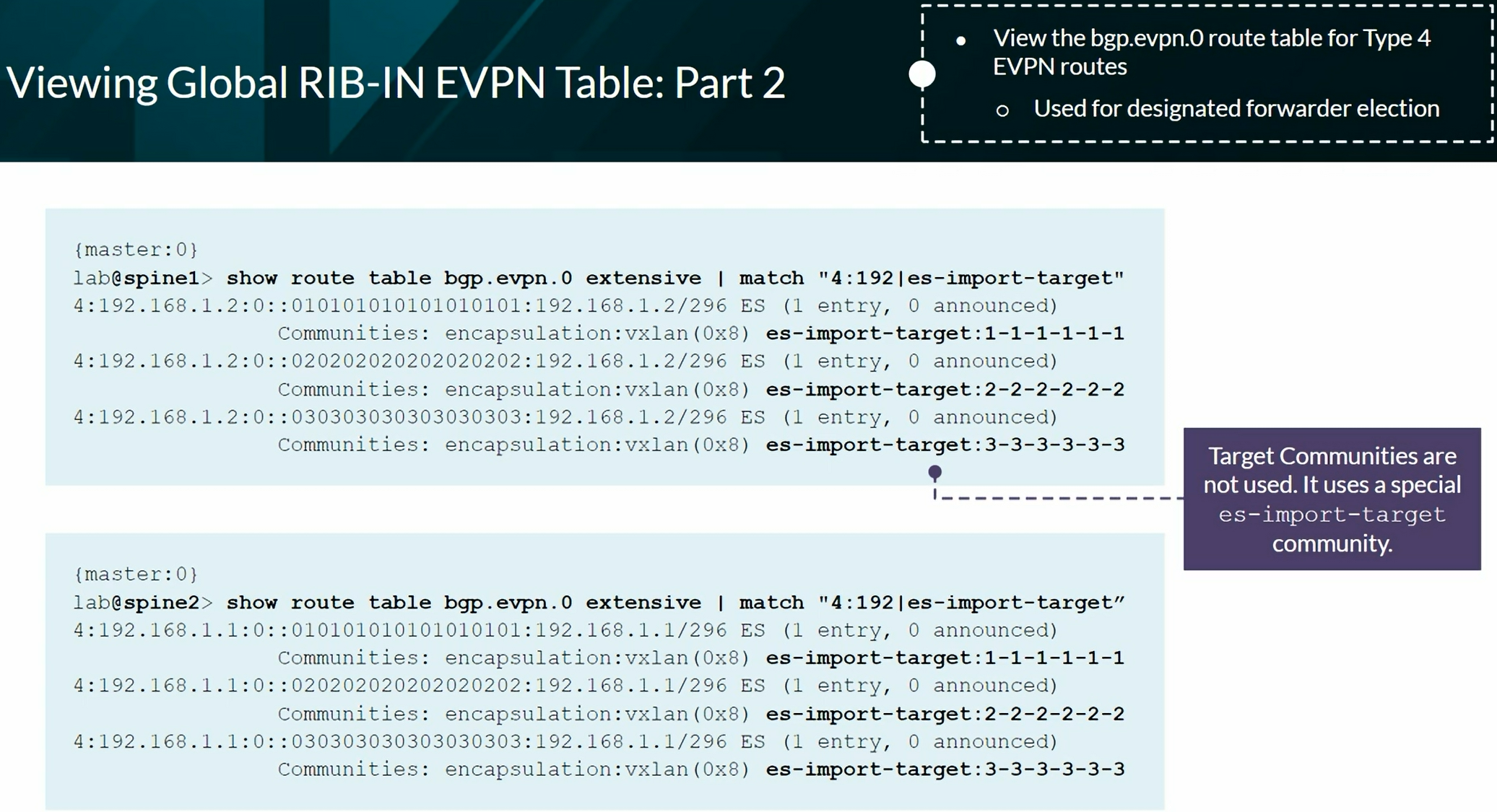
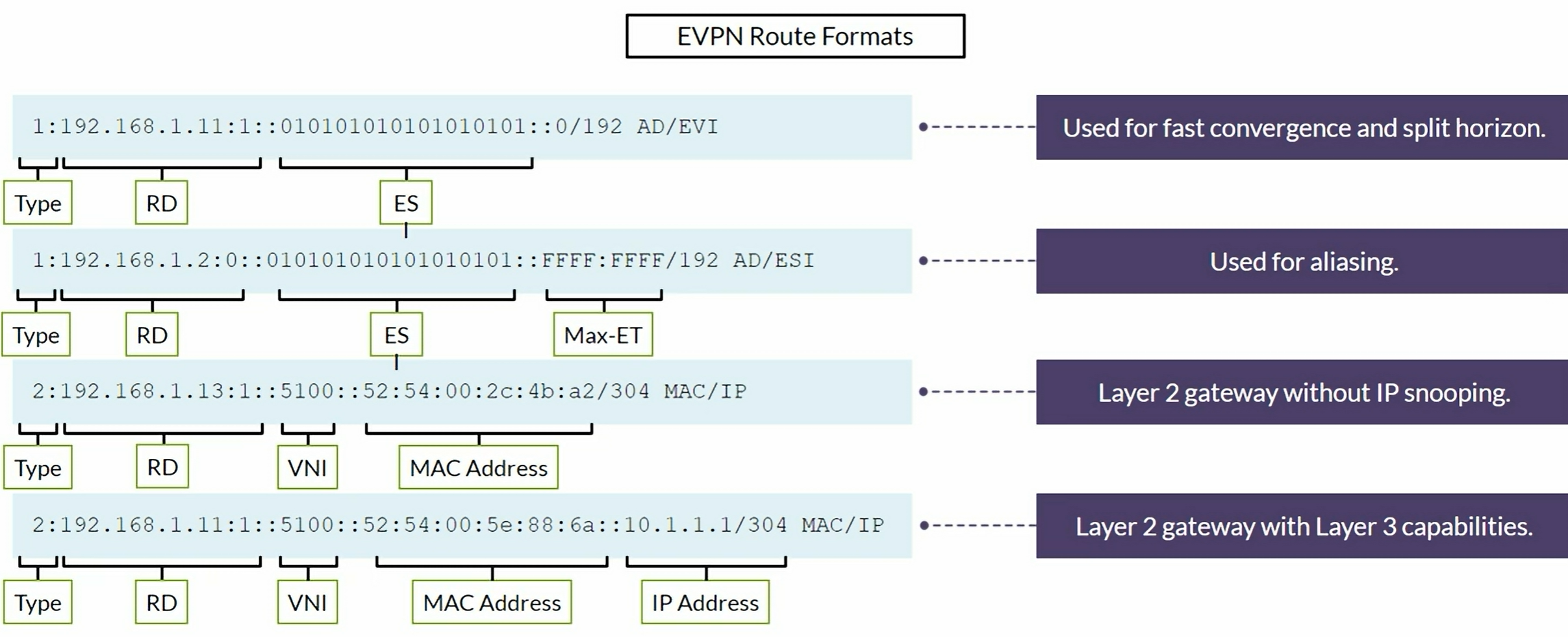
EVPN Type 1 and Type 2 format
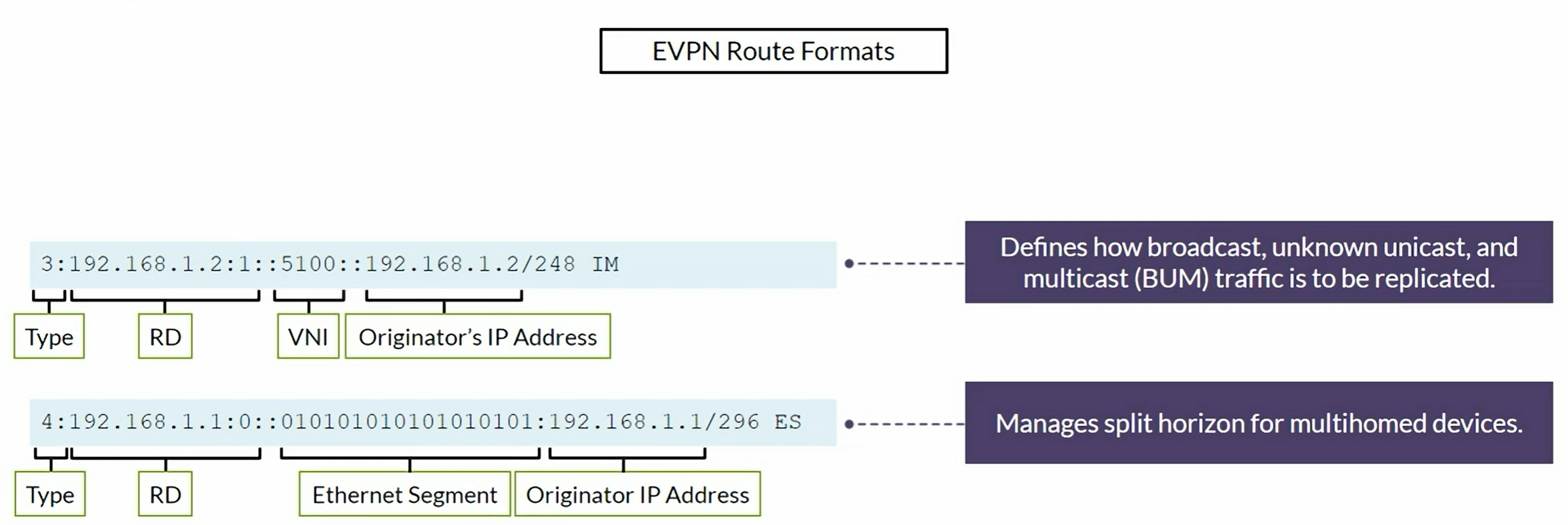
EVPN Type 3 and Type 4 format
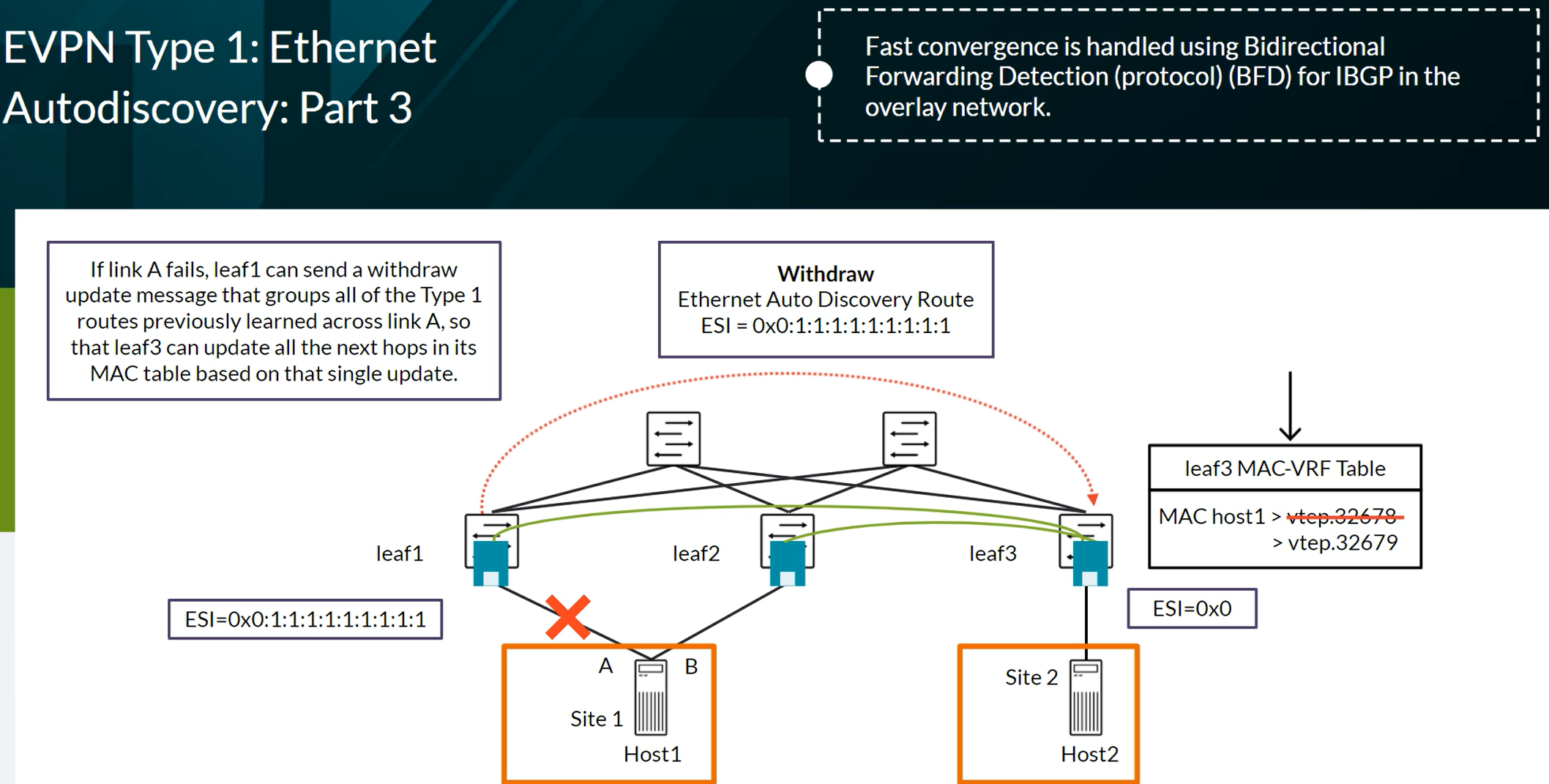
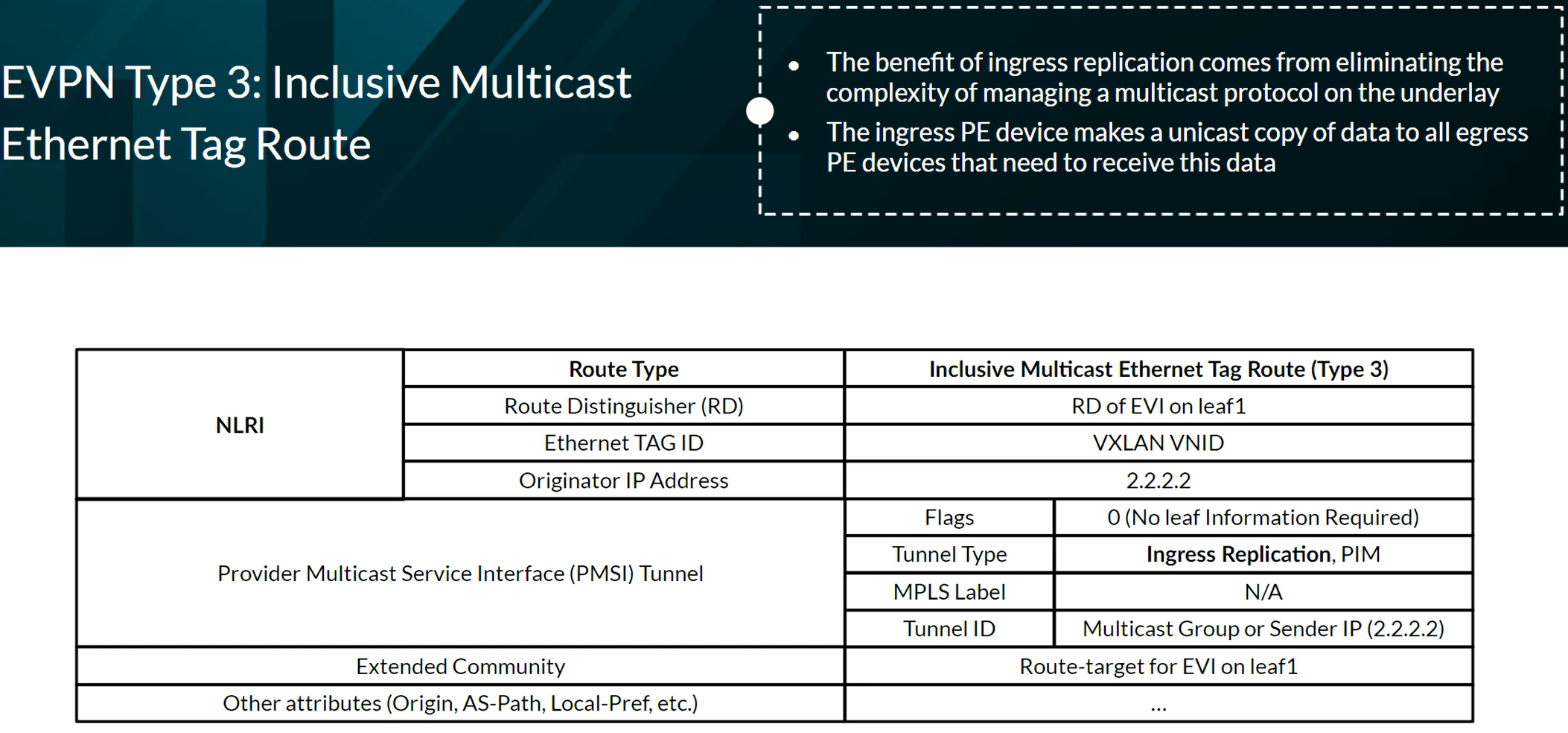
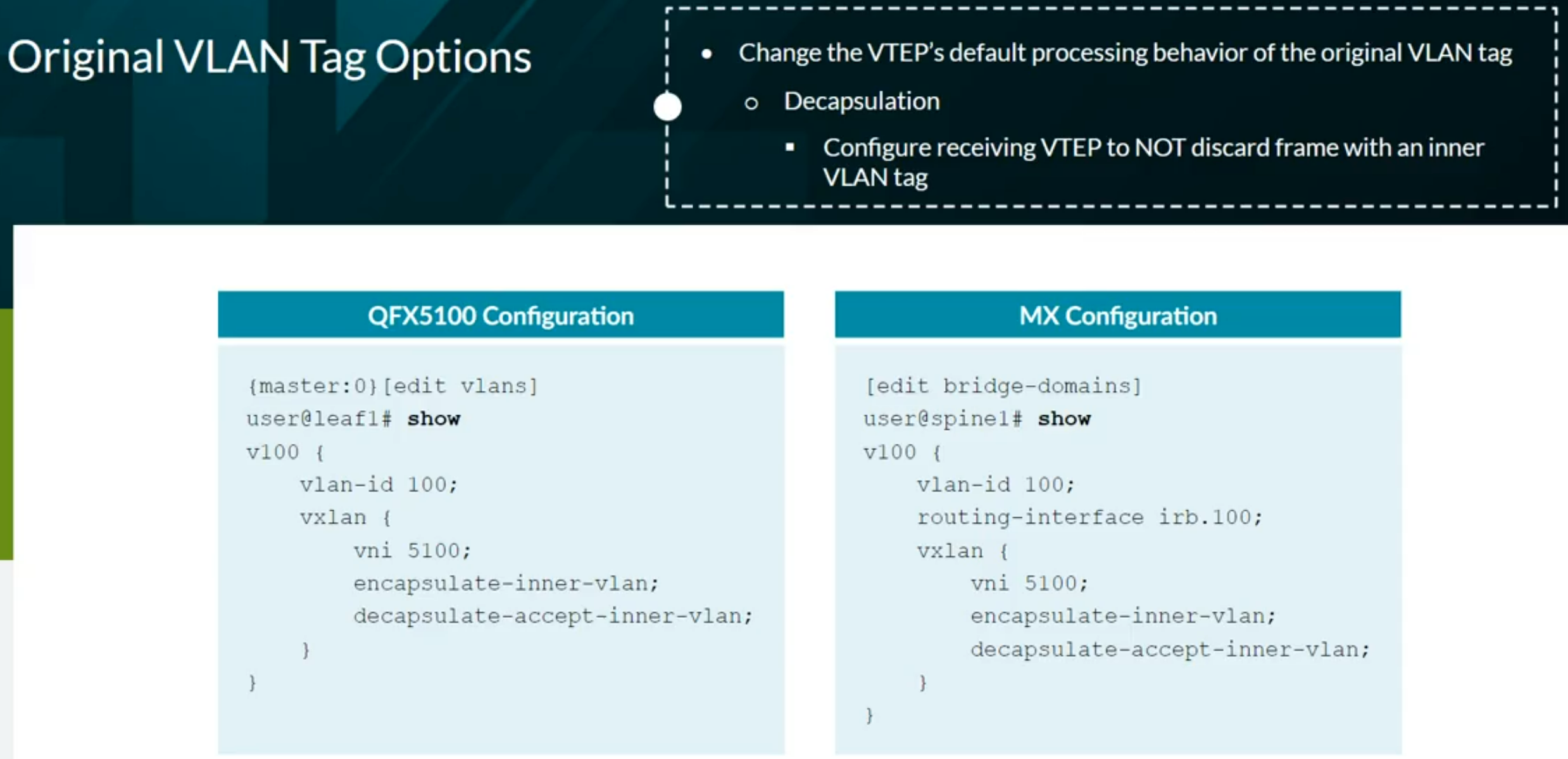
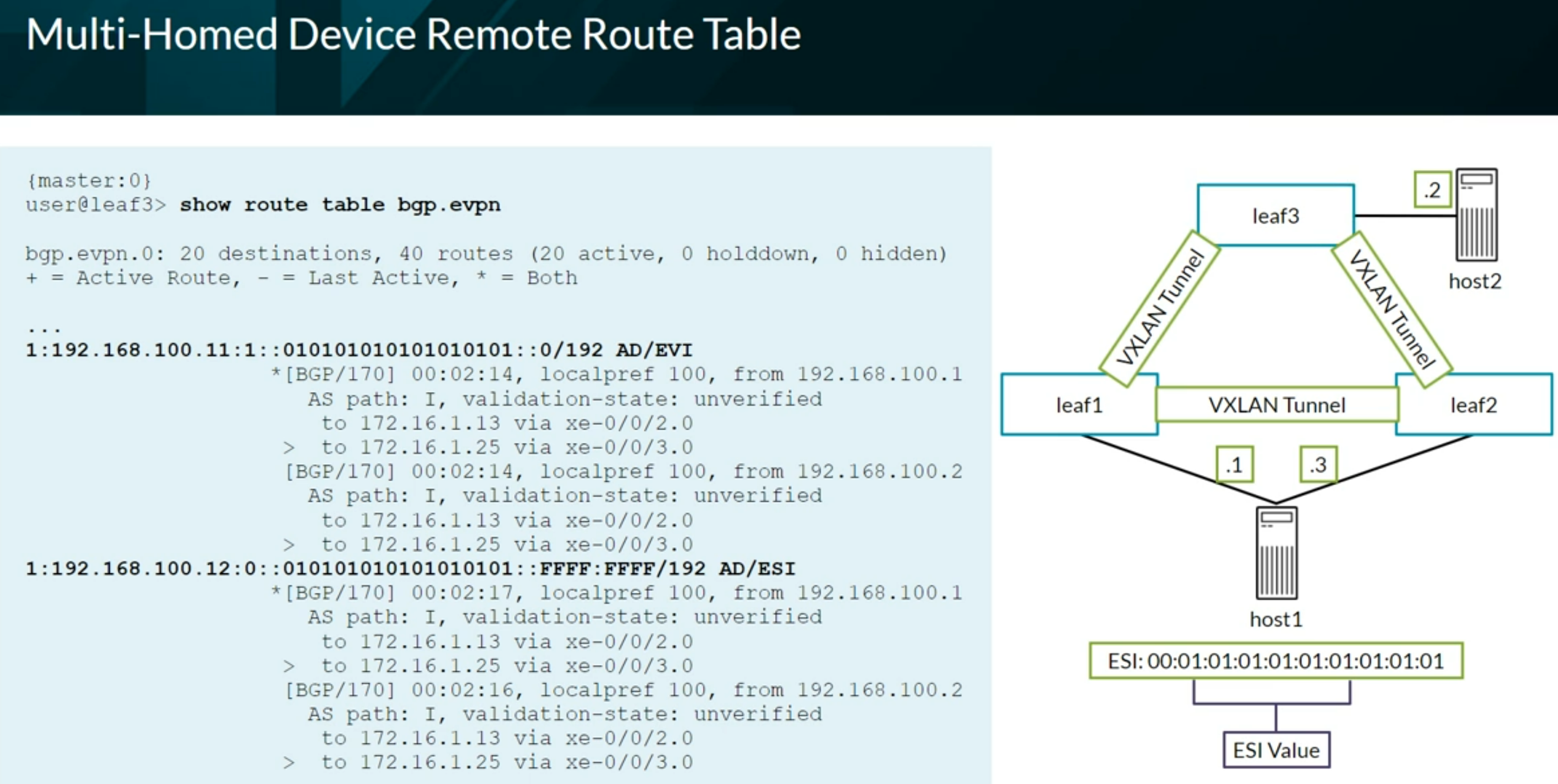
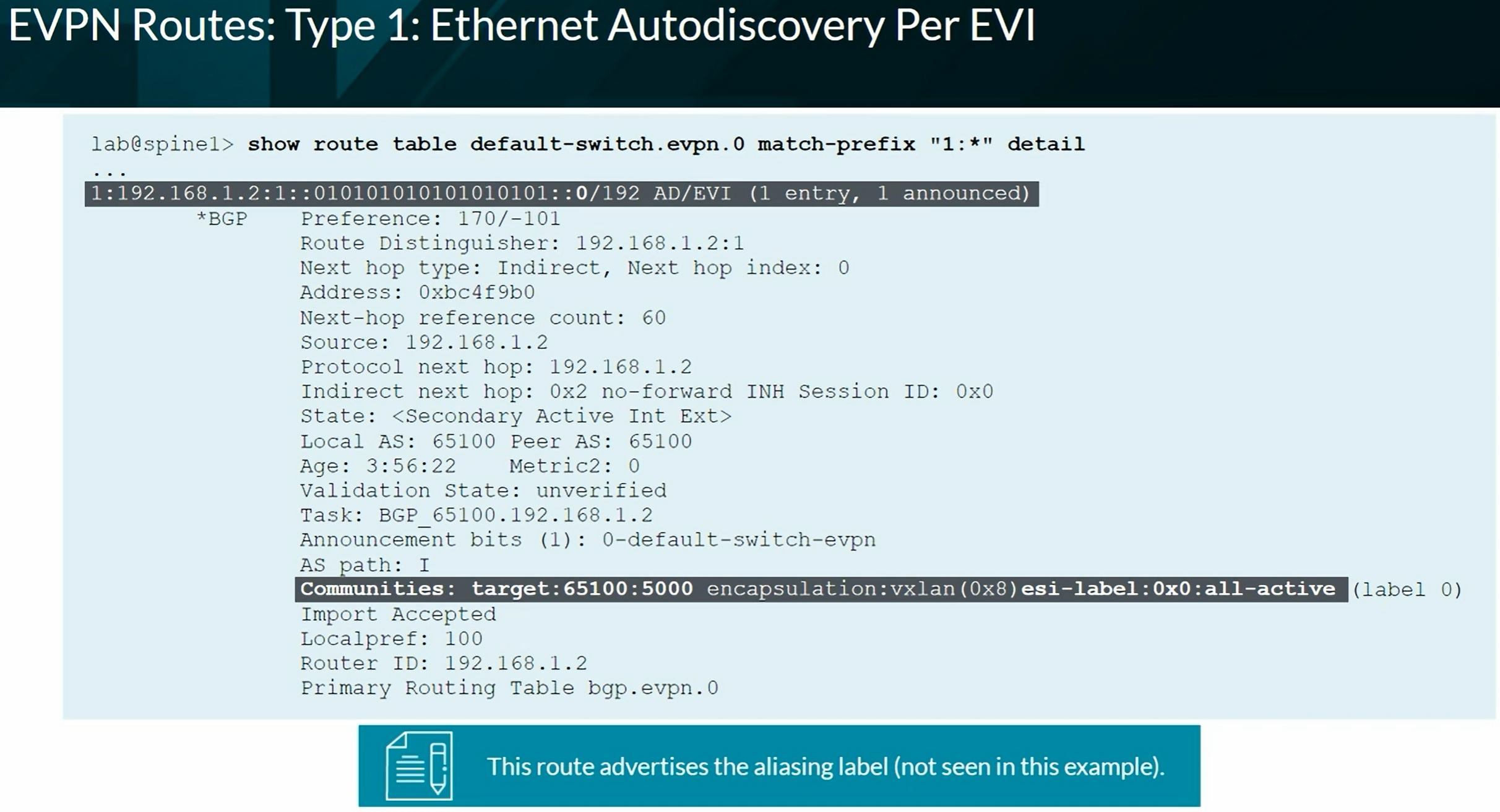
EVPN Type 1 per EVPN instance (EVI). The Ethernet Tag value is 0 (zero) at the end of the route.
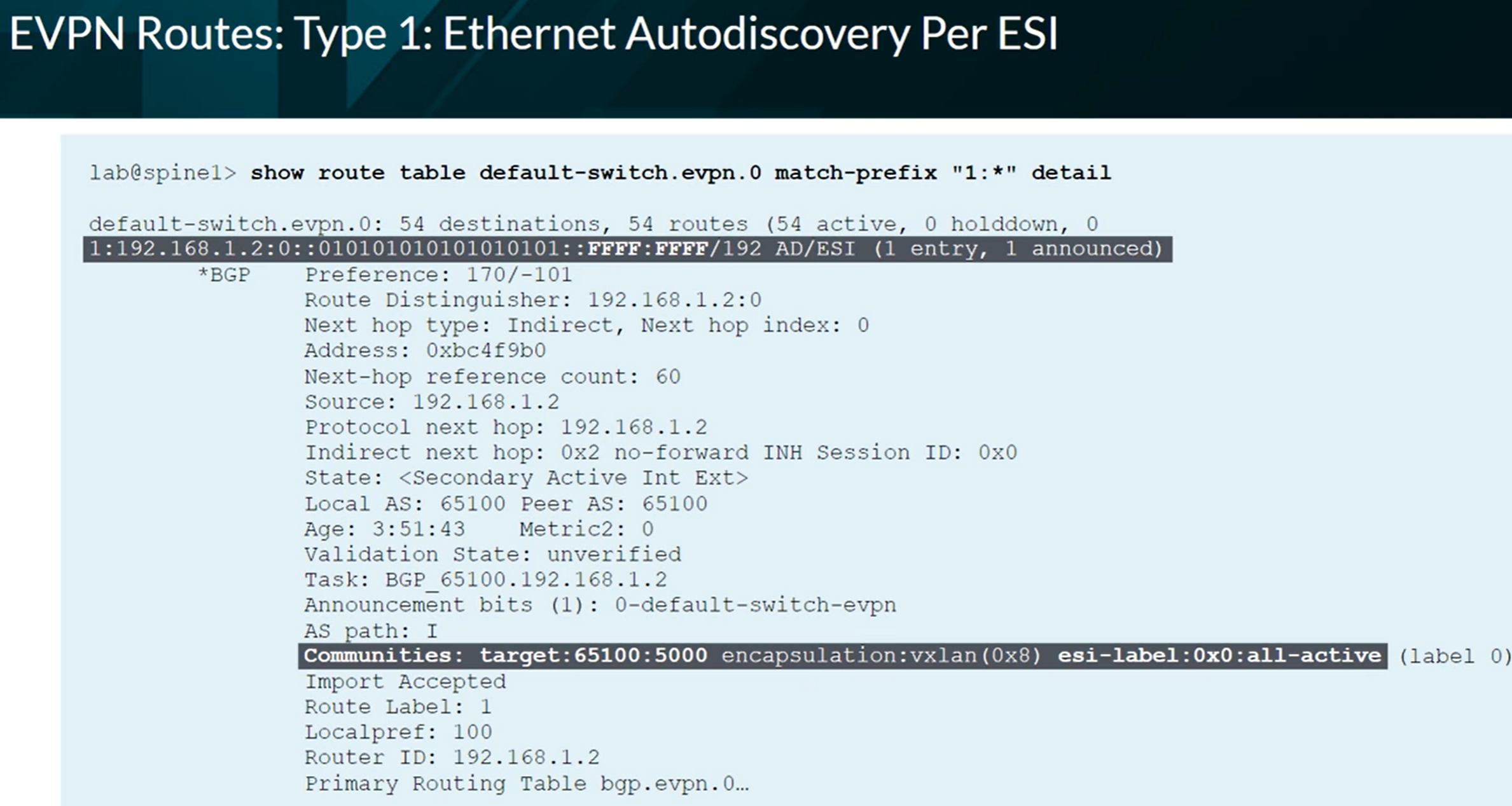
EVPN Type 1 per Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI). We see FFFF:FFFF (Max-ET) at the end of the route.
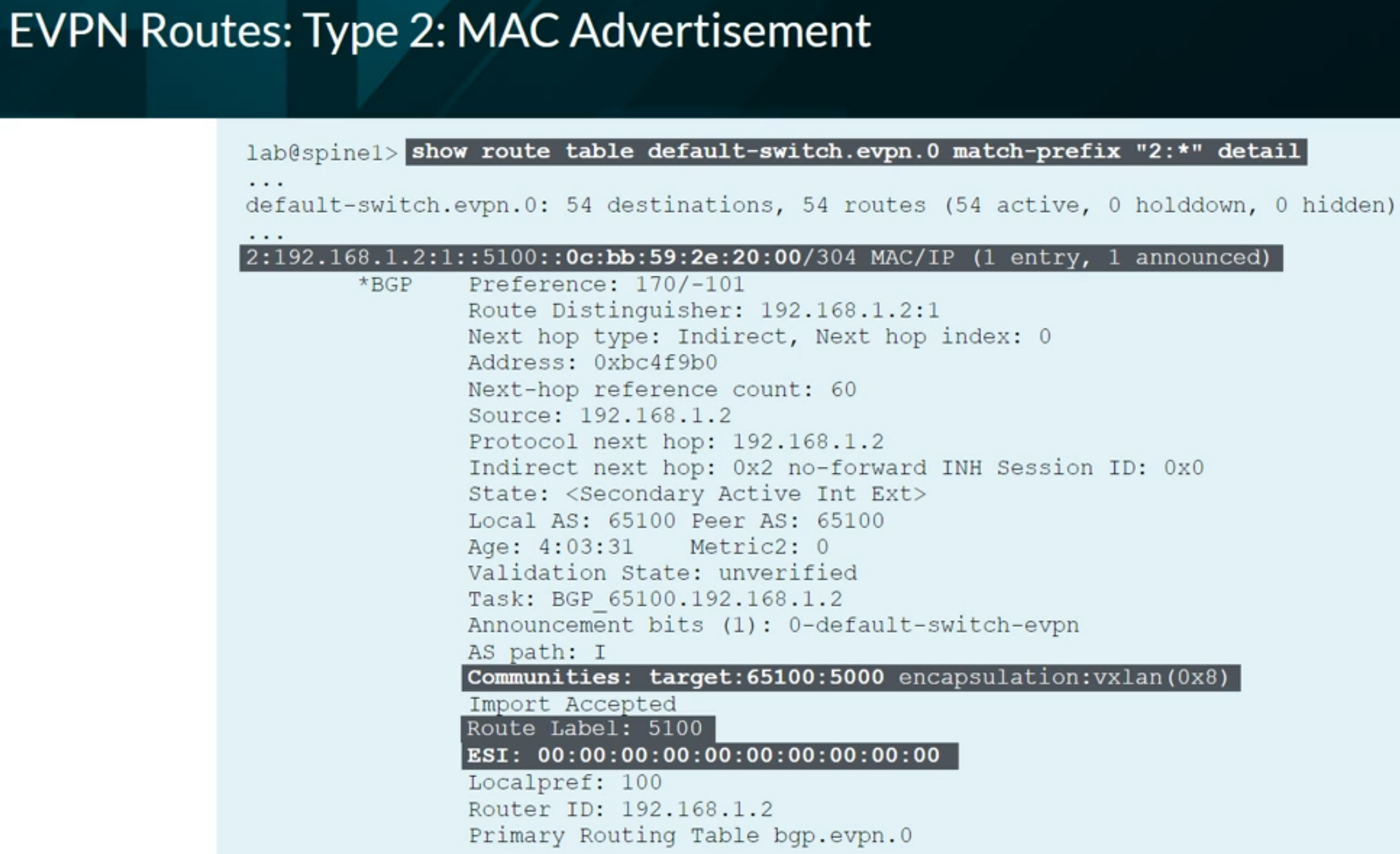
EVPN Type 2 advertising a MAC address.
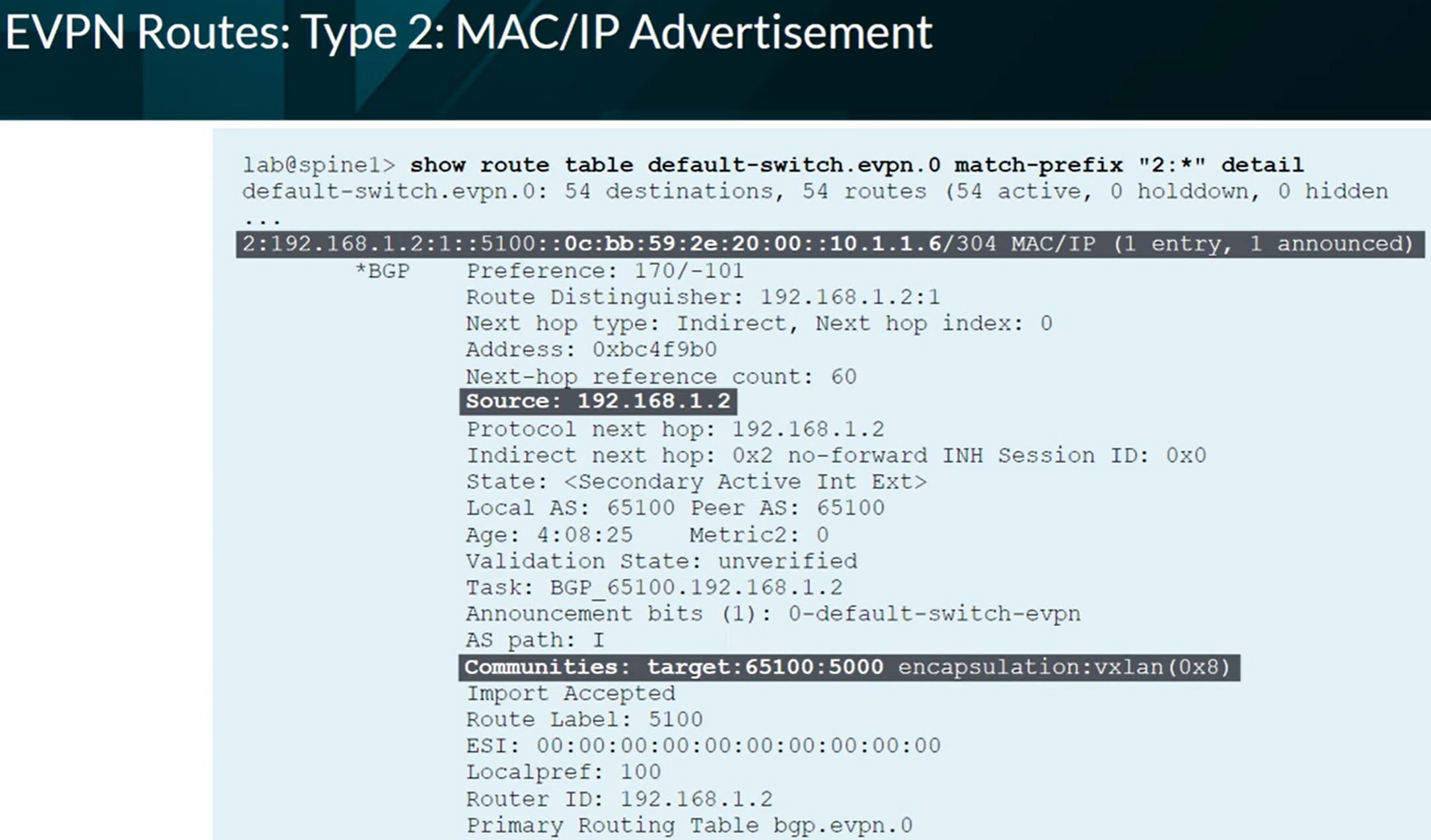
EVPN Type 2 advertising a MAC and an IP address.
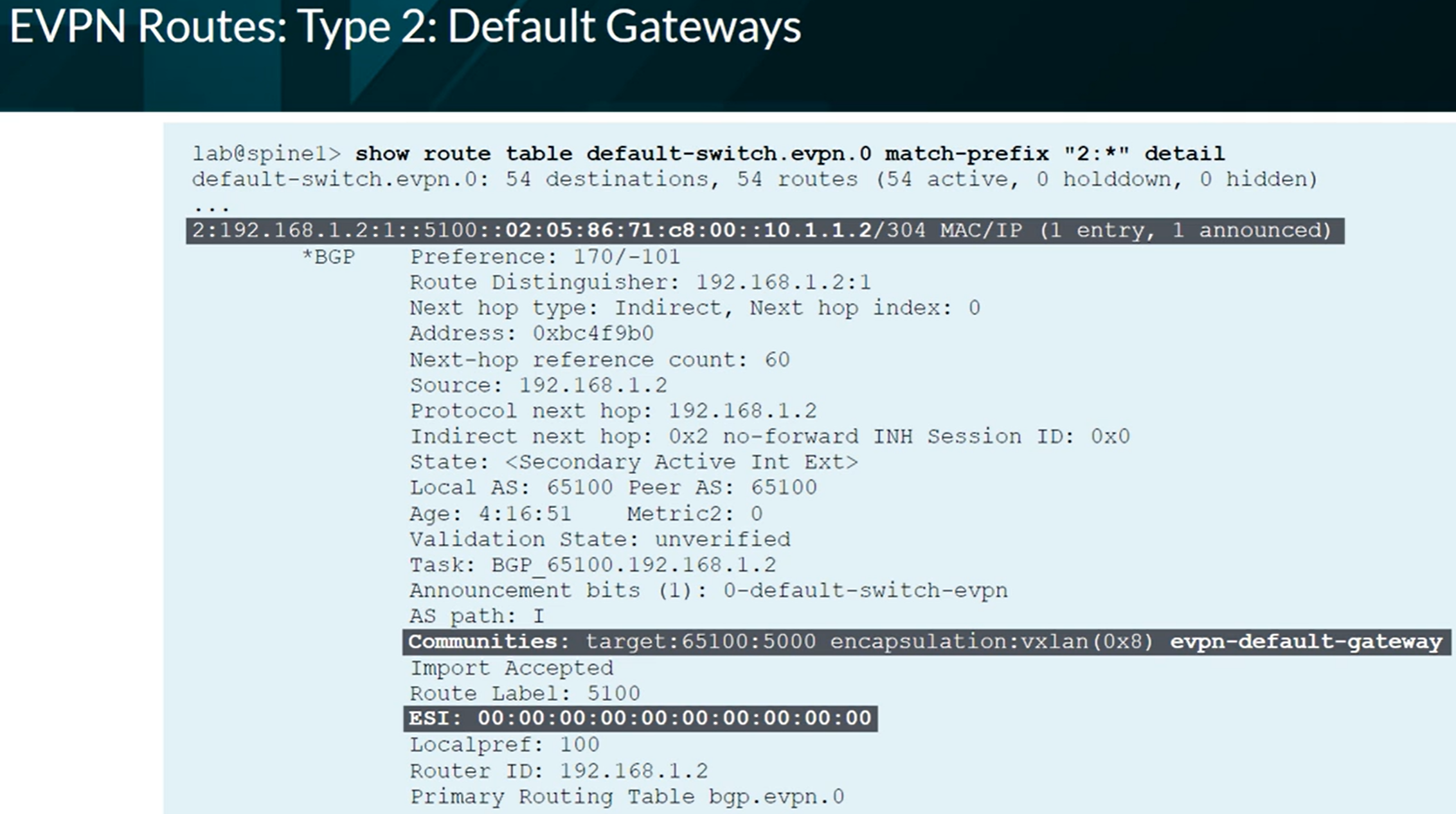
EVPN Type 2 advertising the information of a Virtual Gateway’s IRB
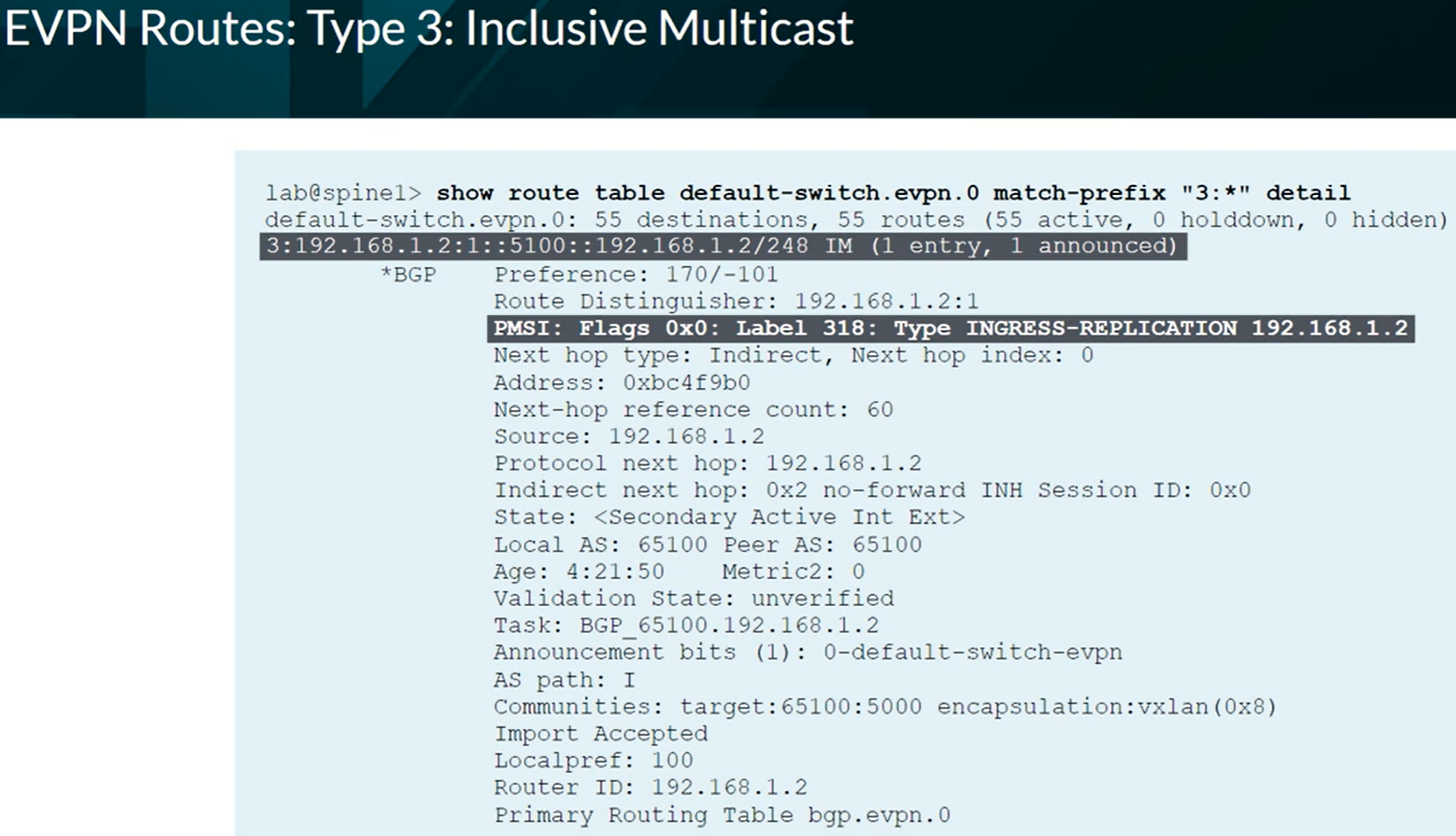
EVPN Type 3 advertising Multicast information
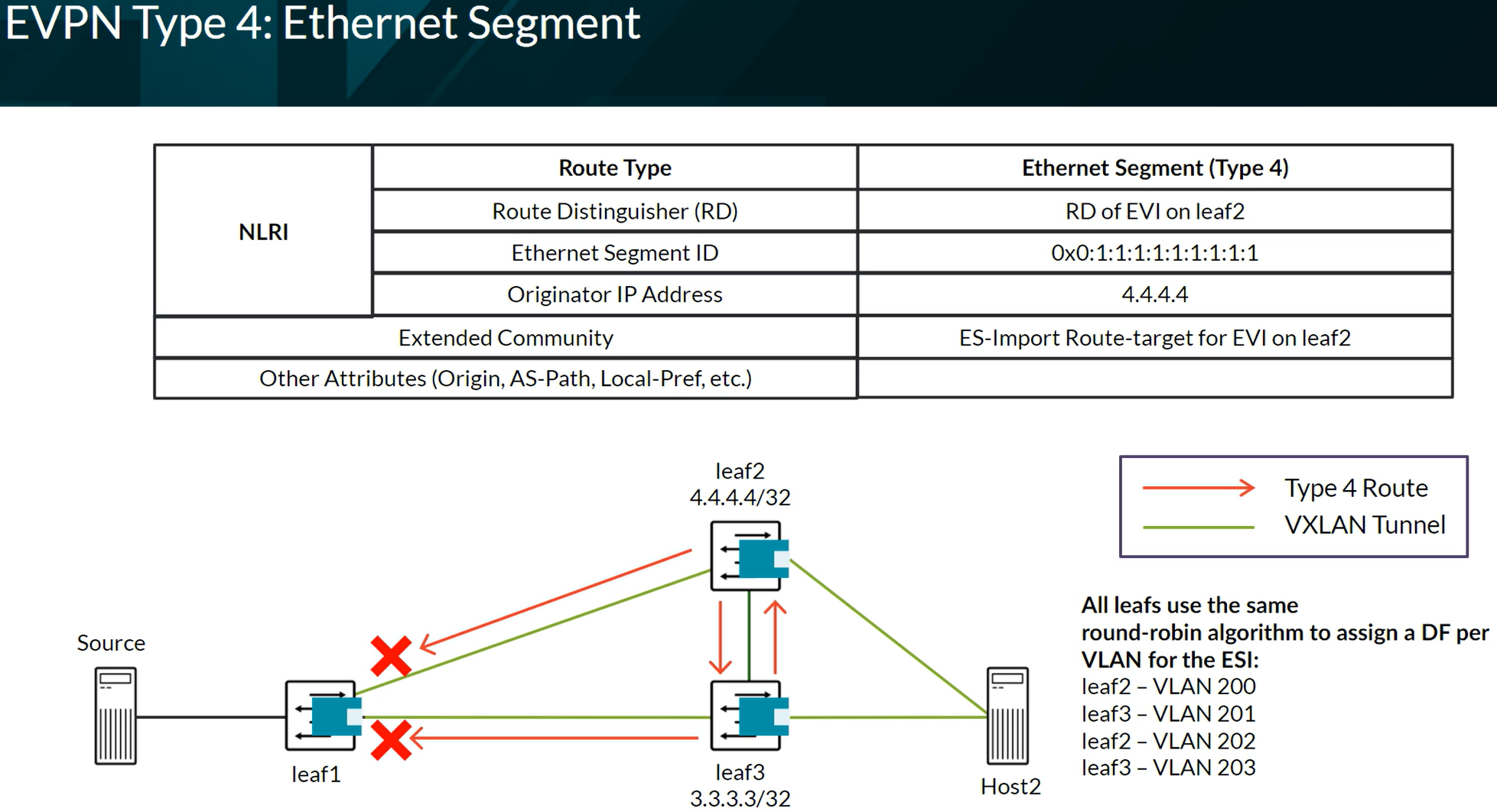
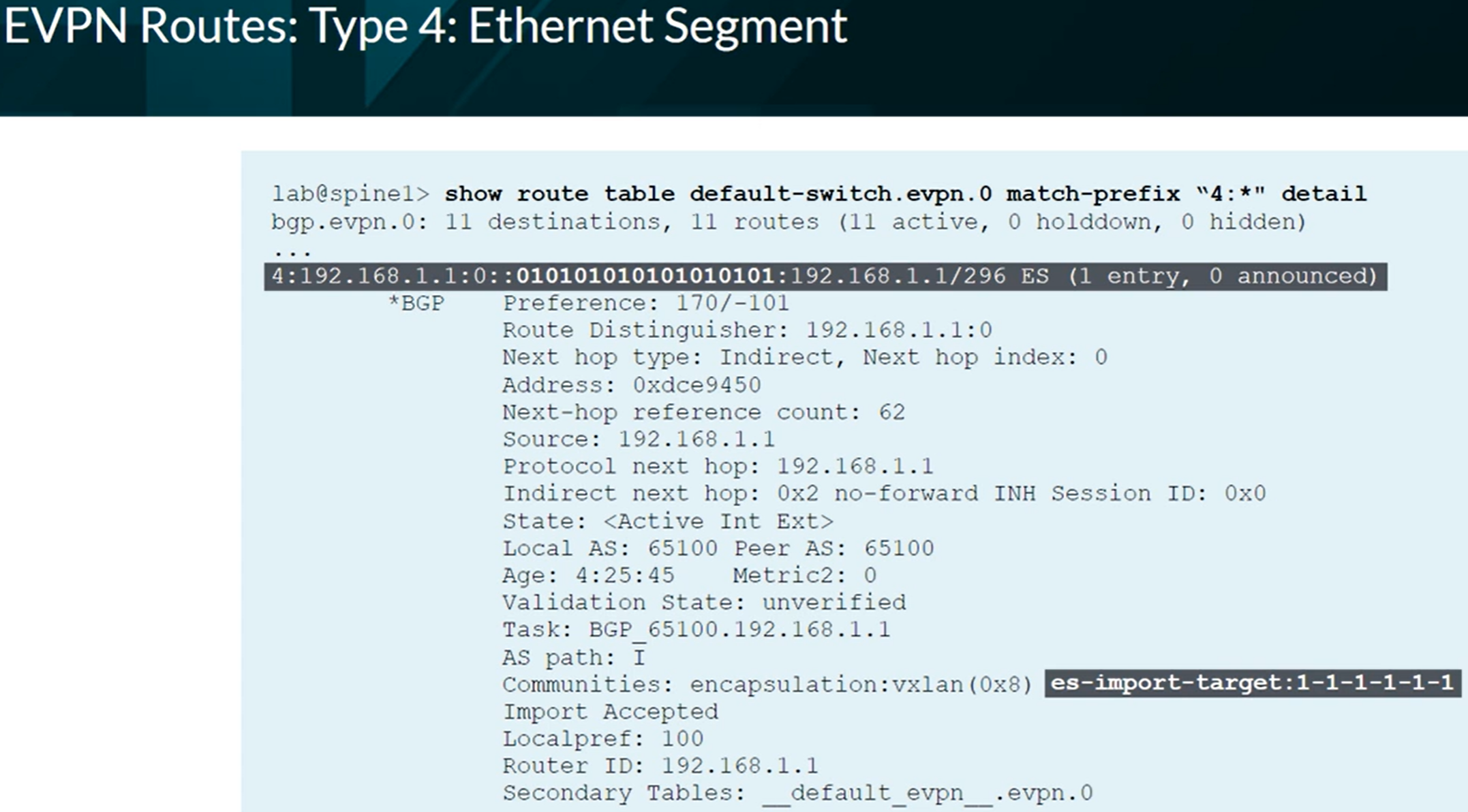
EVPN Type 4 advertising to elect the DR in a multihomed setup
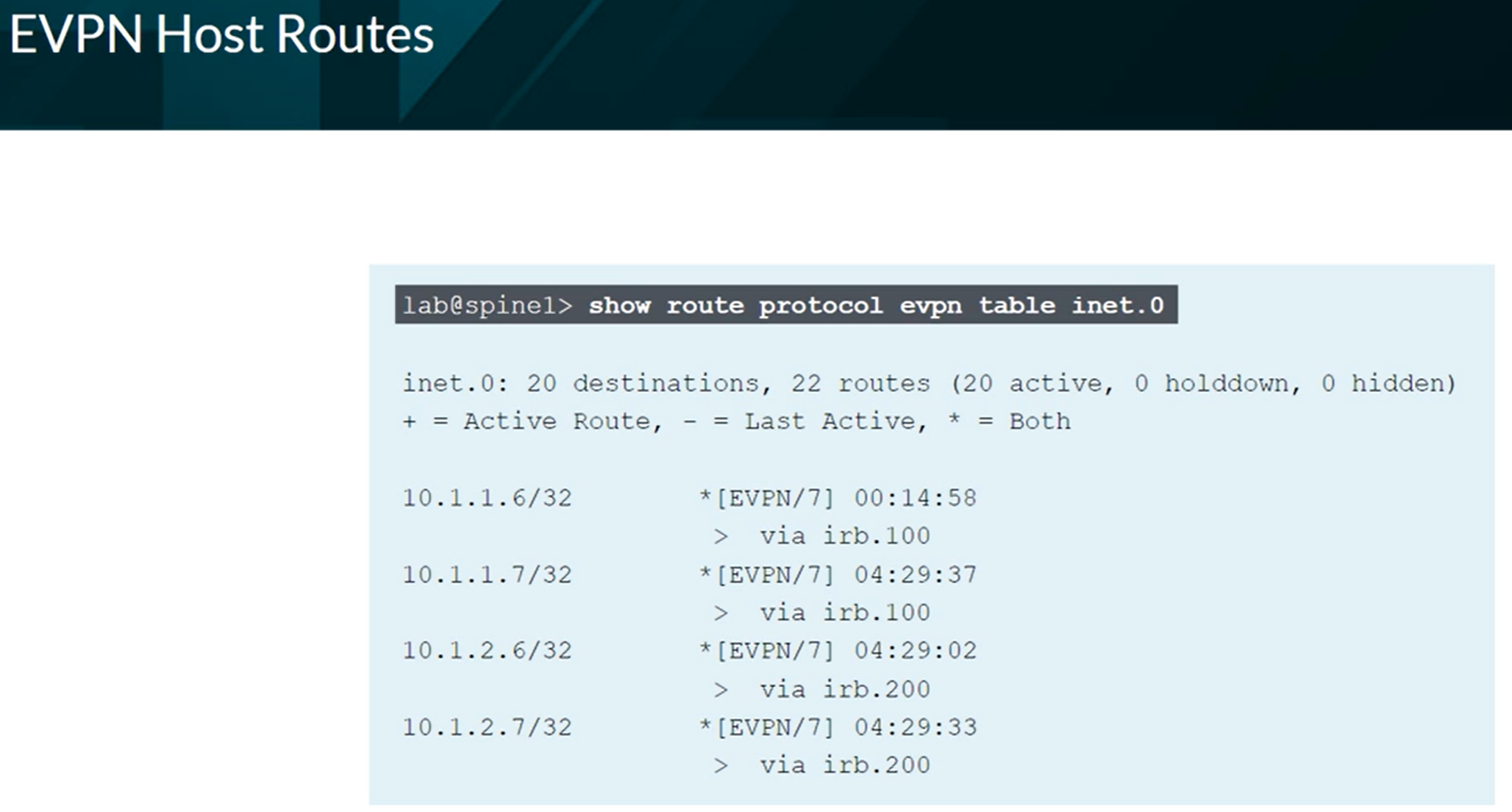
Routes learned from hosts connected to the VXLAN EVPN network on the inet.0 routing table
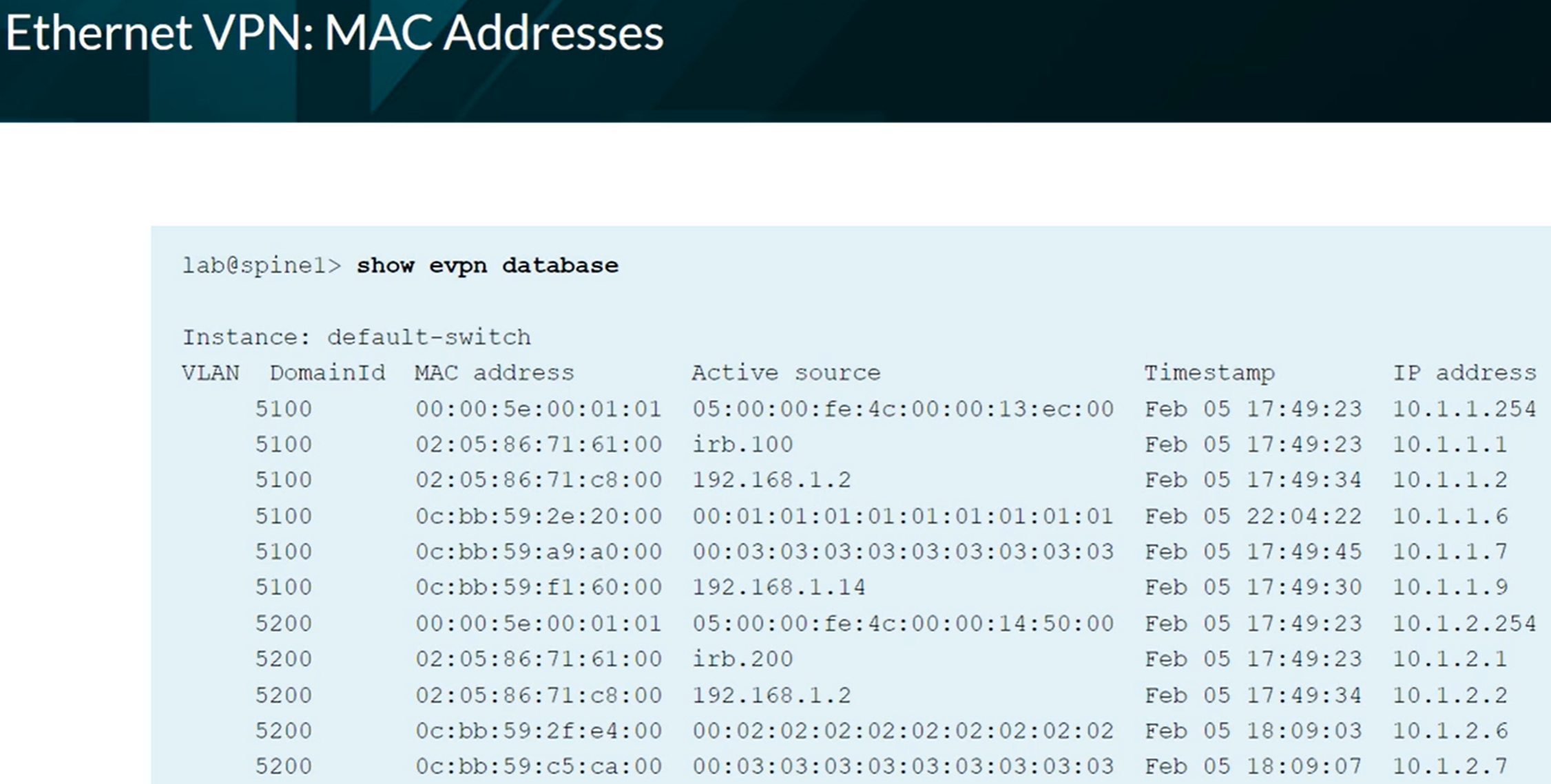
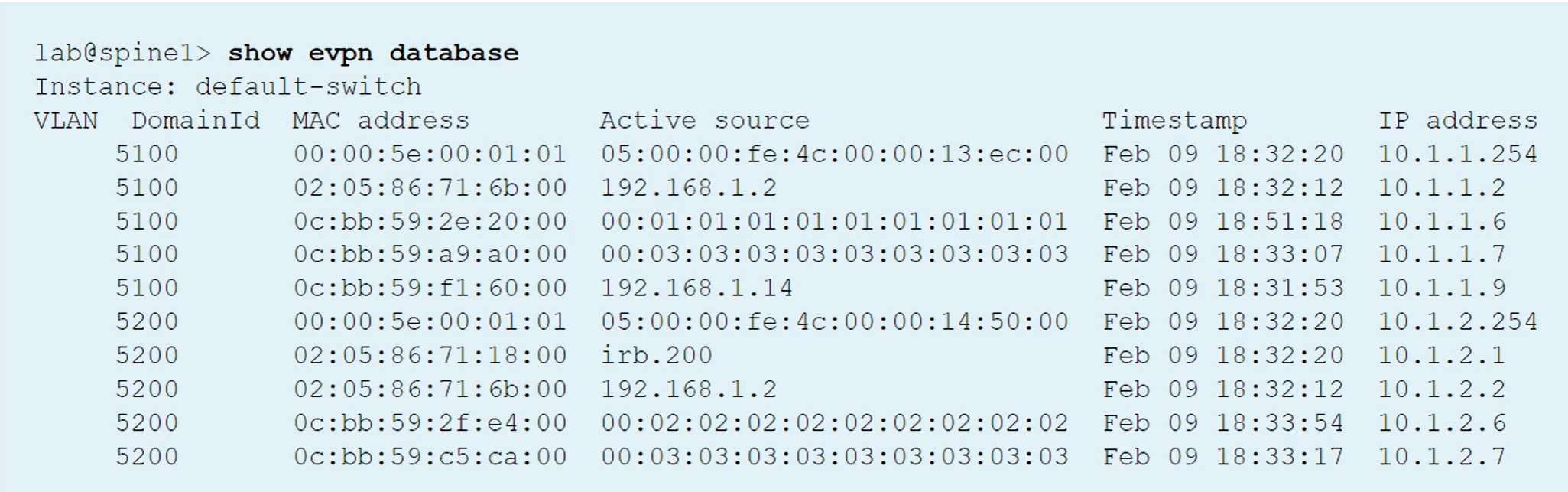
EVPN Database
EVPN Network Topology troubleshooting example
General EVPN Troubleshooting Steps
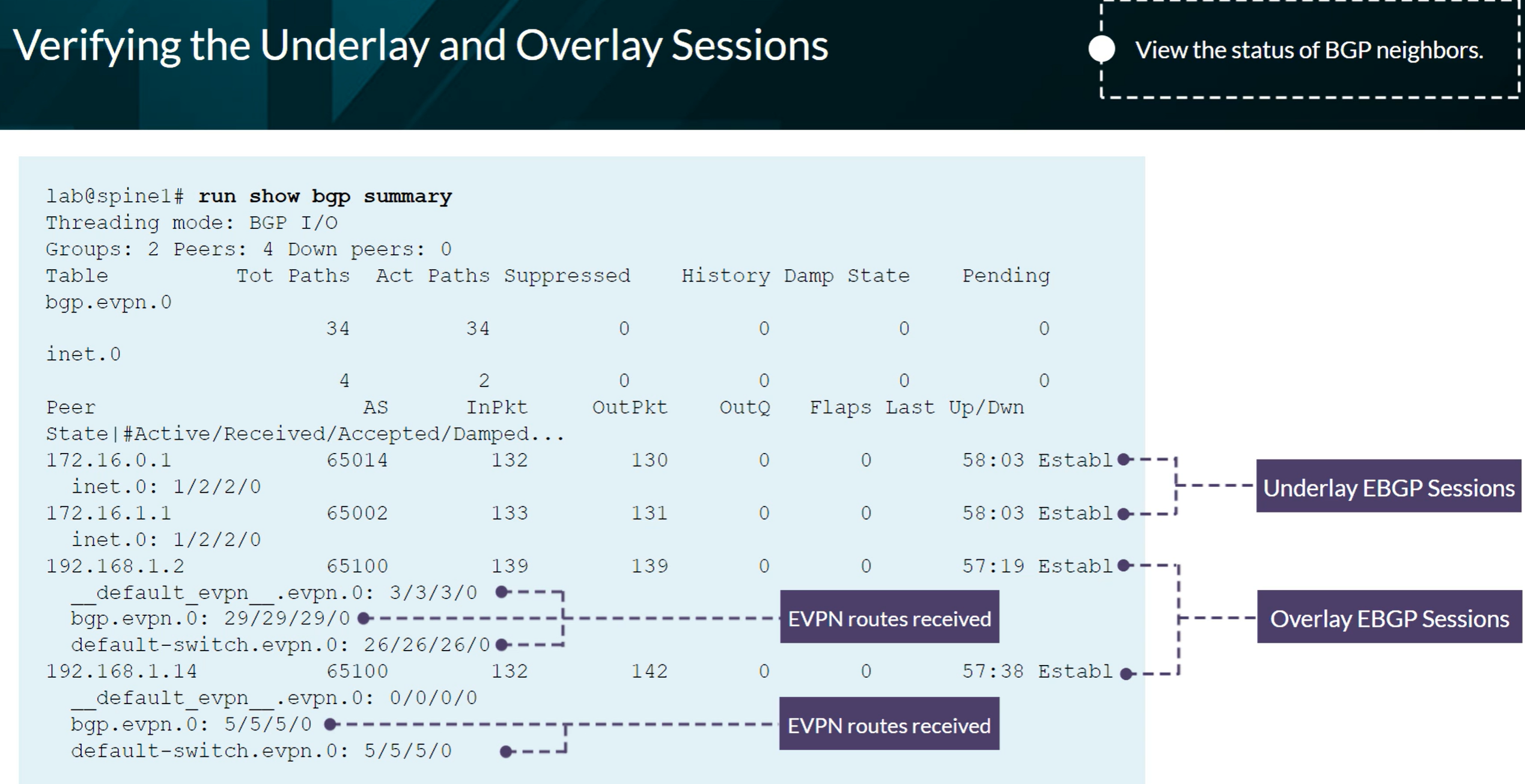
Useful Junos Commands
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| show bgp summary
show bgp neighbor
show route advertising-protocol bgp <NEIGHBOR-IP-ADDRESS>
show route receive-protocol bgp <NEIGHBOR-IP-ADDRESS>
show route table bgp.evpn.0
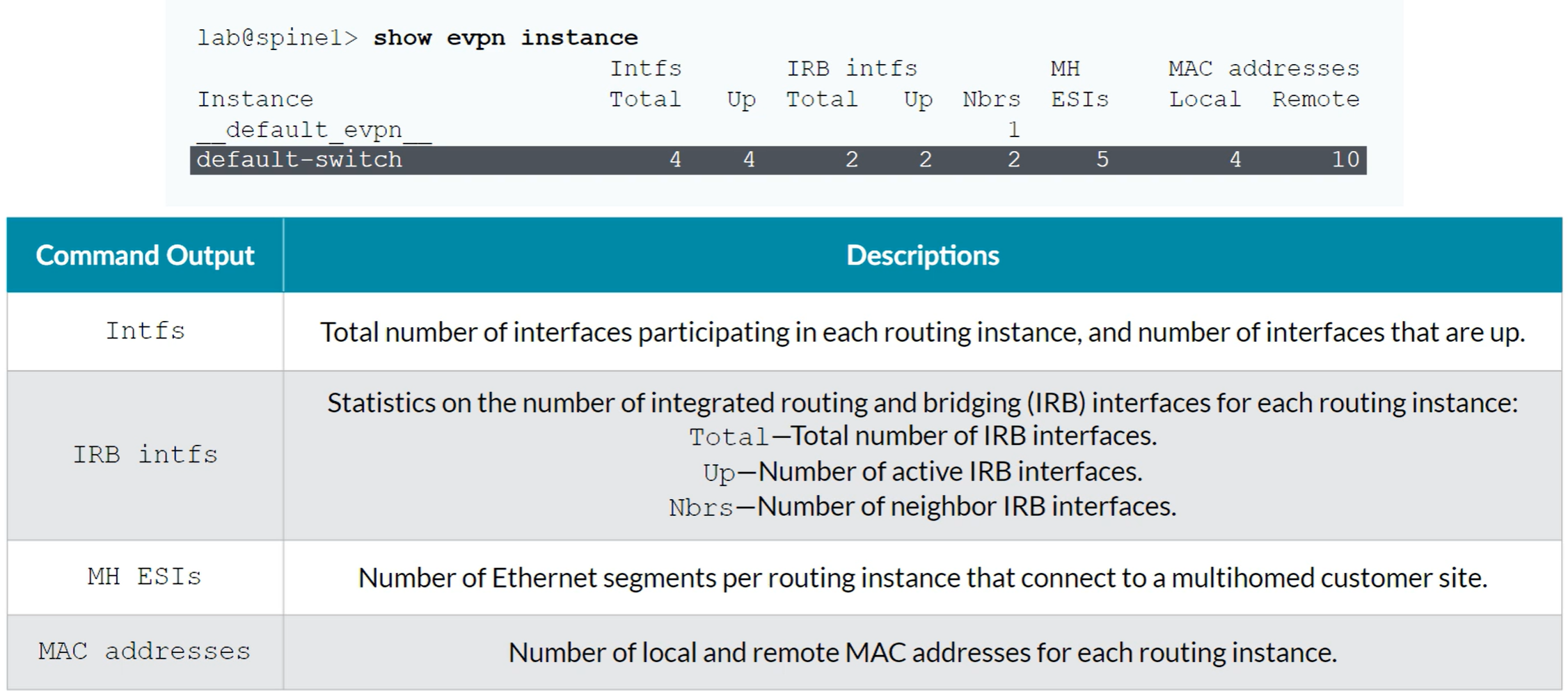
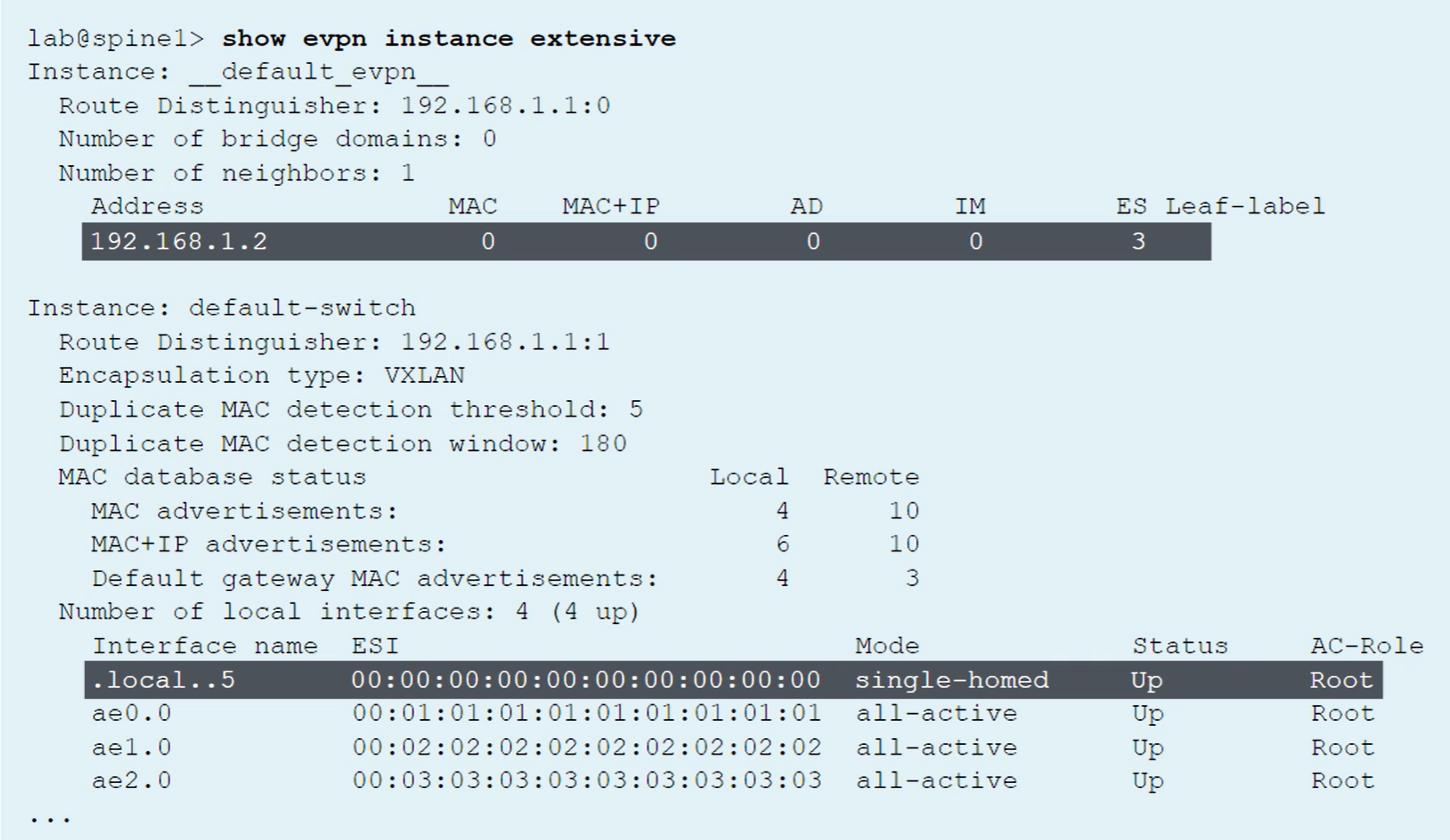
show evpn instance [extensive]
show ethernet-switching table
show interfaces vtep
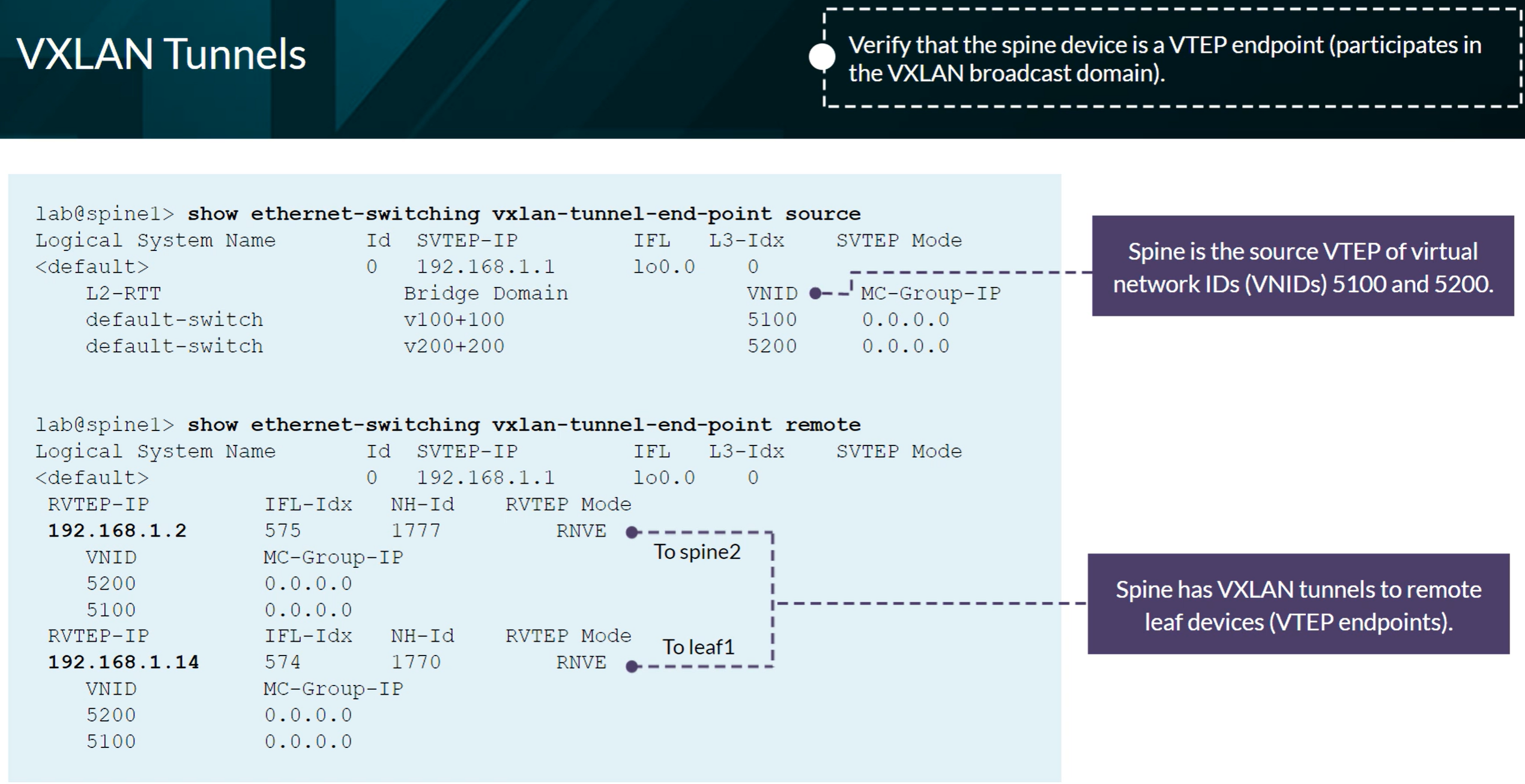
show ethernet-switching vxlan-tunnel-end-point source
show ethernet-switching vxlan-tunnel-end-point remote [mac-table]
|
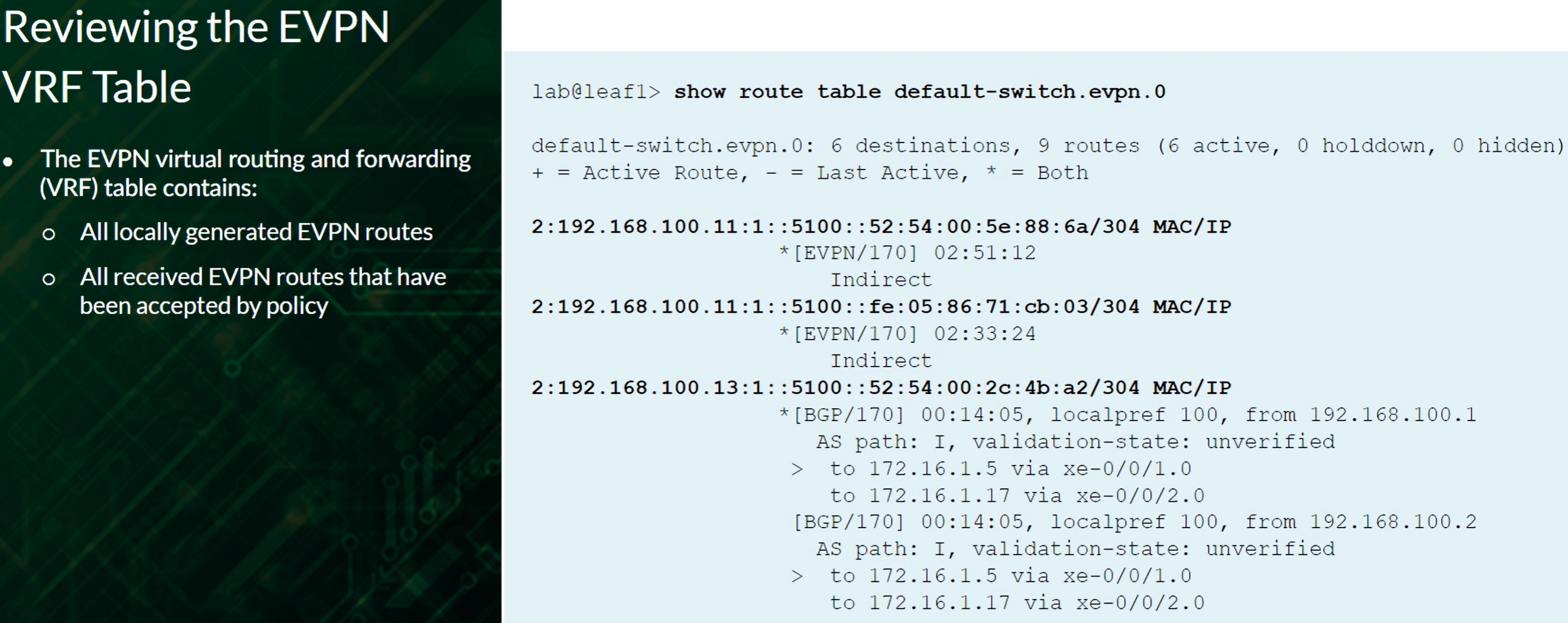
EVPN Routes Type 1, 2 and 3 are installed in the default-switch.evpn.0 Routing Table
EVPN Routes Type 4 are installed in the __default_evpn__.evpn.0 Routing Table
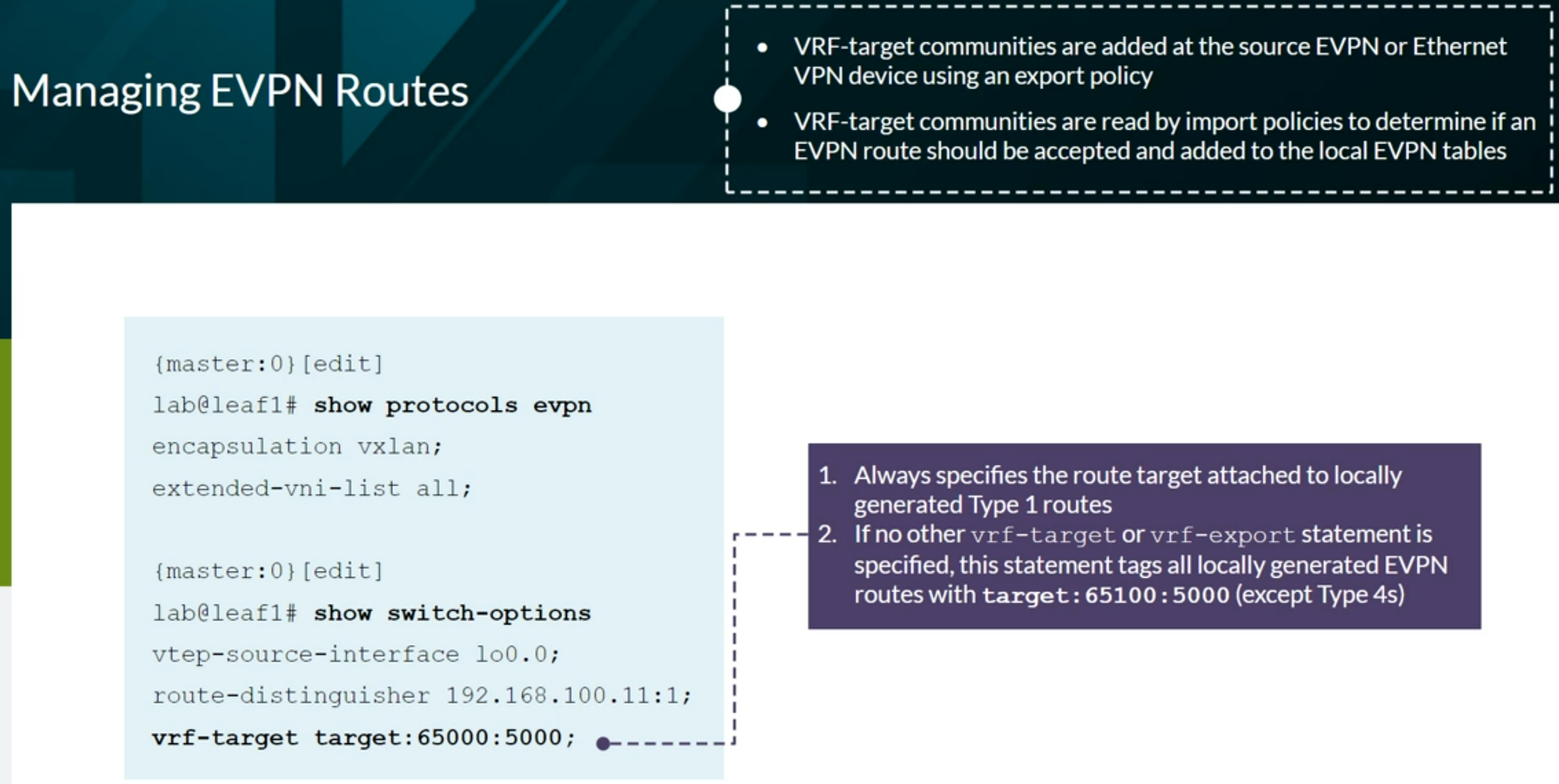
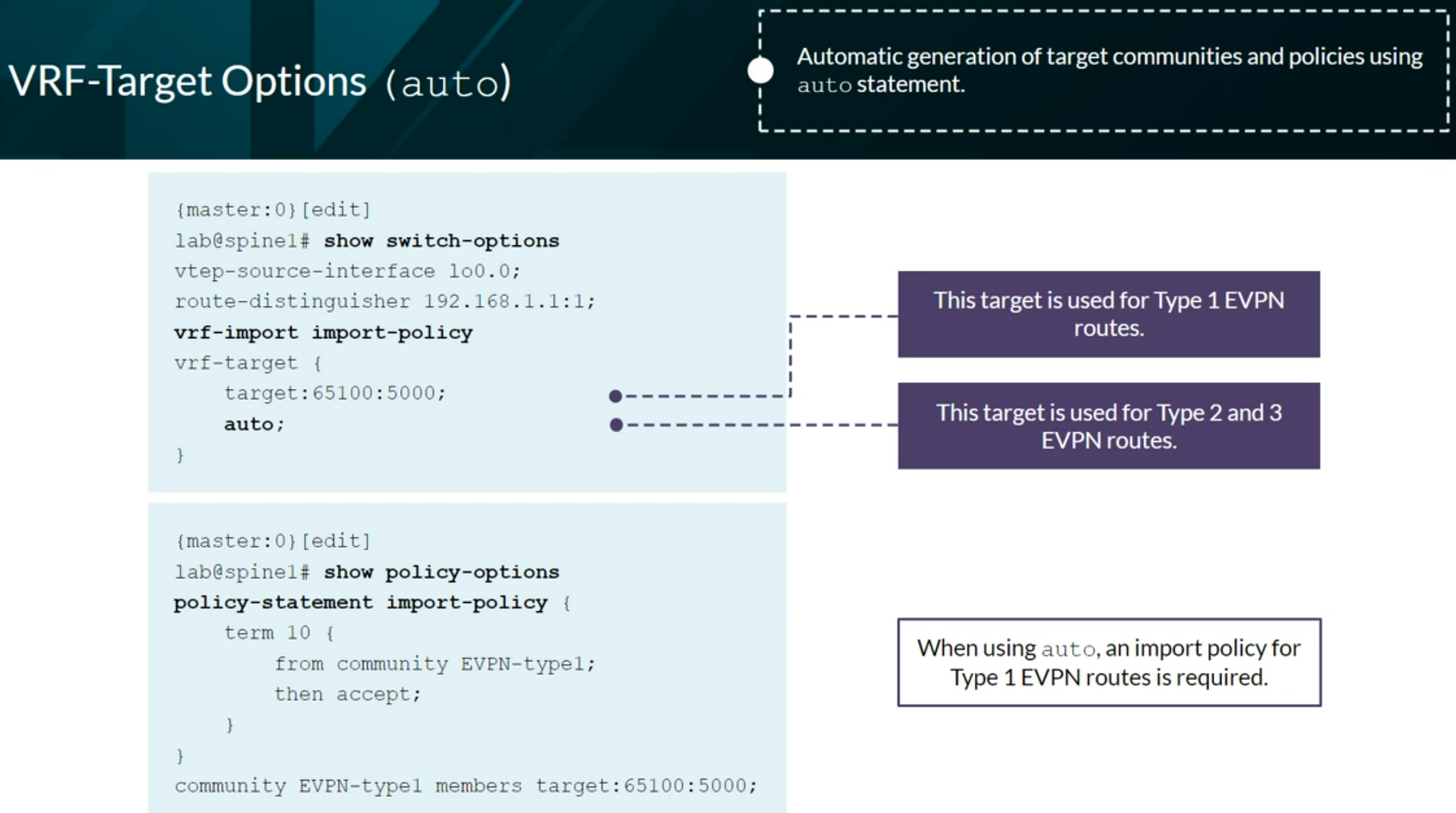
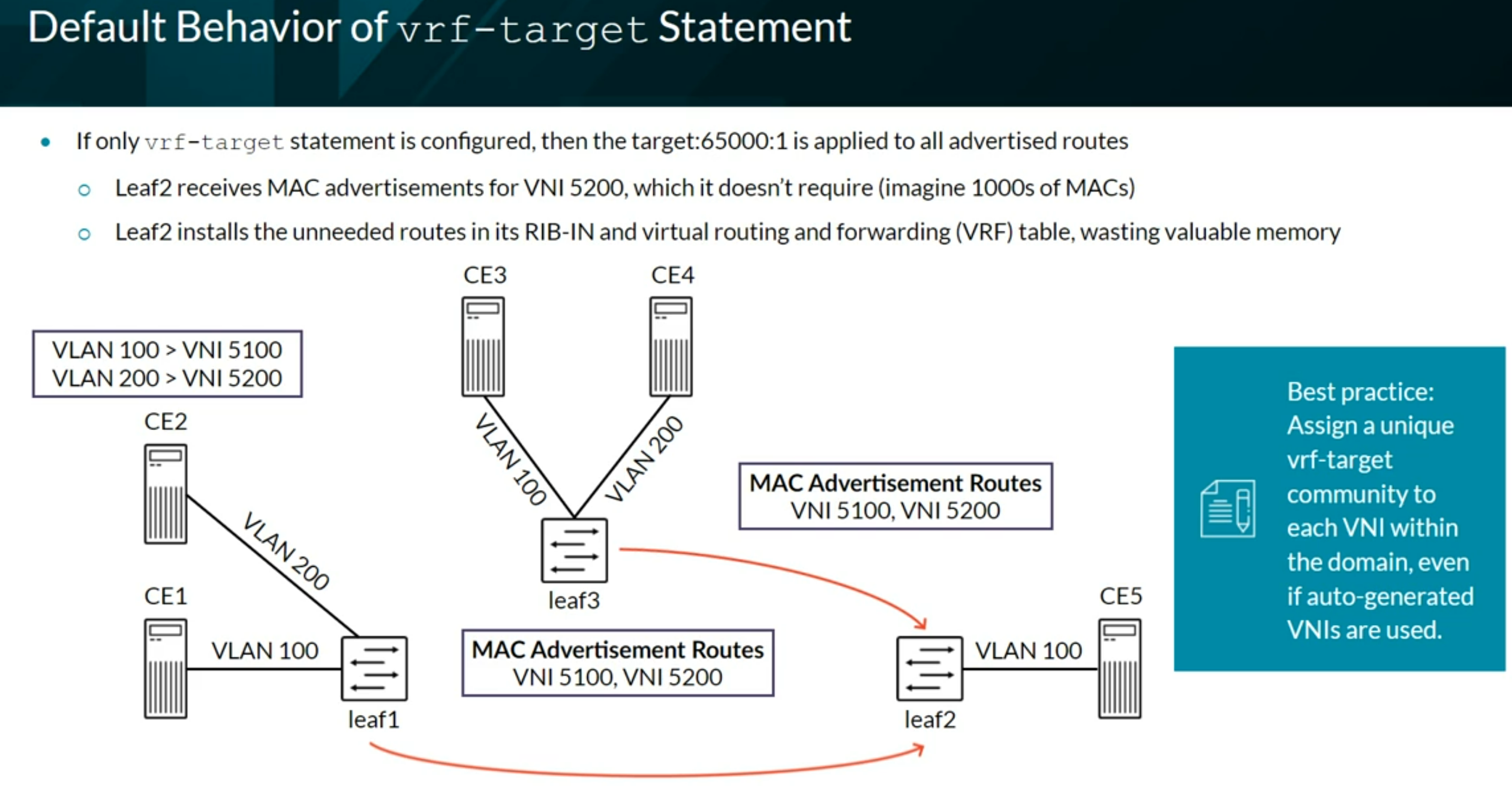
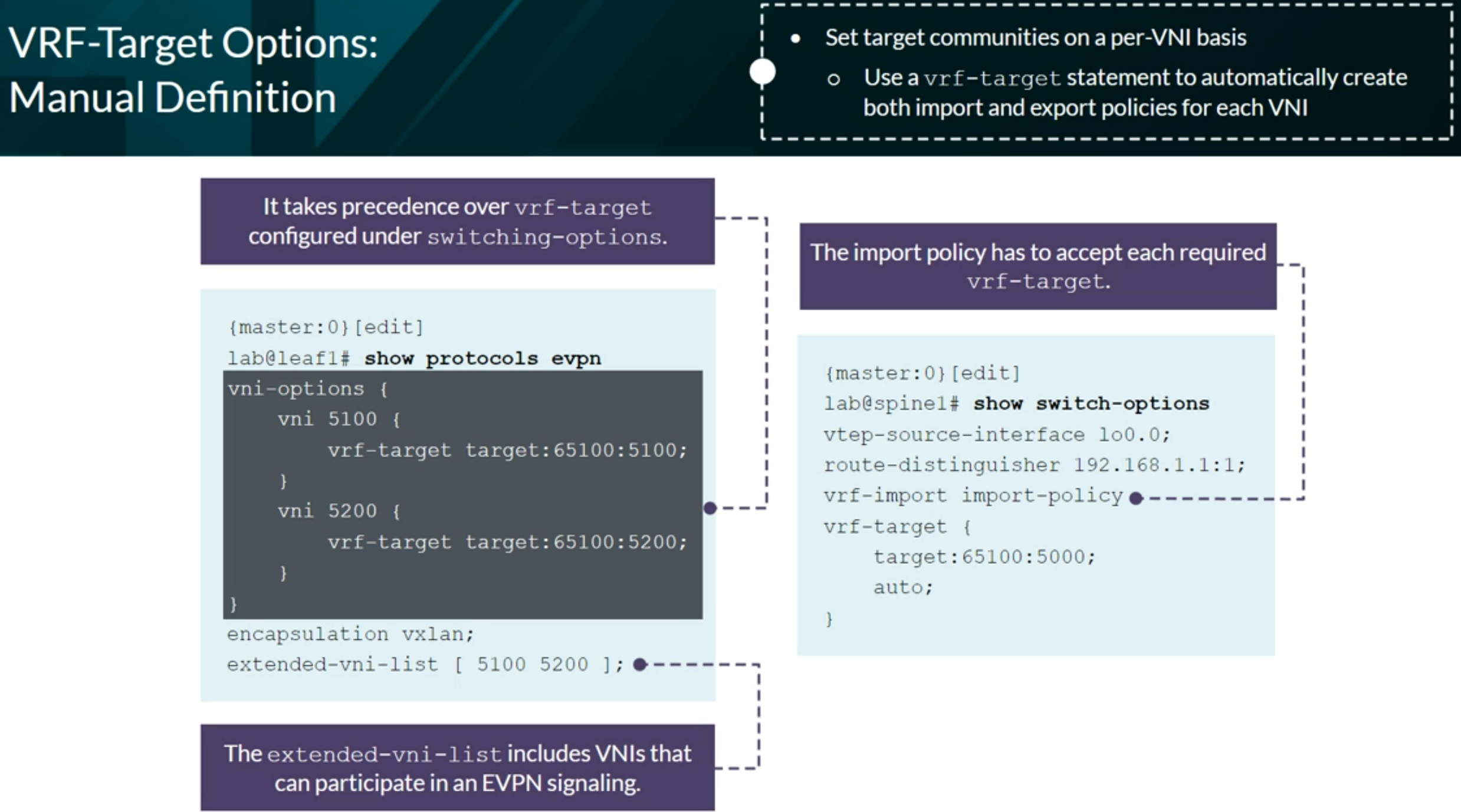
The bgp.evpn.0 table holds all routes from remote peers that have a matching VRF (vrf-target) community defined on the local device. The table holds all EVPN route types and can be viewed using the show route table bgp.evpn.0 command.
Use the keep all BGP command to override the default action of dropping the routes when there is not a matching community configured locally.
If no VRFs are used (Tenants), the routes can be seen in the default-switch.evpn.0 table
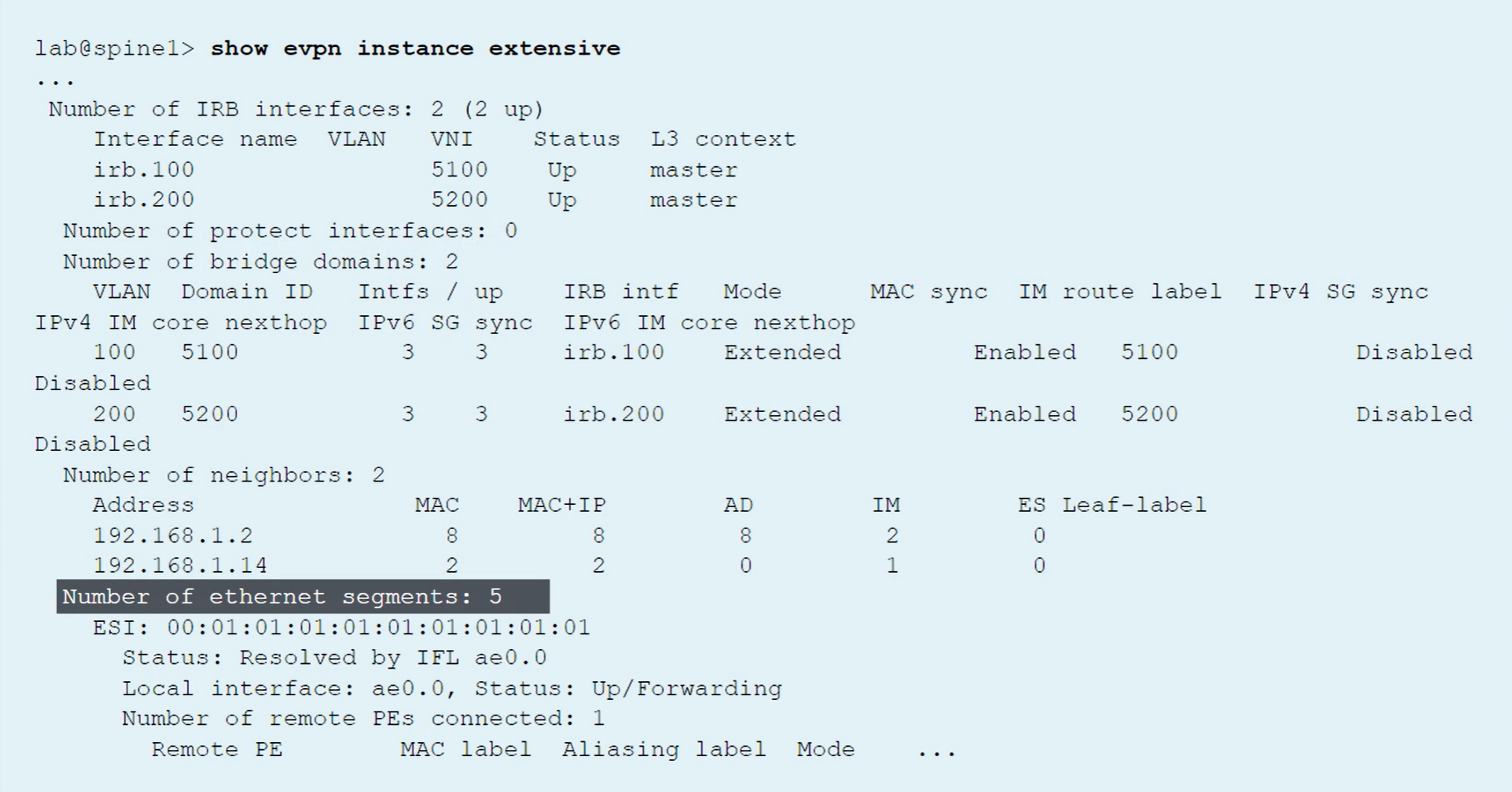
Verifying that an EVPN Instance exists
show evpn instance extensive
show evpn database
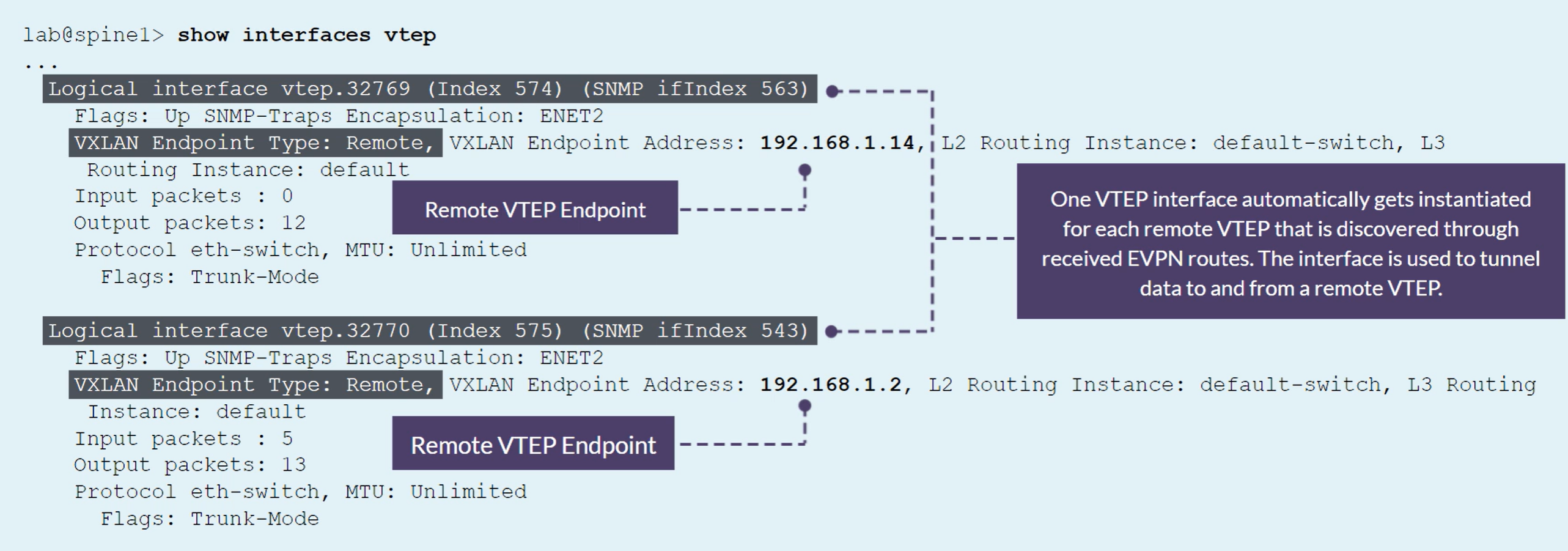
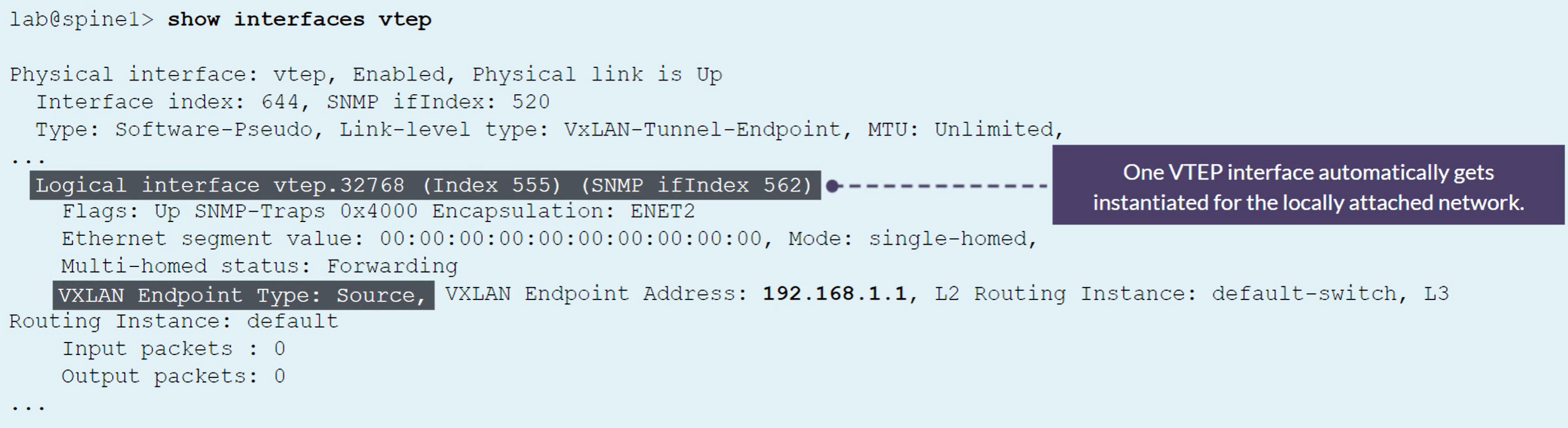
A VTEP interface is automatically created to represent the locally attached network
Other VTEP interfaces are built to tunnel the traffic to the remote VTEP endpoint
To see VLANs to VTEPs association, use the show vlans command
VXLAN Tunnels
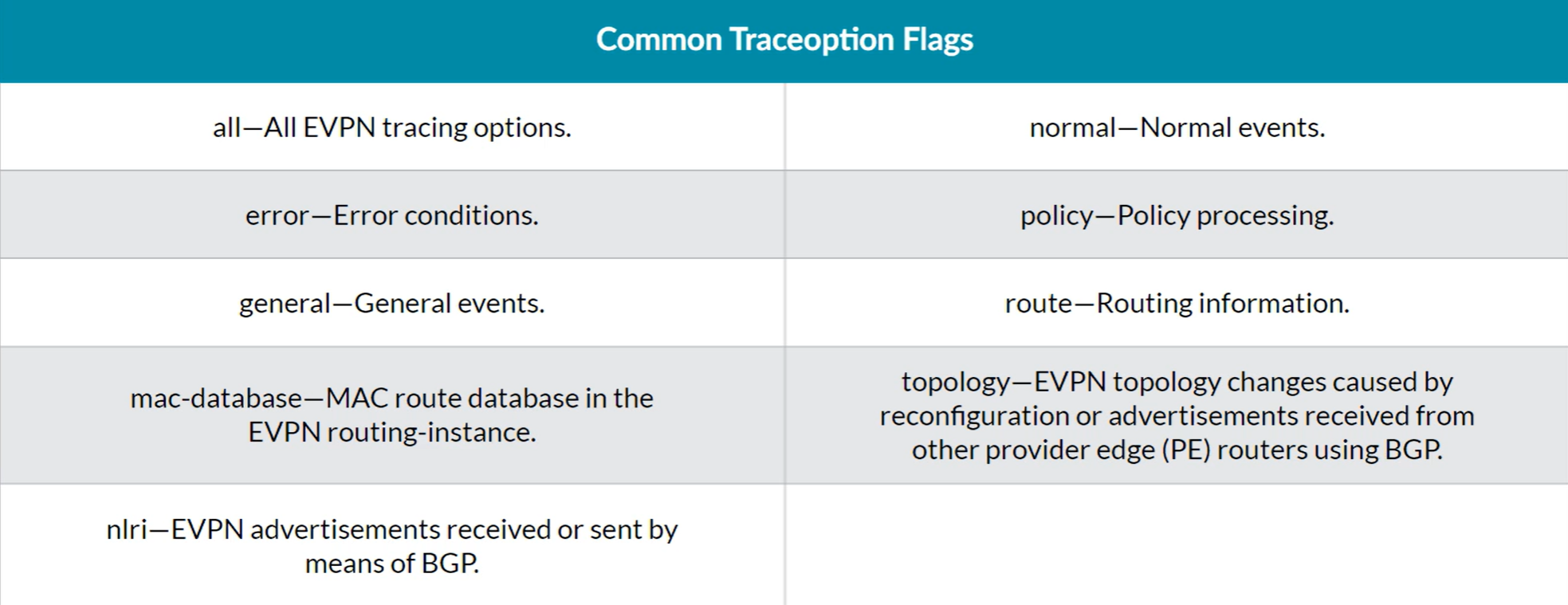
Traceoptions to debug BGP EVPN
IS-IS
- from a Level 2 area to a Level 1 area, an export policy must be explicitly configured to leak routing information.
- from a Level 1 area to a Level 2 area, by default, IS-IS protocol leaks routing information.
Source: Example: Configuring IS-IS Route Leaking from a Level 2 Area to a Level 1 Area
Same as in Cisco:
- By default, Level 2 routers are not leaked into Level 1 areas by L1L2 router
- Level 1 routers always propagate to Level 2 area.
And aboue the Attach bit
In order to reach Level 2 area, L1L2 router sets the Attach bit in Level1 LSP. Level 1 router installs the default route in routing table, this route would point towards L1L2 router.
Source: Configure Attach Bit Set
BGP Route Reflector with next-hop self
set protocols bgp group IBGP export nhs-policy The best practice when setting up next-hop self in a BGP Route Reflector is to have a policy on the BGP global level set as:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| user@router# show policy-options
policy-statement bgp-export {
term ebgp {
from route-type external; <<<---- Only eBGP routes
then {
next-hop self; <<<---- Setting next-hop self
accept;
}
}
term ibgp {
from route-type internal;
then accept;
}
}
|
Source: Best practices for route reflector configuration with regard to next-hop self
clear pim join-distribution
PIM join load balancing only takes effect when the feature is configured. Prior joins are not redistributed to achieve perfect load balancing. In addition, if an interface or neighbor fails, the new joins are redistributed among remaining active interfaces and neighbors. However, when the interface or neighbor is restored, prior joins are not redistributed. The clear pim join-distribution command redistributes the existing flows to new or restored upstream neighbors. Redistributing the existing flows causes traffic to be disrupted, so we recommend that you perform PIM join redistribution during a maintenance window.
Source: Configuring PIM Join Load Balancing
PIM Tunnel services on MX Routers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| chassis {
fpc 4;
pic 1 {
tunnel services {
bandwidth 1g;
}
}
}
|
All RP routers and IP version 4 (IPv4) PIM Sparse-Mode DRs that are connected to a multicast source require a Tunnel Services PIC.
Source: [MX] Setting up an MX-Series node for use as an RP or source DR in a PIM Sparse-Mode network